2-HIT Sepsis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs has the expertise and pharmaceutical industry experience to assist our clients in assessing the test agents’ therapeutic potential against different immunological diseases, including sepsis. We are capable of offering bacterial infection models, host-barrier disruption models, and toxemia models of sepsis to suit your specific research requirements. With our variety of model systems, in combination with a broad array of biomarker analytical capabilities, we can provide custom-specific study designs to fit your unique needs.
Introduction to Sepsis
Sepsis is a leading cause of death in most intensive care units (ICUs). It is a systemic reaction characterized by an early systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) followed by a compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS). In the first phase, i.e. SIRS, patients exhibit a high level of circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), gamma interferon (IFN-γ), IL-1, and IL-6. SIRS is responsible for the significant end-organ damage. However, the concomitant production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10, serve to balance the inflammatory state. As a result, the majority of patients survive the SIRS phase and progress to a protracted period of immunosuppression and hypoinflammation, i.e. CARS. CARS is associated with both mortality and it leads to an immunoparalysis increasing patients' susceptibility to secondary infections. The compromised immunity in critically ill patients makes them more likely to develop nosocomial infections.
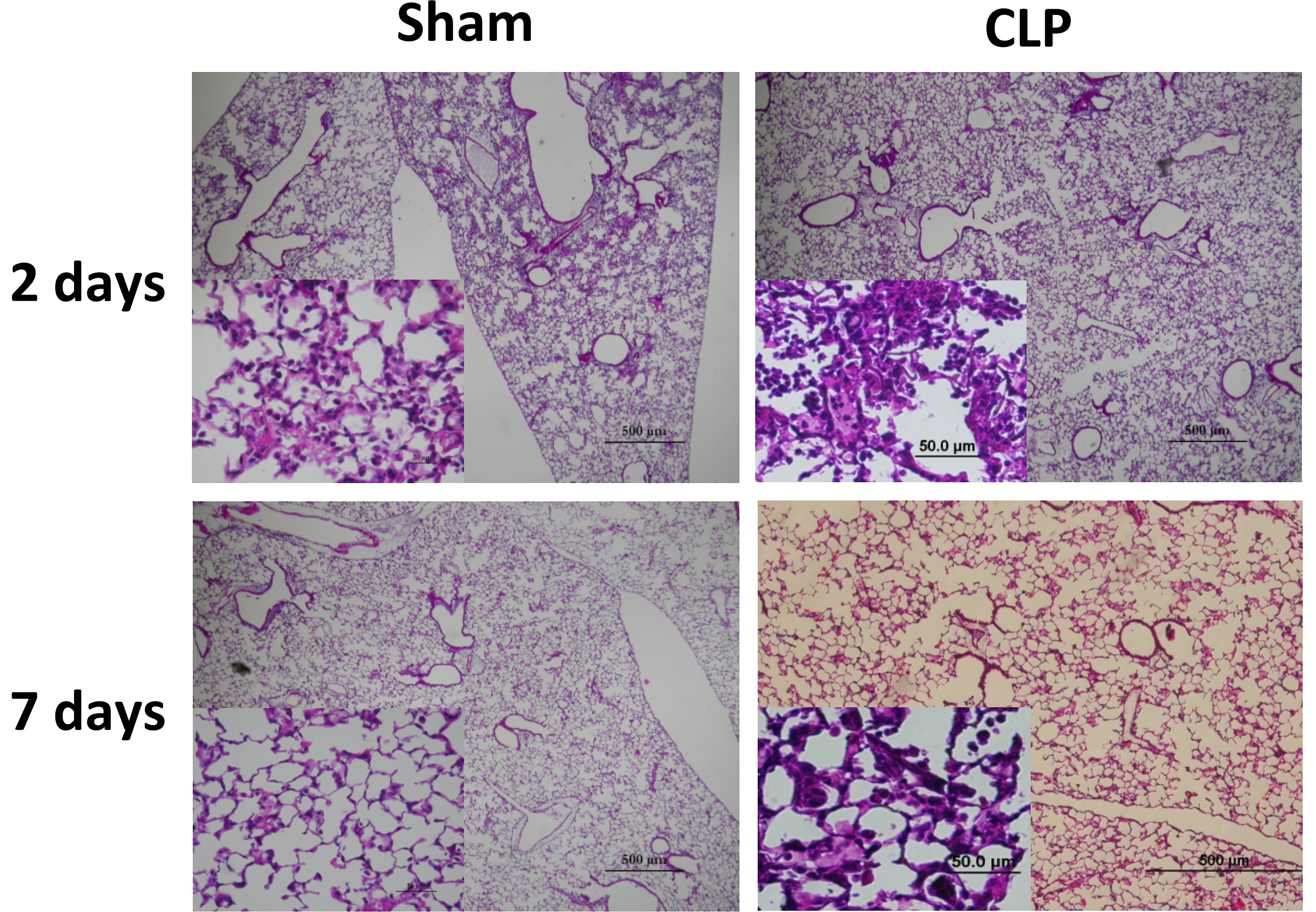 Fig. 1 Lung histology of sham and CLP groups two days after Pseudomonas administration. (Restagno et al. 2016)1, 2
Fig. 1 Lung histology of sham and CLP groups two days after Pseudomonas administration. (Restagno et al. 2016)1, 2
2-HIT Model of Sepsis
2-HIT murine model is developed to reflect the secondary nosocomial infection. In this model, the well-accepted and widely used CLP model is used as the “first hit”. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is used to induce pneumonia in mice 5 days post-CLP as a “second hit”. This model is characterized by:
- Decreased proinflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-6) and increased anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-10)
- High levels of B- and T-cell apoptotic death, reduced bacteria clearance, and a prolonged period of infection
- Useful for a better understanding of the mechanism of the immune dysregulation seen in clinical sepsis
- Useful for evaluation of potential therapies that target specific stages of the immune response
Assessments
Creative Biolabs provides such assessments as:
- Survival recording - Kaplan-Meier survival curves
- Cytokine measurement (e.g. TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10)
- Immunological analysis of splenocytes
- T- and B-cell apoptosis analysis
- Bacterial load measurement
- Histological evaluation
Meanwhile, in order to meet our customers’ specific requirements and their various research objectives, Creative Biolabs also offers other rodent inflammatory & immunological disease models listed as follows that you may be interested in:
- Carrageenan Air Pouch Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Imiquimod (IMQ)-Induced Psoriasis Rodent Models
- Chemical-Induced Rodent Contact Hypersensitivity Model
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (PCA) Model
- Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Rodent Model
- Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis (AIA) Rodent Model
- Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Rodent Model
- Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis (CAIA) Model
- LPS-Induced Rodent Sepsis Model
- Cecum Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Sepsis Model
- Spontaneous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Mouse Models
- Induced Models of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Creative Biolabs continues to expand our in vivo pharmacology capabilities and is willing to custom new models requested by our clients to meet the specific needs of a particular compound or discovery program. Contact us or send us an inquiry for more detailed information or a formal quote.
References
- Restagno, D.; et al. Mice survival and plasmatic cytokine secretion in a “Two Hit” model of sepsis depend on intratracheal Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial load. PloS one. 2016, 11(8): e0162109.
- under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
