Cisplatin induced Acute Renal Failure Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established models for evaluating acute renal failure therapies. These models enable researchers to test and assess the efficacy of potential drugs for preventing or treating AKI, providing invaluable data to support clinical translation.
Introduction
Acute renal failure (ARF), also known as acute kidney injury (AKI), is a rapid decline in kidney function, often occurring within hours to days. This condition is characterized by the inability of the kidneys to filter waste products, regulate fluid balance, and maintain electrolyte homeostasis. It is typically diagnosed based on elevated serum creatinine levels, reduced urine output, and abnormal electrolyte levels. ARF can result from a variety of causes, including prerenal factors (e.g., hypoperfusion due to shock), intrinsic renal damage (e.g., nephrotoxic injury, glomerulonephritis), and postrenal causes (e.g., urinary tract obstruction). The most common form of ARF is acute tubular necrosis (ATN), often induced by nephrotoxins such as drugs (e.g., cisplatin, gentamicin), ischemia, or sepsis. Early intervention is crucial for improving outcomes, as prolonged kidney injury can lead to irreversible damage and progression to chronic kidney disease (CKD). In addition to conventional treatments like dialysis, various experimental drugs are being investigated for their nephroprotective effects.
Cisplatin-Induced Acute Renal Injury Model
The cisplatin-induced acute renal injury model is established by administering a single dose of cisplatin to rodents. This results in renal tubular necrosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and impairment of renal function, reflecting key aspects of acute kidney injury (AKI) observed in humans. This model has become widely used due to its reproducibility and the well-documented histological and biochemical changes it induces. It allows researchers to study the mechanisms of renal injury and to test potential therapies for preventing or mitigating kidney damage. While it offers valuable insights, the model does not fully replicate the complexity of human AKI, particularly in chronic or multi-organ injury settings. Nonetheless, it remains a cornerstone in nephrology research.
- Simulates: This model primarily simulates acute kidney injury induced by nephrotoxic agents, focusing on the cellular and molecular responses to renal damage, such as tubular necrosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
- Evaluates Drugs: It is used to evaluate potential treatments for preventing kidney injury or enhancing renal recovery, including antioxidant therapies, anti-inflammatory drugs, and novel nephroprotective agents. It also helps to assess the efficacy of diuretics, renoprotective agents, and other therapeutic strategies in ameliorating cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.
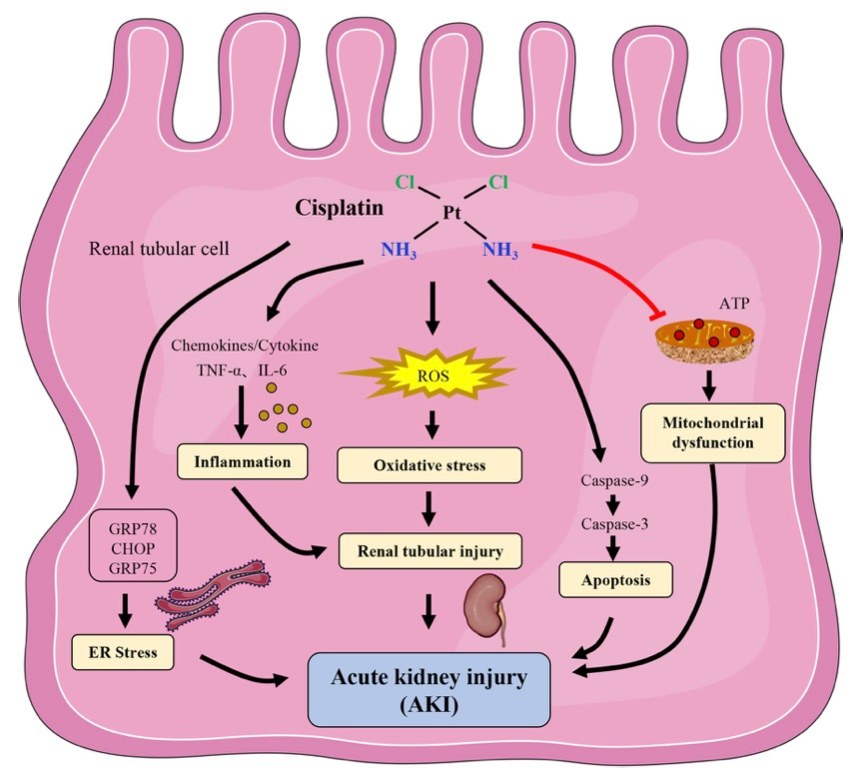 Fig. 1 The mechanism of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.1,3
Fig. 1 The mechanism of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements to evaluate drug efficacy in this model, employing advanced technologies such as:- General observations: body weight, mortality rate, renal function assessment (e.g., blood urea nitrogen [BUN], serum creatinine).
- Histopathology: Tissue damage in the kidneys, including tubular necrosis, glomerular alterations, and inflammation.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detection of inflammatory markers, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and macrophage infiltration.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Measurement of pro-inflammatory cytokines and renal stress markers.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: Assessing the expression of nephrotoxicity-related genes and proteins via RT-qPCR and Western blot.
Our experienced scientific team ensures that these evaluations are tailored to your study objectives, offering robust data to guide your research and drug development.
Related Services
In addition to the cisplatin-induced acute renal injury model, we provide various other methods to induce acute kidney injury, such as ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) and gentamicin administration. Each method has its specific application depending on the research objectives.
- Gentamicin-Induced Acute Renal Failure Model
- Glycerol-Induced Acute Renal Failure Model
- Contrast Agent-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Folic Acid-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
Our advantages
- Wide range of models: We offer various established rodent models for assessing acute kidney injury, providing flexibility in study design.
- Tailored solutions: Our scientific team works closely with clients to customize experimental setups and ensure effective data collection.
- Advanced technologies: We use the latest techniques, including high-throughput screening and detailed molecular profiling.
- Proven track record: Our models have been validated through extensive publications and are trusted by leading researchers in the field.
- Comprehensive support: From experimental design to data analysis, we provide comprehensive support throughout your project.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What are the advantages of using the Cisplatin model for kidney injury?
The model allows researchers to replicate nephrotoxic-induced renal damage and evaluate potential therapies for AKI.
-
2. Can this model be used to study other kidney diseases?
While primarily used for acute kidney injury, the Cisplatin model can also offer insights into chronic kidney disease mechanisms and potential interventions.
-
3. What types of measurements do you offer in this model?
We offer a full range of measurements, including histological analysis, cytokine profiling, gene expression, and renal function tests.
Published Data
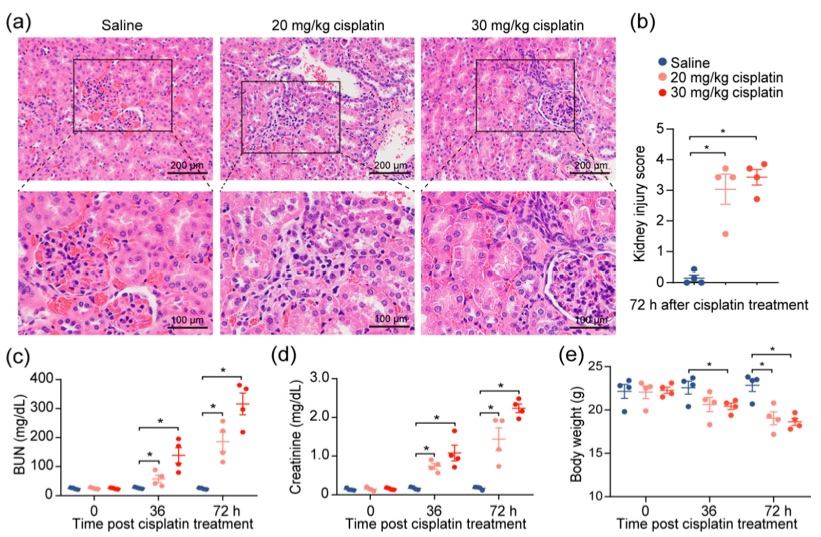 Fig.2 Cisplatin induces acute kidney injury.2,3
Fig.2 Cisplatin induces acute kidney injury.2,3
To investigate the effects of cisplatin on renal function, a previously established cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) mouse model was modified. Following intraperitoneal administration of 20 or 30 mg/kg of cisplatin, severe renal damage was confirmed in the mice, as evidenced by tubular distortion and tubular cell necrosis (Figure 2a, b). A corresponding increase in serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels was observed, with levels rising in accordance with escalating doses of cisplatin (Figure 2c, d), reflecting the renal damage caused by the drug. To eliminate the influence of diet and muscle mass content on serum creatinine and BUN, changes in the body weights of the mice were monitored throughout the experiment. Despite weight loss in the cisplatin-treated mice, no correlation was found between creatinine levels and weight reduction (Figure 2e). These findings demonstrate that cisplatin administration leads to a decrease in kidney function.
References
- Deng, Fei et al. "TRPA1 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via regulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mitochondrial damage." Journal of Translational Medicine vol. 21,1 695. 5 Oct. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-023-04351-9
- Liu, Jun et al. "A Novel Renoprotective Strategy: Upregulation of PD-L1 Mitigates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 22,24 13304. 10 Dec. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413304
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
