The liver is an organ located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. It has various functions, including (i) detoxification of various metabolites, (ii) synthesis of proteins, (iii) production of biochemicals necessary for digestion, (iv) regulation of glycogen storage, (v) decomposition of red blood cells, and (vi) production of hormones. Liver diseases can be inherited or caused by a variety of factors, including viruses, drugs, poisons, alcohol abuse, and obesity. In the early stage, no obvious signs or symptoms can be observed until it's fairly advanced. More than a hundred types or stages of liver diseases have been identified, among which some common ones include hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and failure.
Liver Hepatitis - inflammation (swelling) of the liver as the result of a viral infection or liver damage caused by exposing to harmful substances such as alcohol. There are several different types of hepatitis from A to E. Some types will pass without any serious problems, while others can be long-lasting (chronic) and cause scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), loss of liver function and, in some cases, liver cancer.
Liver Fibrosis - a process that inflamed liver starts to scar under no treatment. (Scar tissue is a kind of fibrous tissue.) Scar tissue can keep blood from flowing through your liver. As more scar tissue builds up, your liver may not work as well as it once did. If your liver disease is diagnosed and treated successfully at this stage, there's still a chance that your liver can heal itself over time.
Liver Cirrhosis - a stage that your liver may become too seriously scarred to be reversed. Cirrhosis can lead to a number of complications, accompanied by a series of symptoms including bleed or bruise easily, jaundice, skin itch, insulin resistance, and type-2 diabetes.
Liver Failure - a life-threatening condition that demands urgent medical care. It means that your liver is losing or has lost all of its function. The first symptoms of liver failure are often nausea, loss of appetite, fatigue, and diarrhea. As time progresses, confusion, disorienting, and drowsiness gradually appear. Immediate treatment is needed. The medical team will try to save whatever part of the liver that still works. If this is not possible, the only option may be a liver transplant.
Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
Diagnosis of liver diseases starts with a health history and a thorough physical examination. Then, different tests can be performed, including blood tests, imaging tests, and tissue analysis. Blood tests (liver function tests), such as proteins, liver enzymes, bilirubin, albumin or platelet count in the blood, help to detect inflammation and liver damage. Imaging tests, including ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can be performed to get an image of the liver and analyze liver damage. For tissue analysis, a liver biopsy is done to determine the disease stage.
In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Immunoassays for Liver Disease Markers
Over recent years, noninvasive biomarkers are widely used as tools for diagnosis and prognosis of liver diseases. A number of markers have been identified, driving the development of IVD immunoassays for disease severity, progression, and regression assessment. Based on the use of highly specific antibodies, biomarkers can be measured quickly and accurately. Besides, the combination of a panel of markers further improved the accuracy of the tests. Commonly used immunoassay formats include ELISA (enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay), LFIA (lateral flow immunoassay), CLIA (chemiluminescent immunoassay), PETIA (particle-enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay, immunohistochemistry, etc. With different labels (such as fluorescent microspheres, biotin, HRP, colloidal gold, and latex) for signal detection, each of them has exhibited different advantages and disadvantages. With the discovery of more and more biomarkers, novel immunoassays should be developed to improve the current situation for live disease diagnosis.
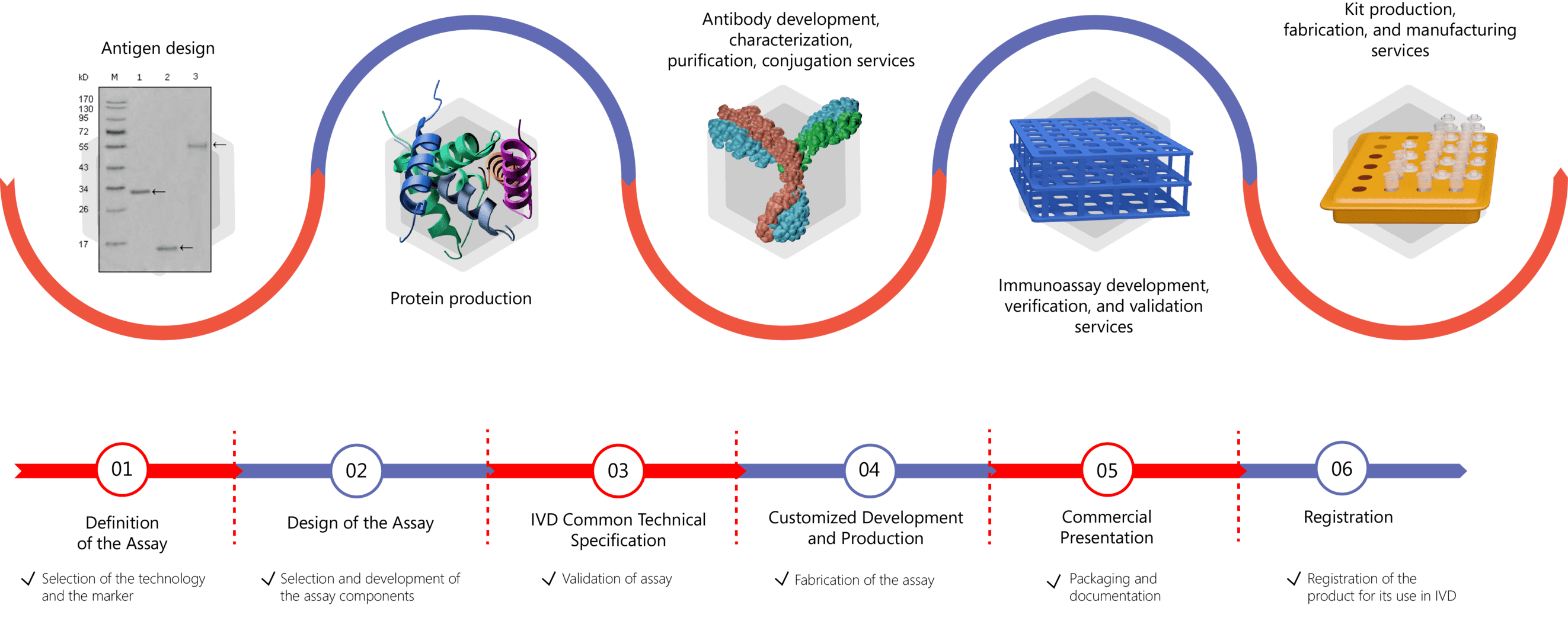
IVD Antibody/Immunoassay Development Services Provided by Creative Biolabs
In order to render more precise antibody-based IVD tools, Creative Biolabs offers customized biomarker-specific antibody development services to obtain high-quality antibody for your IVD immunoassay project. Besides antibody generation, we also offer antibody conjugation, antibody pairing, and one-stop immunoassay development services to our global clients. We help to design immunoassay protocols, perform assay validation, manufacture kits. For more information please click the links below:
- IVD Antibody Development
- Antibody Pair Development
- Antibody & Protein Conjugation
- IVD Immunoassay Development
Please find the biomarker or disease you are interested in below:
Features of Our Services
- Our repertoire includes both established and novel potential liver disease biomarkers
- Abundant experience in various immunoassay technology platforms
- Reasonable prices and short turnaround time
- Services are tailored to meet the IVD needs of our valued clients.
Please feel free to contact us for more information and a formal quote.
References
- Wiegand, J., (2013). “The etiology, diagnosis and prevention of liver cirrhosis: part 1 of a series on liver cirrhosis.” Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 110(6), 85.
- Goldberg, E., (2013). “Acute liver failure in adults: Etiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis.” UpTo-Date Version, 11.
- Kang, J. S., (2017). “Noninvasive Diagnostic and Prognostic Assessment Tools for Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease.” In Liver Cirrhosis-Update and Current Challenges. IntechOpen.
For Research Use Only.