Based on years of experience in antibody discovery and production, Creative Biolabs has developed second to none antibody analysis platform. With our comprehensive analysis platform, we are proud to offer antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) assays for bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) and other therapeutic antibodies.
ADCP attacks and breaks tumor cells following antibody binding by the use of macrophages. It is a potentially powerful mechanism of action (MOA) for antibody drug developers and vaccine makers to consider when measuring product efficacy. However, it is usually ignored in favor of more accessible MOAs driving biological function, for example, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), because the ADCP assays are tedious to be prepared, performed, and reproduced.
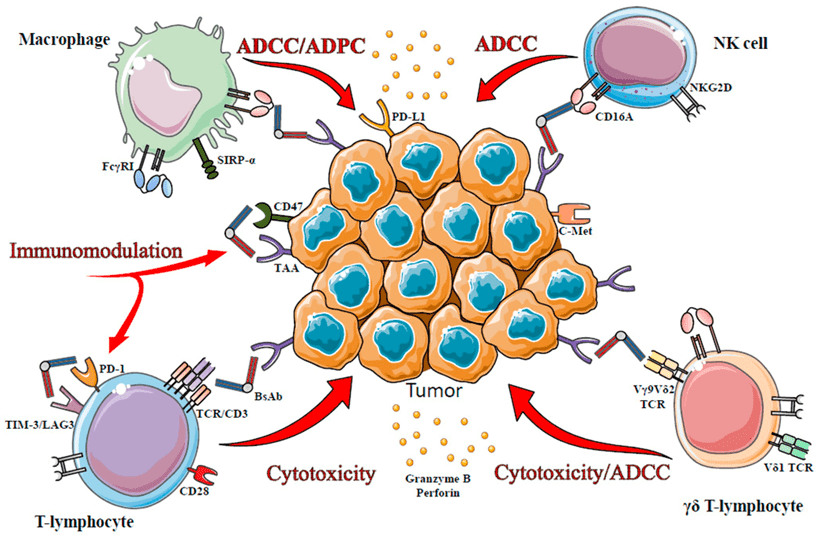
Figure 1. The illustration of the immune effector cells targeted by BsAbs. The MOA of BsAbs is related to the type of recruited immune cells: ADCC and ADCP are triggered by CD16A engagement on macrophages, NK cells or γδ T-cells (Del Bano, J., 2015).
Macrophages play an important role in the efficacy of many antibodies because they manage the process of ADCP. FcγRⅡa (CD32a), as one of those receptors, is considered to be the dominant player in the induction of ADCP by macrophages. Determining ADCP mediated through this receptor is essential in measuring the bioactivity of mAb and any biosimilars that follow. In addition, it has demonstrated that ADCP is improved in vivo by simultaneous treatment with immunomodulatory agents. Thus, the capability to determine ADCP has become more important.
It is a far more tedious process than ADCC to evaluate FcγRⅡa-mediated ADCP using primary monocytes or macrophage cells. In the ADCC assay, commercially available assays to determine cytotoxicity can be used, and blood donor cells can be prepared within a few hours. However, in the ADCP assay, the macrophages must be obtained from primary monocytes, which are isolated from blood donors. Unlike NK effector cells for ADCC, ADCP needs the macrophages to be differentiated in culture for nearly a week. Besides, the effectors macrophages and target cells should be made distinguishable via cell surface markers and labeling. Generally, ADCP assays use U937 cells or PBMC-derived cells differentiated to the mononuclear type. In addition, to generate dose-response curves for measuring ADCP activity, fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) analyses must be carried out.
The Reporter-gene Bioassay
Creative Biolabs has developed a reporter-gene assay that enables fast and more reliable measurement of ADCP of drug candidates. In this reporter-gene assay, primary monocytes were replaced by an engineered reporter cell line stably expressing FcγRⅡa (H131) and NFAT-RE/luc2. As in the primary monocytes, the same signaling for ADCP was activated when the FcγRⅡa was bound by antibody which was combined with a target cell, implying that the report assay reflects the in vivo molecular pathway for Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis via macrophages.
With our well-established ADCP assay platform, the experienced scientists at Creative Biolabs are dedicated to helping you develop therapeutic BsAbs. Our high quality ADCP assay will greatly contribute to the successes of your projects. We also provide various other services regarding BsAbs development. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Reference
-
Del Bano, Joanie, et al. "Taking up cancer immunotherapy challenges: bispecific antibodies, the path forward?" Antibodies 5.1 (2016): 1. (Under open access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
Our products and services are for research use only, and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Welcome! For price inquiries, we will get back to you as soon as possible.
To order, please email
INQUIRY





