Antibodies have exhibited preeminent potential in not only the treatment but also the diagnosis and prognosis of bacterial and viral infections. As one of the leading industries that are specialized in antibody development, Creative Biolabs is providing incomparable services for the development of high-quality in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibodies with low cross-reactivity for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis infections.
Introduction of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) is a nonmotile non-spore-forming, obligate aerobe, acid-fast bacillus that often appears beaded or unstained using Gram stain. It is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. In most of the cases, M. tuberculosis is transmitted through the air and when the infected droplet nuclei are inhaled, M. tuberculosis bacilli land in the alveoli where they are consumed by alveolar macrophages. As a result, M. tuberculosis subverts the alveolar macrophages’ attempts at its degradation and instead replicates inside the macrophages for weeks. As the bacilli multiply, they are frequently carried into regional lymph nodes and can spread to other sites such as the lung apices, vertebrae, etc. During this time, cell-mediated immunity is developed and the tuberculosis infection can be detected. In about 5% to 10% cases, tuberculosis infection progresses to tuberculosis (TB) disease. The diagnostic methods of M. tuberculosis infection mainly include immunodiagnostic tests, culture detection methods, and molecular detection methods.
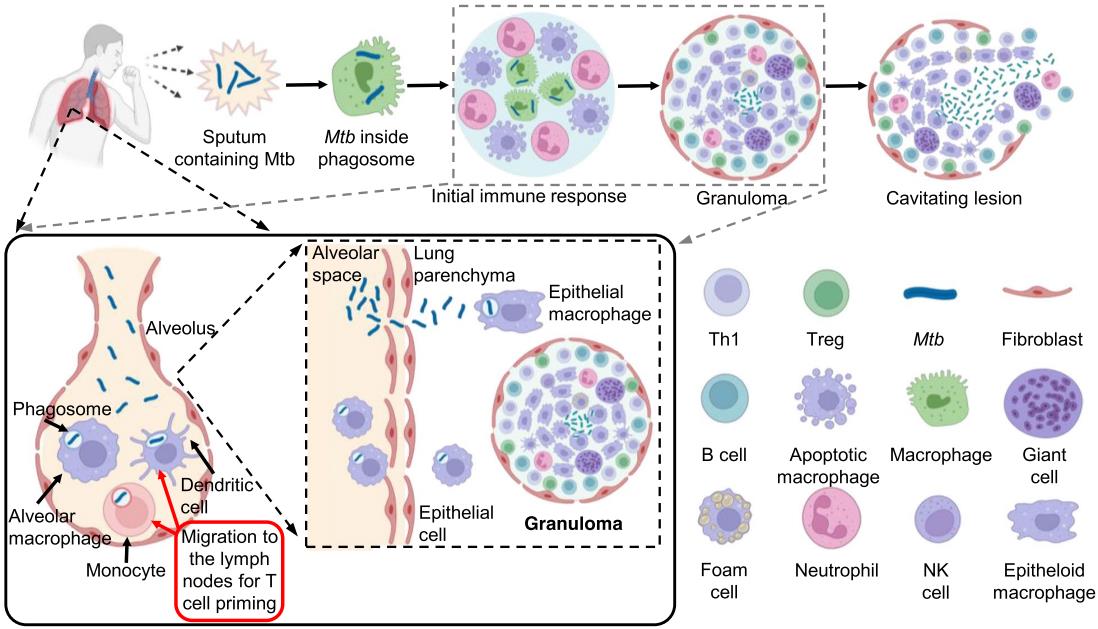 Fig.1 The pathogenesis of M. tuberculosis.1
Fig.1 The pathogenesis of M. tuberculosis.1
Immunodiagnostic Tests
Two commonly used immunodiagnostic tests are the tuberculin skin test (TST) and the IFN-γ release assays (IGRAs). The TST test is based on the fact that infection with M. tuberculosis bacterium produces a delayed-type hypersensitivity skin reaction to the purified protein derivative (PPD). IGRAs are based on the ability of the M. tuberculosis antigens for early secretory antigen target 6 (ESAT-6) and culture filtrate protein 10 (CFP-10) to stimulate host production of IFN-γ.
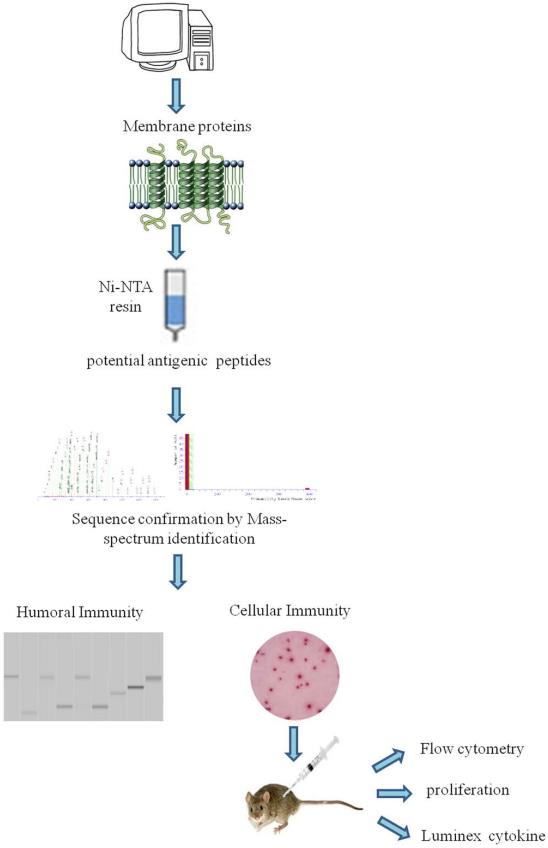 Fig.2 Flow chart for detecting M. tuberculosis H37Rv membrane proteome antigenicity.2
Fig.2 Flow chart for detecting M. tuberculosis H37Rv membrane proteome antigenicity.2
Other Diagnostic Methods
Culture detection method is the World Health Organization (WHO)-recommended gold standard for the diagnosis of TB disease. It is made by culturing M. tuberculosis organisms from a specimen taken from the patient (e.g., sputum, pus, cerebrospinal fluid). However, this traditional method has long turnaround time. Molecular detection methods utilize the nucleic acid-based amplification test (NAAT) for the detection and identification of M. tuberculosis from direct specimens. These molecular assays are rapid and sensitive and are recommended by the WHO as initial diagnostic tests. Besides, clinical diagnosis of TB diseases also involves the use of radiography, such as chest X-ray and CT.
Although a number of diagnostic tools are currently available for M. tuberculosis infections, more and more simple, rapid, and sensitive tests are constantly developed, such as immunochromatographic assays. To battle against the challenges of M. tuberculosis diagnosis, Creative Biolabs offers first-class IVD antibody development services for different diagnostic assay development purposes. Besides, we also offer diagnostic immunoassay development services, including feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, assay optimization, and kit production. Please contact us to discuss your project in detail and experience the great value of our expert services.
References
- Yan, Weizhu, et al. "The pathogenic mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: implication for new drug development." Molecular Biomedicine 3.1 (2022): 48. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Li, Haifeng, et al. "Analysis of the antigenic properties of membrane proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis." Scientific Reports 9.1 (2019): 3042. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.