Creative Biolabs provides high-quality biotin labeling services for global biomedical research. Leveraging extensive experience and advanced technology, we design and execute custom antibody conjugation projects in close collaboration with our clients. Our expert team ensures rapid, optimized, and high-quality conjugate outcomes.
Introduction to Biotin Labeling
Biotin, or vitamin B7, is a small, biologically active molecule that functions as a coenzyme. It can be coupled to oligonucleotides at multiple terminal and internal sites. Biotinylation, the covalent attachment of biotin to proteins, nucleic acids, or other molecules, is widely used in detection systems, particularly for low-abundance targets undetectable by labeled antibodies alone. This process is generally rapid, specific, and unlikely to perturb the molecule's natural function due to biotin's small size. Critically, multiple biotin molecules can be conjugated to an antibody with exceptionally high affinity, fast association rates, and specificity, a characteristic not observed with streptavidin or avidin conjugation. This amplification significantly enhances the detection of low-level proteins.
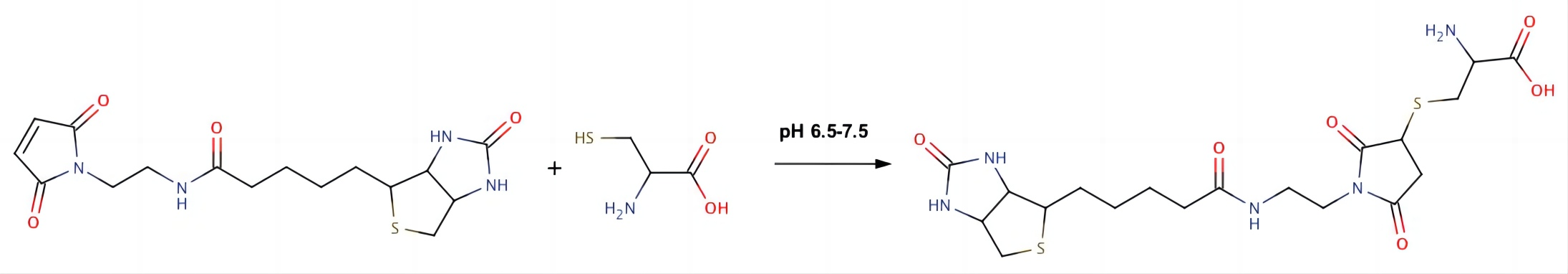 Fig.1 Biotin maleimide cysteine reaction. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Biotin maleimide cysteine reaction. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Advantages of Biotinylation
Exceptional Sensitivity and Specificity: The robust biotin-streptavidin interaction ensures minimal background noise and high signal-to-noise ratios, allowing for the detection of even low-abundance targets.
Versatility: Biotin can be conjugated to a vast array of biomolecules without significantly altering their native structure or biological activity.
Signal Amplification: Multiple biotins can be attached to a single molecule, or multiple streptavidin-reporter conjugates can bind, leading to enhanced signal generation.
Stability: The biotin-streptavidin complex is highly stable across various conditions, providing reliable and reproducible results.
Ease of Use: Biotinylated molecules are readily detected or captured using readily available streptavidin conjugates, simplifying experimental workflows.
Biotin Labeling Services Provided by Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we offer unparalleled expertise in comprehensive biotin labeling and modification services, designed to meet the precise demands of both academic research and industrial production. For over two decades, our seasoned scientists have provided specialized protein biotin labeling services, mastering the art of labeling virtually any protein with biotin while meticulously preserving its native bioactivity. Our state-of-the-art protein biotinylation platform ensures not only efficiency but also the highest levels of quality. We have innovated and refined multiple biotinylation approaches, ensuring we can precisely satisfy the unique requirements of our global clientele.
Our detailed service types include:
Protein Biotinylation
We expertly conjugate biotin to a wide spectrum of proteins, accommodating various sizes, structures, and native functions, ensuring minimal impact on their biological activity.
Antibody Biotinylation
Specialized in labeling monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, our service supports enhanced detection and purification in immunological assays, providing robust and sensitive reagents.
Peptide Biotinylation
Precision biotinylation of synthetic or recombinant peptides for applications in epitope mapping, binding assays, and affinity purification.
Nucleic Acid Biotinylation
We provide efficient biotinylation of DNA and RNA probes, essential for hybridization assays, gene expression studies, and sequence capture.
Site-Specific Biotinylation
Leveraging advanced conjugation chemistries, we offer precise, site-specific biotinylation. This method ensures biotin attachment at a pre-determined location, preserving critical functional domains and enabling superior control over experimental design.
Biotin Conjugation to Small Molecules, Lipids, and Carbohydrates
Our capabilities extend to custom biotin modification of various small molecules, lipids, and complex polysaccharides for diverse research applications.
Biotin-Streptavidin Binding Studies
Beyond conjugation, we offer comprehensive studies to validate the functional binding affinity of your biotinylated molecules with streptavidin, ensuring optimal performance in your downstream applications.
Biotin Labeling Project Workflow
We begin each project with a detailed consultation to determine your individual biomolecule, application, and desired labeling parameters.
Following the discussion, a detailed proposal outlining the methodology, timelines, and costs is provided for your review and approval.
Upon receipt of your sample, our expert team prepares the biomolecule and proceeds with the chosen biotinylation strategy, utilizing pre-activated biotin reagents and optimized reaction conditions.
The biotinylated product undergoes rigorous purification steps to remove unreacted biotin, excess reagents, and any byproducts, followed by concentration to your desired specification.
Every labeled product is subjected to extensive quality assurance testing to confirm labeling efficiency, purity, and functional integrity.
Comprehensive data reports, including synthesis records and analytical results (HPLC, MS, GC, NMR, etc.), are provided, followed by the secure delivery of your biotinylated product.
Applications of Biotin Labeling
- Purification
The biotin tag can be used in the technique of affinity chromatography in conjunction with a column attached to avidin (or streptavidin or neutravidin), the natural ligand for biotin. Tagging the protein with iminobiotin can be utilized to isolate the tagged protein since the biotin analog has significant binding to avidin/streptavidin at alkaline pH but loses affinity when the pH is lowered. As a result, an avidin/streptavidin column can release an iminobiotin-tagged functional protein by reducing the pH (to around pH 4).
- Detection
Anti-biotin antibodies or avidin/streptavidin-tagged detection techniques such as enzyme reporters or fluorescence probes, which can be employed to detect the protein, may facilitate localization using fluorescence or electron microscopy, ELISA assays, ELISPOT assays, western blots, and other immunoanalytical approaches. It is vital to highlight that utilizing monovalent streptavidin for detection prevents aggregation or aggregation of biotinylated targets.
- Identifying and isolating
The non-covalent bond formed by biotin and avidin or streptavidin is nearly as strong as a covalent bond and has a higher binding affinity than most antigen and antibody interactions. Based on this highly strong binding, labeling proteins with biotin is a useful tool for applications such as affinity chromatography, which separates the biotinylated protein from a mixture of other proteins and biochemicals using immobilized avidin or streptavidin. Biotinylation of MHC molecules to generate MHC multimers has also been shown to be an efficient approach for detecting and separating antigen-specific T-cell populations.
- Protein-protein interactions
Protein biotinylation in living cells is developed to explore protein-protein interactions and proximity. One of the interacting proteins is biotinylated, while the other is being detected using a streptavidin-conjugated detection method. This method is frequently employed in pull-down assays and proximity-dependent labeling procedures.
Published Data
1. Cell Type-Specific Biotin Labeling for Proteomic Differences Profiling
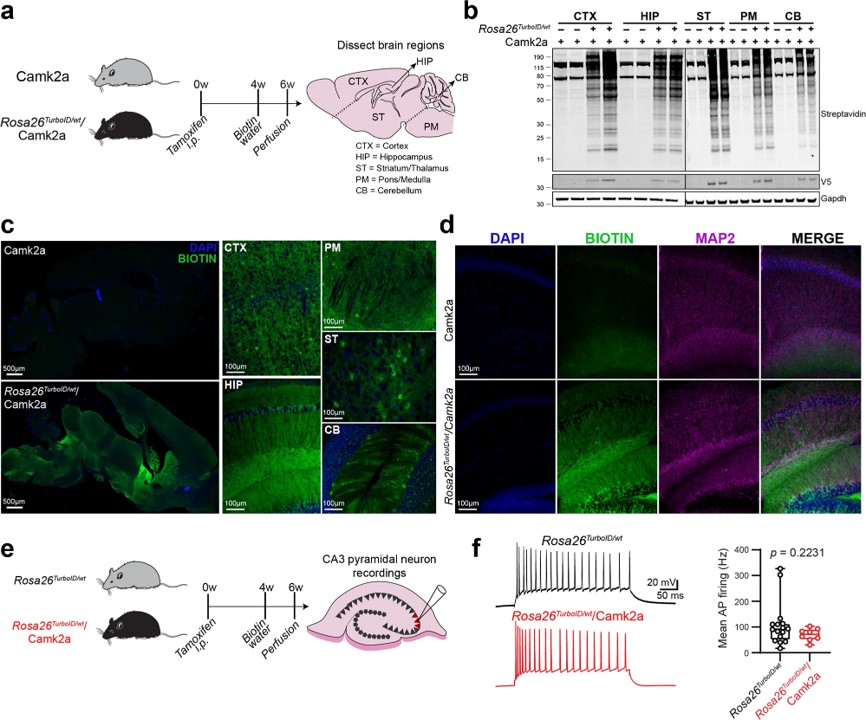 Fig.1 Biotin labeling of Camk2a-neuronal protein.1
Fig.1 Biotin labeling of Camk2a-neuronal protein.1
Researchers developed a mouse model for cell-type-specific expression of biotin ligase TurboID, which enabled in vivo protein biotinylation. Using adenoviral and transgenic methods, they achieved widespread protein biotinylation of neurons, labeling proteins across neuronal soma and axons all over the brain. This allowed the identification of over 2,000 neuron-derived proteins, including transporters, synaptic proteins, ion channels, and potential drug targets. The team compared the proteomes of Camk2a-neurons and Aldh1l1-astrocytes, revealing region-specific differences that may contribute to selective vulnerability to neurological diseases. Additionally, they applied an antibody-based technique to explore differences in signaling phospho-proteins and cytokines between neurons and astrocytes. This approach offers a powerful tool for studying cell-type-specific proteomes in various tissues under both normal and disease conditions.
2. Proximity-Dependent Biotin Labeling for Protein-Protein Interactions Characterization
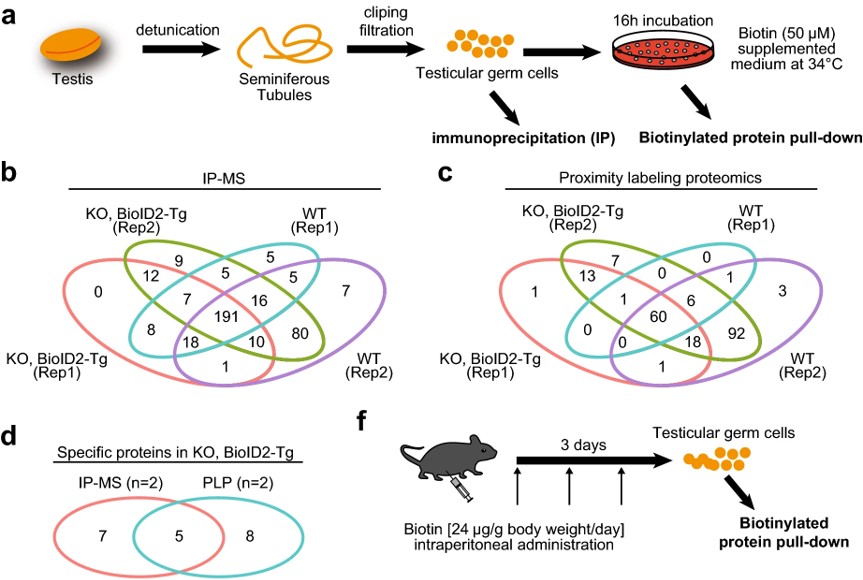 Fig.2 Interactome analysis of TESMIN.2
Fig.2 Interactome analysis of TESMIN.2
Proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID) is a promising method for mapping transient protein-protein interactions. In this study, researchers applied proximity labeling proteomics to the testis by creating two transgenic mouse lines expressing biotin ligases (BioID2 or TurboID) fused with TESMIN, a protein that translocates from the cytosol to the nucleus during meiotic progression and is essential for reproduction. The BioID2 fusion rescued fertility defects in Tesmin KO male mice, demonstrating that TESMIN-BioID2 can functionally replace TESMIN. Biotinylated protein pull-down followed by mass spectrometry identified components of the MYBL1-MuvB complex, which regulate cell-cycle gene expression. This study highlights the utility of proximity labeling proteomics in fully identifying TESMIN-associated proteins in male germ cells.
Features of Our Services
- Rich Experience: With years of experience in the field, we've successfully delivered hundreds of uniquely biotinylated proteins and antibodies for diverse clients.
- Mature Technology: Our advanced platform utilizes cutting-edge chemistry and optimized protocols. This ensures high-quality biotin labeling with exceptional sensitivity, always preserving your biomolecule's native activity.
- Short Duration: We prioritize your research timelines. Many projects see a rapid turnaround, often completed within 1-2 business days from sample receipt, all at a competitive price.
- Precise Control: Our methodologies offer tailored solutions, including site-specific biotinylation. This precision maintains optimal protein functionality and enables highly specific downstream applications.
- Comprehensive Characterization: Beyond standard checks, we employ a full suite of advanced analytical tools, including MS, HPLC, GC, and NMR. This guarantees unparalleled accuracy in verifying your product's purity and integrity.
Q&A
-
Q: How do you ensure the biotinylated molecule retains its biological activity?
A: Preserving the functionality of your biomolecule is our paramount concern. We achieve this by employing gentle, optimized conjugation chemistries and carefully controlled reaction conditions that minimize structural perturbation. Our advanced techniques, including the option for site-specific biotinylation, ensure that critical functional domains remain unaltered. Post-labeling, every product undergoes rigorous functional assays to confirm the retention of biological activity.
-
Q: What quality control procedures do you use for biotinylated products?
A: Our commitment to quality is unwavering. Each biotinylated product undergoes a multi-faceted quality control process. This includes techniques such as mass spectrometry (MS) for verifying biotinylation efficiency, SDS-PAGE for assessing purity and integrity, and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for purification and quantification. For advanced characterization, we also utilize gas chromatography (GC) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), providing detailed structural and purity data.
-
Q: Can you perform site-specific biotinylation? What are its advantages?
A: Absolutely. We specialize in site-specific biotinylation, a superior method compared to random labeling. This technique allows us to attach biotin at a precisely predetermined location on your biomolecule. The primary advantage is the meticulous preservation of the molecule's functional sites, preventing interference with its biological activity. It also enables controlled orientation of the labeled molecule in assays, leading to more accurate and reproducible results.
-
Q: Can you also help with downstream applications, such as biotin-streptavidin binding studies?
A: Yes, our expertise extends beyond just the labeling process. We offer comprehensive biotin-streptavidin binding studies as an additional service. This allows us to functionally validate the interaction between your biotinylated molecule and streptavidin, ensuring optimal binding affinity and performance for your specific assays. This added layer of validation provides confidence in your experimental outcomes.
-
Q: What if my biomolecule is sensitive or unstable? Can it still be biotinylated?
A: We specialize in handling sensitive and challenging biomolecules. Our experienced scientists employ optimized, gentle chemistries and carefully controlled reaction conditions to minimize denaturation or degradation during the labeling process. We consider factors like pH, temperature, and solvent compatibility to preserve the stability and integrity of your unique sample. Please discuss any specific sensitivities with our team during the initial consultation.
Creative Biolabs is committed to offering high-quality biotin labeling services for worldwide customers. With advanced technology and proficient scientists, we can assure you both biotinylation efficiency and protein activity preservation. Moreover, our biotin labeling service is reproducible and quality guaranteed. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us and get a quote. We will get in touch with you within 24 hours and design an optimal method for your project.
References
- Rayaprolu, Sruti, et al. "Cell type-specific biotin labeling in vivo resolves regional neuronal and astrocyte proteomic differences in mouse brain." Nature Communications 13.1 (2022): 2927. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Oura, Seiya, et al. "Proximity-dependent biotin labeling in testicular germ cells identified TESMIN-associated proteins." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 22198. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only part of the original image.
For Research Use Only.