Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an important molecule within the human body, but many of its roles in physiology and pathophysiology are not well understood. To better understand the importance of H2O2 in biological systems, it is essential that researchers are able to quantify H2O2 in various settings such as in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo systems.
Introduction
H2O2 is a reactive oxygen species (ROS) that is present throughout the body, playing various roles in physiological processes. At high levels, H2O2 can be detrimental to the body, resulting in cell damage, inflammatory disease, and even cancer. However, low physiological concentration of H2O2 makes accurate detection difficult. To improve the understanding of H2O2‘s role in biological systems, researchers have developed different sensors to detect and quantify H2O2 under various conditions. The two classes of sensors that are typically used for H2O2 detection are light detecting sensors and electrochemical sensors.
Electrochemical Sensors
Two types of electrochemical probes are frequently used for H2O2 detection, namely potentiometric and amperometric. The working principle of the two probes is different.
- Potentiometric probes measure the potential (voltage) between a working and reference electrode in a system that has no significant current flow. The working electrode needs to be modified so that changes in potential correlate to changes in H2O2 concentration, and the reference electrode must remain constant so that it can serve as a reference, or comparison, to the working electrode.
- Amperometric sensors rely on the principle that changes in current are correlated to change in concentration. Thus, amperometric sensors use two or three electrodes to measure the change in the current of a sample while the potential (voltage) is held constant.
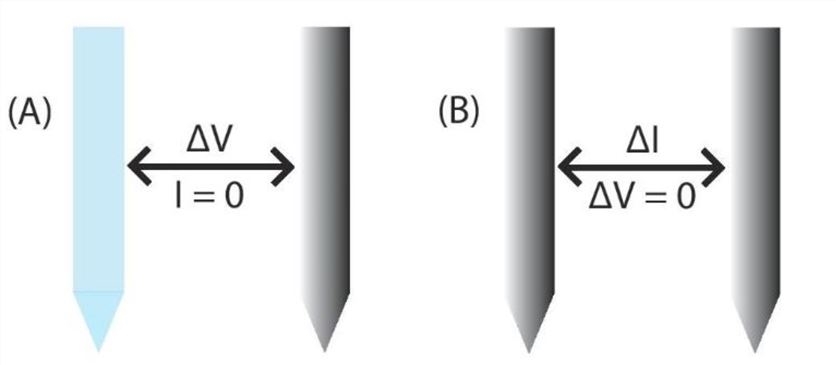 Fig.1 Comparison of dual electrochemical sensing techniques.1, 3
Fig.1 Comparison of dual electrochemical sensing techniques.1, 3
In the electrochemical methods, different types of modified electrodes have been used. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzyme is one of the mostly used materials for the modification of electrode.
Owing to the expensiveness and unstableness of HRP, finding alternatives to reduce the cost and to improve the performance of H2O2 biosensors is scientifically important. Hb can be utilized as the HRP substitute in the detection of H2O2 in virtue of the low cost and the stable property of in solution. Although Hb does not play a role as an electron transfer carrier in biological systems, it has been shown to possess enzyme-like catalytic activity.
 Fig.2 Electrochemical detection of H2O2.2, 3
Fig.2 Electrochemical detection of H2O2.2, 3
With the development of nanoscience and nanotechnology, carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are widely used with Hb for the construction of biosensor. The nanomaterial-based electrochemical H2O2 biosensor usually possesses a larger linear range and better sensitivity, and it is more applicable to industrial and environmental monitoring.
References
- Meier, Jakob, et al. "Hydrogen peroxide sensors for biomedical applications." Chemosensors 7.4 (2019): 64.
- Ahmad, Touqeer, et al. "Recent advances in electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) released from cancer cells." Nanomaterials 12.9 (2022): 1475.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.