As an incomparable antibody service provider, Creative Biolabs provides high-quality in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development services to help our clients with their diagnostic immunoassay development. With a wealth of experience and professional scientists, now we provide IVD antibody development services against Chlamydia.
Introduction of Chlamydia
Chlamydia, also known as Chlamydia trachomatis (Ctr), is a Gram-negative, obligate intracellular pathogen that causes the most common sexually transmitted bacterial infection in humans and is the leading cause of preventable blindness worldwide. Most people have no symptoms after infected initially. If left untreated, it will develop numerous symptoms after a few weeks. In women, the infection can ascend to the upper genital tract, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which can then lead to tubal factor infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain. And an infection in men can result in a series of symptoms, including discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. Moreover, repeated infections of the eyes can result in trachoma which is a common cause of blindness in developing countries.
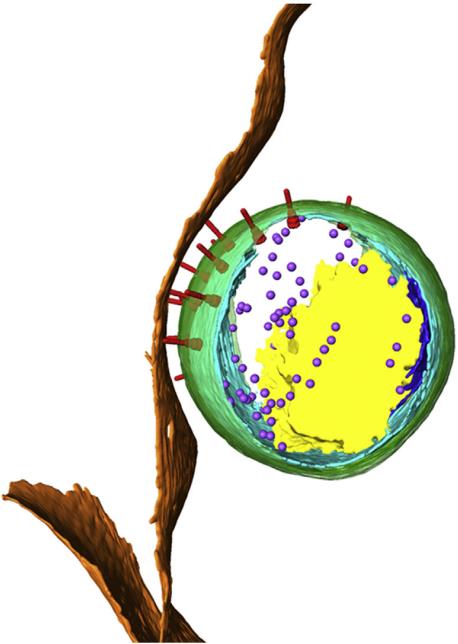 Fig.1 Polarised structure of the C. trachomatis elementary body in contact with the host cell.1
Fig.1 Polarised structure of the C. trachomatis elementary body in contact with the host cell.1
Correlation of Chlamydia and STDs
The obligate intracellular pathogen Chlamydia trachomatis is a major cause of sexually transmitted disease and infertility worldwide. It can be infected via numerous sexually transmitted routes, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Importantly, it can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. Studies have suggested that it is most prevalent among sexually active young adults, with the majority of infections being asymptomatic and remaining undiagnosed. In addition, the eye infections may be spread by personal contact, flies, and contaminated towels especially in areas with poor sanitation.
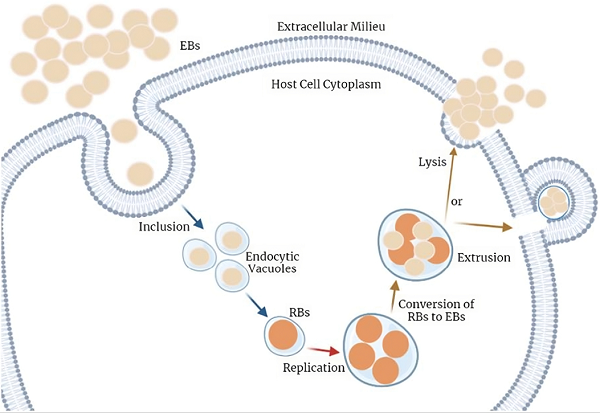 Fig.2 C. trachomatis cell cycle of infection.2
Fig.2 C. trachomatis cell cycle of infection.2
Introduction of C. pneumoniae
Chlamydophila pneumoniae, an obligate intracellular pathogen, has been proven to cause both epidemic and endemic respiratory tract infections around the world. It is a significant cause of both lower and upper acute respiratory diseases and accounts for approximately 10% cases of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Infection often appears as a mild, self-limiting illness but outbreaks of C. pneumoniae infection have been reported within families, in schools, military barracks, and small communities. The clinical presentation of respiratory illness caused by C. pneumoniae is often indistinguishable from that of viral or mycoplasma etiology. Consequently, different laboratory diagnostic tools have been developed not only for diagnosis but for early and appropriate interventions or patient management. These laboratory diagnostic tools include culture assay, antigen detection tests, serology assay, etc.
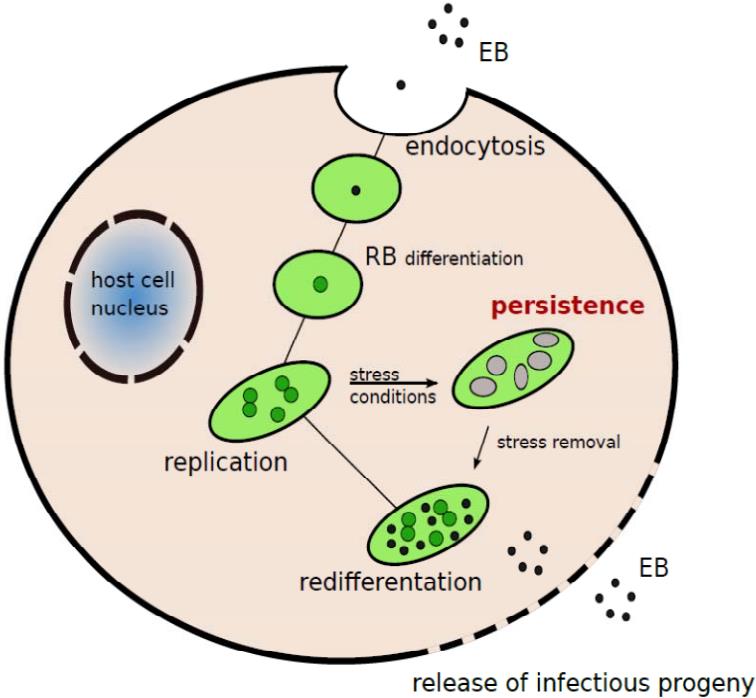 Fig.3 Schematic representation of C. pneumoniae developmental cycle.3
Fig.3 Schematic representation of C. pneumoniae developmental cycle.3
Antigen Detection Tests
Antigen detection tests include direct fluorescent antibody assays (DFA) and enzyme immunoassays (EIA), which are frequently used IVD tools for C. pneumoniae infection diagnosis. DFAs use the fluorescein-conjugated monoclonal antibodies for staining of cell cultures. This method is estimated to have a sensitivity of 20 to 60%. However, the reading is quite subjective and thus the specificity is highly dependent on the expertise of the technologist. EIAs have been used for detection of C. pneumoniae from swabs. The sensitivity of EIAs is reported to be comparable with that of DFAs, but they lack specificity because EIA is based on the capture of the genus-specific chlamydial lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Serology
Serology has so far been the most commonly used method for diagnosis of C. pneumoniae infections. It can be further divided into several classes: complement fixation (CF), EIA-antibody tests, and microimmunofluorescence (MIF) test. The CF test has been traditionally used for the serodiagnosis of respiratory chlamydial infections, however, it cannot be used to distinguish the antibody response resulting from C. trachomatis, C. psittaci or C. pneumoniae infections because the chlamydial antigen involved in CF is the genus-specific LPS. As with CF, the EIA test also detects LPS group antigen (genus-specific). The MIF assay is used to detect species-specific antibodies and is the gold standard for chlamydia serology today. The antigen of MIF uses purified elementary antibodies (EBs) but antibody cross-reactivity among chlamydia species can be observed due to the presence of antibodies against LPS or other impurities in the antigen preparation. Generally, MIF test is so far the most sensitive test for diagnosis of C. pneumoniae infection, if performed with expertise and with properly collected paired sera. However, the CF tests and the EIAs are much less technically demanding than the MIF, and the LPS antibodies are produced early in infection, which means a more rapid diagnosis.
IVD Antibody Development Service Targeting Chlamydia
In the past years, IVD technology has successfully become an essential segment of the global healthcare industry. IVD antibodies have greatly improved the well-being of the common public for it enables the easily identifying of numerous diseases, conditions, or infections. With years of experience and advanced technology, Creative Biolabs provides high-quality IVD antibody development services targeting Chlamydia for worldwide customers. Besides antibody generation, we offer diagnostic immunoassay development services, including feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, assay optimization, and kit production.
If you are interested in our services, please don’t hesitate to contact us and get a quote.
References
- Nans, Andrea, Charlotte Ford, and Richard D. Hayward. "Host-pathogen reorganisation during host cell entry by Chlamydia trachomatis." Microbes and infection 17.11-12 (2015): 727-731. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Rodrigues, Rafaela, Carlos Sousa, and Nuno Vale. "Chlamydia trachomatis as a current health problem: challenges and opportunities." Diagnostics 12.8 (2022): 1795. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Di Pietro, Marisa, et al. "Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in atherosclerotic lesion development through oxidative stress: a brief overview." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14.7 (2013): 15105-15120. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.