All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is an immediate complication occurring with the intervention of anti-T cell antibody infusions such as CAR-T cells infused with ATG, OKT3, TGN1412 etc. CRS is non-antigen-specific and a life-threatening toxicity with its relative severe cases known as cytokine storms. It is an unnatural setting with the magnitude of immune activation typically required for achieving clinical benefit by immunotherapeutic intervention. CRS is drawing increasingly attention along with the extensive application of immune-based therapies, especially adoptive T cell therapies.
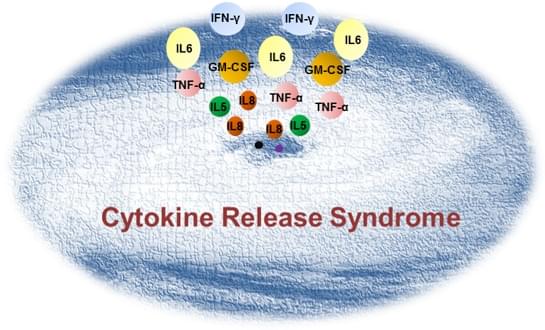
Pathophysiology
When antigens bind to the lymphocyte cell receptor or, vice versa, when lymphocyte cell receptors recognize antigens on tumor cells, lymphocytes are activated and then release cytokines as part of the systemic inflammatory response similar to that found in severe infection showing fever, hypotension, pyrexia and rigors. CRS takes place when massive lymphocytes (B cells, T cells, and/or natural killer cells) and/or myeloid cells (macrophages, dendritic cells, and monocytes) become activated and release massive amount of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL6, IL8, IL10, TNF-α, IFN-γ etc.) in a short time period.
Clinical Manifestations
Common clinical manifestations of CRS include fever ± rigors, malaise, fatigue, anorexia, myalgias, arthalgias, nausea, vomiting, and headache and so on. Symptoms typically reflected on different organs are as follows.
Dermatological signs: rash
Gastrointestinal reaction: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Respiratory reaction: tachypnea, hypoxemia
Cardiovascular symptoms: tachycardia, widened pulse pressure, hypotension, increased cardiac output (early), potentially diminished cardiac output (late)
Coagulation: elevated D-dimer, hypofibrinogenemia ± bleeding
Renal disease: azotemia
Hepatic toxicity: transaminitis, hyperbilirubinemia
Neurovirulence: headache, mental status changes, confusion, delirium, word finding difficulty or frank aphasia, hallucinations, tremor, dymetria, altered gait, seizures
Therapeutic Strategies
Despite the fact that immunosuppression such as IL6 blockage could reverse the CRS induced by adoptive cell therapy, early and aggressive immunosuppression is not suitable due to the limited efficacy, especially for cases of patients at risk. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to assist customers in preclinical studies focusing on the exploration of the CRS prevention. Current approaches include but not limited to the following.
Cytokine blockage
Emerging clinical experiences at several institutions have shown the effectiveness of tocilizumab® for severe or life-threatening CRS. Tocilizumab®, a humanized IgG1k anti-human IL-6R mAb, was initially approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and later had been introduced into the severe CRS coping strategies following CAR-T cell therapy. It showed impressive anti-high fever effects. Other examples such as anti-TNF-α and IL-1 mAbs could also provide benefit and have been used continuously.
Corticosteroids therapy
Corticosteroids are currently considered as second-line therapy for CRS due to the clinical observation of lower response to them than to tocilizumab® as well as their other widespread effects on the immune system.
CRS grading and algorithm treatment
Owing to the discrepancy at disease burden and CRS degree, it is essential to outline a proactive management strategy incorporating a grading system and treatment algorithm to define the specific approach of immunosuppression intervention (time and dosage).
Suicide gene transfer
Herpes-simplex-thymidine-kinase and inducible-caspase-9 are the most extensively validated suicide genes to date and have been involved in the clinical trials. Suicide gene addition to cellular products enables selective ablation of CAR redirected cells in order to prevent CRS inclusive collateral damage and to ensure the safety of gene modified cell therapy.
Creative Biolabs possesses the most exquisite expertise on gene modification, CAR-T/TCR-T development and application, which makes us a unique service provider for your in vivo preclinical researches. We commit to the mission of targeting the challenges towards CAR-T/TCR-T clinical therapy.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION