In vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibodies play an essential role in disease diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Creative Biolabs is professional in the filed of IVD antibody development and antibody pair development. We have experienced experts and advanced platforms that enable us to provide unparalleled services targeting a panel of biomarkers. Here, we introduced the potential of NO66 as a diagnostic marker for renal cancer.
Introduction of NO66
NO66 (Nucleolar protein 66), also known as RIOX1 (Ribosomal oxygenase 1), is a type of oxygenase that can act as a ribosomal histidine hydroxylase. Importantly, it is classified into a member of JmjC domain-containing histone demethylases (HDMs) with specific specificity towards histone H3 methylated on both Lys4 (H3K4me) and Lys36 (H3K36me), thereby, playing a key role in histone code. NO66 belongs to a protein-coding gene located on the chromosome 14q24.3. NO66 is reported highly conserved in eukaryotes, which was originally identified as a dual-location protein present in the nucleolus and nucleoplasm. By the way, there is an important paralog of NO66 gene that is ribosomal oxygenase 2 (RIOX2).
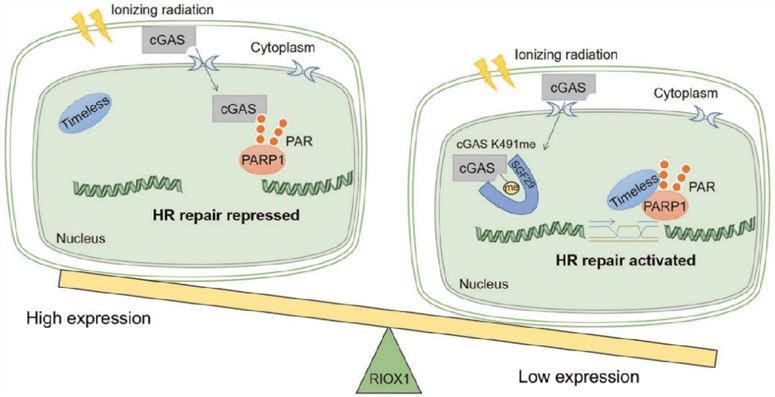 Fig.1 RIOX1 (NO66)-mediated repression of homologous recombination repair.1
Fig.1 RIOX1 (NO66)-mediated repression of homologous recombination repair.1
NO66, a Jumonji family protein, was previously found to participate in the control of Osterix (Osx) transcriptional activity through proteomics and mass spectrometry (MS) approaches. NO66 can interact with Osx and then mediate inhibition of Osx-target promoters, which leads to negative regulation on osteoblast differentiation. It is also shown that NO66 associates with the PRC2 complex (Polycomb repressive complex 2) and remove the H3K36me3 mark, hence eventually causing the silencing of mouse embryonic stem cell genes. In addition, a recent report has demonstrated that NO66 catalyzes β-carbon histidine hydroxylation of the 60S ribosomal protein Rpl8, but the mechanism unclear.
NO66 Marker in Diseases
The conclusion that NO66 is selectively expressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues have been identified. High expression levels of NO66 are associated with the cancer metastasis, including lymphatic duct invasion, venous invasion, and lymph node metastasis. NO66 is an independent prognostic factor for overall survival through multivariate analysis. In vitro assays indicate that NO66 levels are closely correlated to malignant potentials, such as proliferation, migration and anti-apoptotic activity. The cancer-selective expression patterns and its involvement in metastatic phenotypes suggest that NO66 is a crucial biomarker.
Although the basic concept of epigenetic drugs is well-established, there are still certain limitations on their clinical applications. It is reported that NO66 has the capability to interact with the c-MYC, an oncogenic transcription factor, and facilitates the c-MYC-centered oncogenic transcriptional program. Another study demonstrates that NO66 can interact with enhancer of EZH2 (Zeste homolog 2), a crucial component of the PRC2, and collectively regulates target genes in embryonic stem cells. Based on these findings, NO66 is considered as a cancer-specific histone modifier in human tumorigenesis. And increasing evidence focuses on the oncogenic potential of NO66 and constructs its function as a novel biomarker as well as a therapeutic target in malignancies, especially renal carcinomas.
NO66 and Renal Cell Tumors
Renal cell carcinomas (RCC) are the most lethal of the common urological cancers. As follows, the SMYD2 expression is significantly higher and SETD3's is lower in renal carcinoma than in normal samples, while no statistically significant difference is disclosed for NO66 expression. Statistically significant NO66 levels are highly observed in chromophobe RCC compared to papillary RCC and clear cell RCC. Correlation analysis reveals that SMYD2 is obviously co-expressed with SETD3 and SETD3 with NO66 in RCC.
IVD Antibody Development Service for NO66 Marker
With our versatile IVD platform, Creative Biolabs is proud to develop novel NO66-specific antibody from scratch to commercial IVD kit (we can also start with provided antibody candidates). Besides, we help develop high-quality IVD immunoassays of different formats, giving expert support in feasibility analysis, protocol establishment, assay design, validation, and kit production. Our services are customized to suit the specific requirements of our clients. Please contact us for more details if you are interested in our service.
Reference
- Xiao, Yanxuan, et al. "RIOX1-demethylated cGAS regulates ionizing radiation-elicited DNA repair." Bone research 10.1 (2022): 19. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.