5/6 Nephrectomy Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers various models, including the 5/6 nephrectomy, to assess drug efficacy for CKD treatment and advance your research.
Introduction
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a global epidemic characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function, leading to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in its most severe form. CKD encompasses a wide range of kidney pathologies, including glomerulonephritis, diabetic nephropathy, and hypertensive nephropathy. It is defined by a sustained decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), typically measured through serum creatinine levels and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio. As kidney function deteriorates, fibrosis, inflammation, and glomerulosclerosis become prominent, often leading to irreversible damage. Early detection and timely intervention are critical in managing CKD progression and preventing the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation. The 5/6 nephrectomy model is widely utilized in preclinical studies to mimic the pathophysiological processes of CKD and evaluate novel therapeutic agents.
5/6 Nephrectomy Model
The 5/6 Nephrectomy Model is established by surgically removing approximately 5/6 of the kidney mass in rodents, typically through a combination of unilateral nephrectomy and partial resection of the contralateral kidney. This method induces a rapid and sustained decline in renal function, leading to the development of glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis—hallmarks of CKD. This model closely replicates the progression of CKD, including the onset of renal hypertrophy, increased blood pressure, and fibrosis, making it ideal for evaluating therapeutic strategies targeting kidney injury and repair. The model is highly reproducible and provides valuable insights into the pathophysiology of CKD. However, it can be associated with some mortality due to the degree of renal impairment, especially in the early stages following surgery.
Simulates: It closely mimics the gradual loss of kidney function and the development of complications associated with CKD, such as proteinuria and elevated serum creatinine levels.
Evaluates Drugs: The 5/6 nephrectomy model is commonly used to evaluate drugs targeting fibrosis, kidney function preservation, inflammation, and renal hypertrophy.
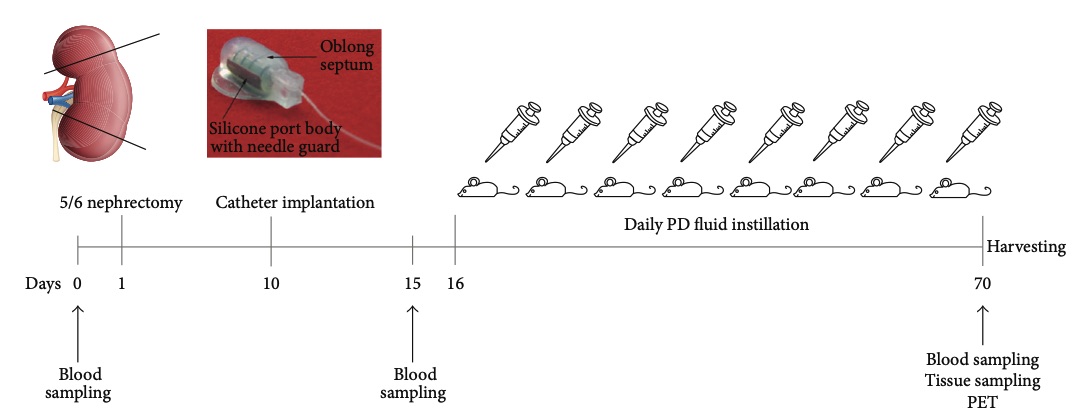 Fig. 1 Experimental design for the 5/6 nephrectomy model.1,3
Fig. 1 Experimental design for the 5/6 nephrectomy model.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat
-
Measurements
We provide a wide array of measurements to assess drug efficacy in the 5/6 Nephrectomy Model, including but not limited to:- General observations: body weight, renal function (serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen levels), and survival rate.
- Histopathological analysis: evaluation of fibrosis (e.g., Masson's Trichrome stain), glomerulosclerosis, and tubular atrophy.
- Immunohistochemistry: assessment of kidney injury markers, including TGF-β, α-SMA, and collagen deposition.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): inflammatory cytokine levels such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis for fibrosis-related genes (e.g., Col1a1, FN1) and kidney function markers (e.g., NGAL, KIM-1).
Our expert team is available for experimental design consultation, model selection, and data analysis to ensure your research progresses smoothly.
Related Services
In addition to the 5/6 Nephrectomy Model, we also provide other chronic kidney disease models. These models offer alternative platforms for evaluating kidney injury and therapies targeting renal fibrosis.
- Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) Model
- Bilateral Ureteral Obstruction induced Renal Fibrosis Model
- Adriamycin induced Nephropathy (AN) Rodent Model
- Folic Acid (FA) induced Renal Fibrosis Model
- Adenine induced Chronic Renal Failure Model
Our advantages
- Customizable Research Protocols: We offer flexible protocols tailored to specific research needs, ensuring optimal data collection and analysis.
- Validated Models: Our models, including the 5/6 nephrectomy model, are thoroughly validated and reproducible, providing reliable results for CKD studies.
- Expert Support: Our team of experienced scientists assists with every aspect of your project, from study design to data interpretation.
- Comprehensive Testing Capabilities: We use state-of-the-art technology to evaluate a wide range of biomarkers and histological changes, ensuring comprehensive assessments of drug efficacy.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Our models provide a cost-efficient way to study CKD progression and treatment, offering high-quality data at competitive prices.
- Ethical Standards: All models are ethically approved, ensuring your research complies with regulatory guidelines.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. How long does it take to see results in the 5/6 nephrectomy model?
Significant kidney damage and fibrosis develop within 4-6 weeks post-surgery, with progressive renal dysfunction observable during this period.
-
2. What are the primary advantages of using the 5/6 nephrectomy model?
This model closely mimics human CKD, providing a reliable and reproducible method to study renal fibrosis and evaluate therapeutics.
-
3. Can the model be used to test drugs for both acute and chronic kidney disease?
While primarily used for chronic kidney disease, this model can also be useful for assessing acute kidney injury in early stages following surgery.
-
4. What are the key indicators for evaluating kidney function in this model?
Serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen levels, and histopathological analysis (fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis) are key indicators of kidney function in this model.
-
5. How customizable are the research protocols?
We provide fully customizable research protocols to meet your specific needs, ensuring that all aspects of the study are tailored to your objectives.
Published Data
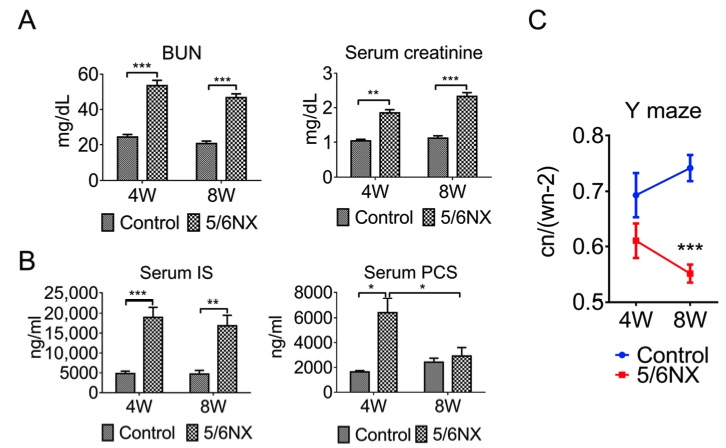 Fig. 2 The 5/6 nephrectomy-induced chronic kidney disease (CKD) mouse models show impaired working memory.2,3
Fig. 2 The 5/6 nephrectomy-induced chronic kidney disease (CKD) mouse models show impaired working memory.2,3
The 5/6 nephrectomy-induced chronic kidney disease (CKD) mouse models displayed impaired working memory. At both 4 and 8 weeks post-surgery, the serum levels of BUN (panel (2A)), creatinine (panel (2A)), and indoxyl sulfate (IS, panel (2B)) were significantly higher in the 5/6 nephrectomy group compared to the sham-control group. P-cresol sulfate (PCS) levels were significantly elevated at week 4 but returned to baseline levels by week 8 (panel (2B)). These results demonstrate that the 5/6 nephrectomy procedure effectively establishes CKD in animal models. To assess cognitive function, a Y-maze behavioral test was conducted at both 4 and 8 weeks after the procedure, focusing on working memory, which is associated with hippocampal function (panel (2C)). The Y-maze test revealed a significant decline in cognitive performance in the 5/6 nephrectomy group at 8 weeks, compared to the sham control group.
References
- Ferrantelli, E et al. "A Novel Mouse Model of Peritoneal Dialysis: Combination of Uraemia and Long-Term Exposure to PD Fluid." BioMed research international vol. 2015 (2015): 106902. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/106902
- Li, Lung-Chih et al. "The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia." Biomedicines vol. 9,9 1252. 17 Sep. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091252
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
