Creative Biolabs is the world leading service provider for the discovery of in vitro diagnostics (IVD) antibodies. Based on our years of experience and advanced platform, we are confident in offering the best and most suitable IVD assays service against various markers for colorectal cancer (CRC) and prostate cancer (PCa).
MicroRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are some small non-coding RNAs (18-22 nucleotides in length) that suppress the expression of target genes at the post-transcriptional level such as interfering with transcription or inhibiting translation. MiR-200 family has a series of members including miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-200c, and miR-429. These miRNAs are recognized as powerful markers for epithelial cells and regulators of EMT (Epithelial-mesenchymal transition) in colorectal cancer cells, together with ovarian cancer cells, breast cancer cells, and lung cancer cells. The expression level of miRNAs is detected differentially between tumor and normal tissues and varies among tumor types. Evolving studies suggest that miRNAs play a crucial role in carcinogenesis and cancer development via their capacity to affect the gene expression that can regulate the tumorigenic processes. The implication has led to the notion of miRNAs as potential markers for the early diagnosis of cancer, predicting prognosis or treatment responses, or as targets in cancer therapeutic strategies.
MiR-141 and Colorectal Cancer
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of endogenous, small (18~25 nucleotides) non-coding RNAs which negatively regulate gene expressions by directly binding to the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of the target messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Increasing evidence has demonstrated abnormal miRNA profiles and confirmed their involvement in tumor initiation and progression. As one important member of the miR-200 family, microRNA (miR)-141 is aberrantly expressed in many human malignant tumors, participating in various cellular processes including epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug resistance.
A current analysis has been examined that miR-141 can be served as non-invasive, blood-based biomarkers for CRC by detecting the relative levels of three different microRNAs in a cohort of 102 plasma samples. The initial results indicated that plasma miR-141 levels are significantly elevated in the plasma of CRC patients with Stage IV disease and could readily distinguish distant metastasis cases from normal controls and patients with other stages. These findings are also testified in an independent cohort of 156 plasma samples from Tianjin, China. Their further proof provided supporting evidence that plasma miR-141 is a potential prognostic factor that predicted for poor survival in patients with CRC.
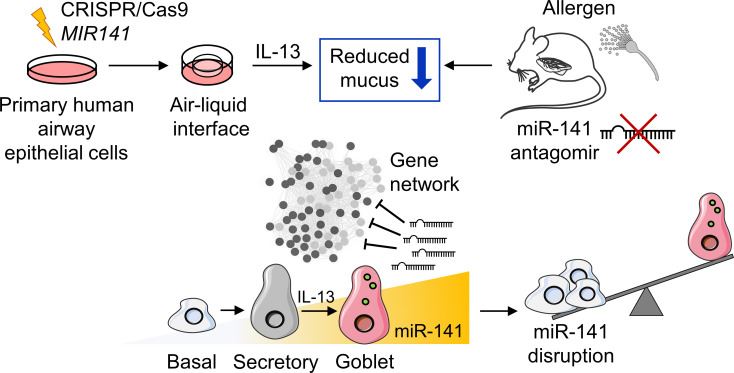 Fig.1 Epithelial miR-141 regulates IL-13–induced airway mucus production.1
Fig.1 Epithelial miR-141 regulates IL-13–induced airway mucus production.1
CRC Treatments
CRC keeps the third most commonly diagnosed malignancy in the world. The lethal reason of CRC is that asymptomatic in the early stages, no effective method to monitor recurrence after early-stage therapy, and suboptimal for the treatment of recurrent and metastatic CRC. Recently, colonoscopy screening has contributed to the early detection of CRC and a decrease in mortality. Nevertheless, the invasive pattern and high cost of the procedure have blocked its popularity globally. The fecal occult blood test has lower sensitivity (23.9%), although less invasive. Therefore, the identification of non-invasive circulating biomarkers for CRC detection, prognosis, and monitoring is thus an urgent need to improve compliance rates.
miR-141 as Marker of Human Malignancies
Based on high-throughput techniques, a great deal of deregulated miRNAs is screened out in various human malignancies and suggested to possess oncogenic or tumor suppressive activities. For instance, miR-141 is overexpressed in prostate cancer, ovarian and NSCLC tissues, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, classic papillary thyroid carcinoma, bladder cancer, and colorectal cancers. Interestingly, dysregulation of miR-141 is depending on the type of cancers. In other words, miR-141 plays a dual role in tumorigenicity and can modulate cellular motility and control “stemness”. This phenomenon strongly suggests that miR-141 is a core oncogene or tumor suppressor gene and provides new options for the targeting of cancer therapeutic agents.
miR-141 in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Emerging evidence suggested that specific miRNA profiles were capable of distinguishing malignant and non-malignant tissues, raising the feasibility of miRNAs in early detection of cancer, prognosis informing, and treatment response monitoring. It was reported that the expression level of miR-141 in prostate tumor tissues was significantly lower than that in corresponding nontumorous tissues.
As a novel biomarker for PCa, plasma miR-141 level can be used to screen for metastatic PCa with high sensitivity. Growth of early-stage PCa is androgen-dependent. The serum prostate specific antigen test along with digital rectal examination has been widely used in detection of early stage PCa. Serum PSA test is also used to monitor PCa recurrence after a set of therapies. It was reported that circulating miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 could help to distinguish PCa patients with metastasis from those with local advanced disease. Among the three miRNAs, miR-141 was the most powerful discriminator of metastatic PCa, indicating the potential of miR-141 as a supplement to PSA testing in clinical application. Skeleton is the most common metastatic organ in patients with PCa. It was reported that serum miR-141 levels were increased in patients with bone metastatic PCa and that patients with higher levels of miR-141 suffered more bone lesions.
Creative Biolabs is good at offering in vitro diagnostics (IVD) antibody development services and IVD assay services owing advanced platforms and technologies for various scientific investigations. We have established well-recognized standard operation procedures of miR-141 IVD assays with high-sensitivity. Please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Siddiqui, Sana, et al. "Epithelial miR-141 regulates IL-13–induced airway mucus production." JCI insight 6.5 (2021). Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.