Hepatotoxicity
With extensive knowledge of in vitro drug cytotoxicity, Creative Biolabs is confident in accelerating your drug development process by delivering world-class lead compound screening service for hepatotoxicity potential.
Hepatotoxicity is a major concern during discovering, developing and launching new drugs, which is the most common reason for drug development failures and market withdraw even after approval. As the main detoxifying organ in the human body, the liver plays a central role in the metabolism of virtually every drug compounds. Substances that disturb the normal metabolic processes or elicit cellular stress in the liver can cause drug-induced liver injuries (DILI). DILI observed in the clinic is often idiosyncratic with various mechanisms and low incidence rates, which makes it difficult to recapitulate. However, most DILI are generated through six pathways:
- Disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis results in disassembly of actin fibrils at hepatocyte surface, causing bleeding, rupture of the cell membrane and even cell lysis.
- Interference of transport pump and actin filaments next to canaliculus may cause cholestatic disease.
- High-energy reactions by heme-containing cytochrome P-450 system can lead to covalent binding of the drug to enzyme (non-functioning adducts).
- Immune response resulting from membrane-binding drug-enzyme adducts.
- Activation of apoptotic pathways by the TNF-α receptor, Fas, etc.
- Mitochondrial function inhibition by oxidative stress, i.e. accumulation of lactate and reactive oxygen species.
Given the non-ignorable essential and the increasing attention paid to drug hepatotoxicity, fully profiling of DILI potential by predictive in vitro assays can allow optimizing of drug components during the early development stage, which enhances both safety and efficacy. Currently, Creative Biolabs has combined multiple effective in vitro models with high content analysis (HCA) technology, providing a thorough and reliable approach for detecting hepatotoxicity potentials while supplying detailed mechanism information underlying the observed toxicity.
Cell-based Hepatotoxicity Assay
We employ human primary hepatocyte (HPH) and human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells to serve as predictive in vitro models. After 24-72 hours compound incubation, multiple parameters will be measured, including but not limited to:
- Cell viability.
- Reactive oxygen species level: fluorescence assay with 6-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (CM-H2DFFDA).
- Mitochondrial membrane potential: TMRE staining.
- Cytoplasmic membrane disturbance: cytoplasmic staining with TOTO-3 dye.
- Apoptosis: active caspase staining and nuclear shrinkage.
- Cellular stress: Heat shock protein 27 (HSP 27) staining.
- Cytoplasmic calcium: Fluo-4 calcium sensitive staining.
Incorporated with high content analysis, our cell-based assay can offer objective and consistent data of multiple cytotoxic parameters. We also conduct 10-concentration dose formulation analysis to generate accurate IC50 values.
3D-based Microtissue Assay
By culturing hepatocytes on specific scaffolds, Creative Biolabs has established a 3D-based model to better mimic the complex and functional in vivo environment in the liver. This so-called microtissue has proved to acquire hepatocyte functions (such as active detoxifying, albumin synthesis) and remain stable for long-term culture, showing distinct advantages over conventional 2D monolayer model. Key mechanism criteria including glutathione depletion, ROS formulation, mitochondrial disruption, and cellular ATP depletion. Exposure to test compounds can be as long as 14 days, permitting investigation for long-term effects. This method enables multiparametric high content screening for possible hepatotoxic substances in a novel microtissue model closer to the in vivo physiology of native human hepatic tissues.
With our proven technology systems and experience expert team, Creative Biolabs is the right choice to deliver comprehensive risk assessment profiles and decision-making guides focusing on in vitro hepatotoxicity. We can formulate customized plans and conduct tailored protocols with different endpoints and parameters to address specific demands from clients.
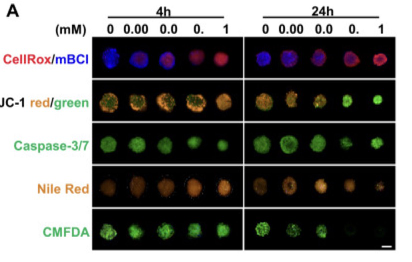 Fig.1 Representative confocal images of the hepatic cellular alterations induced by DLX.1
Fig.1 Representative confocal images of the hepatic cellular alterations induced by DLX.1
For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
Reference
- Juan Liu, et al. "High-content imaging of human hepatic spheroids for researching the mechanism of duloxetine-induced hepatotoxicity." Cell Death Dis 13.8 (2022): 669. under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part A of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
