As a leading CRO of antibody generation and development, Creative Biolabs offers application-specific antibody development services to global clients. With experienced scientists and advanced technology, we have established a series of high-quality in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development services against biomarkers of different diseases. Here, we introduce our IVD antibody development services for GDF-15 marker.
Growth Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15)
Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), a member of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) superfamily, is highly expressed in several cells, including cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells and so on. GDF-15 is formed as an approximately 40 kDa propeptide form, and its N terminus is divided resulting in a 30 kDa disulfide linked dimeric active protein form. GDF-15 highly expressed responses to diverse kinds of cytokines and growth factors, for example, TNF-α, TGF-β, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and angiotensin II. The expression of GDF-15 is highly induced in cardiomyocytes after ischemia/reperfusion and the cardiomyocytes is a primary source of GDF-15 in the infarct border zone. GDF-15 serves a crucial role in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, etc. In addition, raised GDF-15 expression is a symbol of various cancers such as colon, prostate and breast.
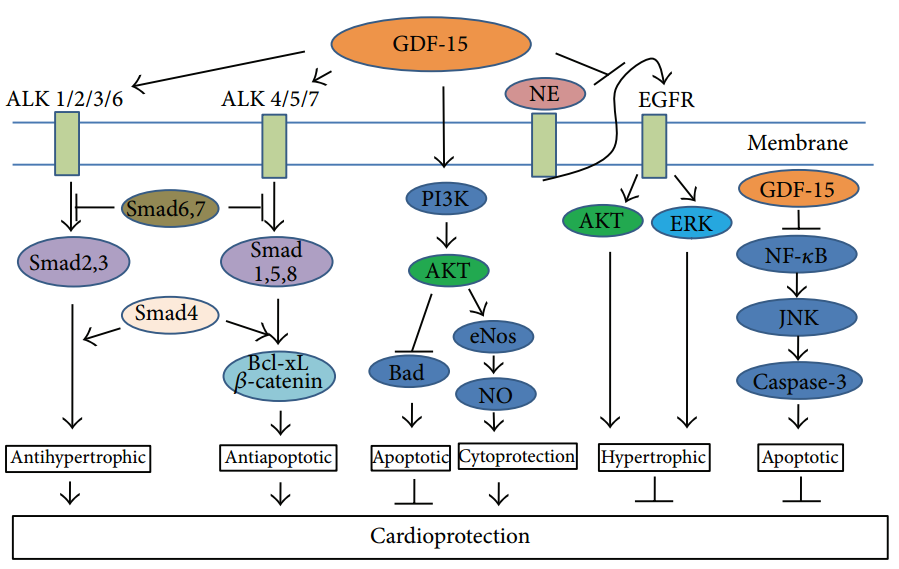 Fig.1 Signaling pathways regulated by GDF-15 is very important for cardioprotection.1
Fig.1 Signaling pathways regulated by GDF-15 is very important for cardioprotection.1
GDF-15 Marker of Heart Failure
The pivotal process causing HF is cardiac remodeling in response to chronic disease stresses. HF is more than a disease. It is a syndrome with various distinct subtypes. A number of markers of diagnostic and prognostic have been developed in HF, including GDF-15 highly expressed in inflammatory conditions. Many researchers found that it was beneficial to use GDF-15 as a member of multi-biomarker method in prognosticating patients with HF. A research has revealed that the circulating levels of GDF-15 were highly increased in patients with HF, about 75% of patients with stable left-sided HF displayed with GDF-15 levels > 1,200 ng/L. Besides, the GDF-15 levels were also raised in patients with ischemic or nonischemic HF. It has been extensively accepted that a multimarker strategy uniting GDF-15 with NT-proBNP may contribute to the identification of HF patients.
GDF-15 Marker of Diabetes
Diabetes is a usual cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD), with high glucose level in blood on account of less insulin secretion from pancreas or insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM) are two main types of diabetes. One major symptom of diabetes is hyperglycemia, research has indicated that elevated GDF-15 defends endothelial cells against high glucose caused cellular injury by activating signaling pathway. It has proven that GDF-15 was increased in patients with diabetes, but not NT-proBNP. Serum GDF-15 levels are positively connected with glucose, HbA1c and body weight. It has demonstrated that serum concentration of GDF-15 was raised about 2-fold in T2DM women patients, contrasted to control subjects.
DGF-15 Marker of Metabolic Disease
It has been shown that GDF-15 released from macrophages, liver and white adipose tissue may act as a metabolic regulator. GDF-15, like adiponectin and leptin, acts as adipokine which can regulate the lipid and glucose metabolism, protect from chronic inflammation in adipose tissue, increase insulin sensitivity, and regulate food intake and body weight. The increase of serum GDF-15 levels in obese and type 2 diabetic women keeps associated with body mass index (BMI), body fat, glucose and C-reactive proteins. Higher level of GDF-15 is related to the increased cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality. It acts the important role in development and progression of numerous diseases such as heart failure, diabetes, cancer, coronary artery diseases and cognitive impairment. It is also reported that the GDF-15 levels can work as a biomarker for the use of metformin in people with dysglycemia in which the concentration of GDF-15 reflects the dose of metformin. In addition, some studies indicate that GDF-15 outperforms FGF-21 as an indicator of mitochondrial diseases.
IVD Antibody Development Services for GDF-15 Marker
IVD antibodies have been widely used in the diagnosis of numerous diseases. Antibody-based immunoassays are the most generally used diagnostic assays for the detection of biomolecules. With advanced technology and professional scientists, Creative Biolabs is capable of offering a full range of IVD antibody development services against various markers for global customers, including GDF-15 marker. For more details and information, please feel free to contact us and get a quote.
Reference
- Adela, Ramu, and Sanjay K. Banerjee. "GDF‐15 as a target and biomarker for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: a translational prospective." Journal of diabetes research 2015.1 (2015): 490842.
For Research Use Only.