Hi-Affi™ Humanized CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
As a leading provider in the field of antibody discovery, development and manufacture, Creative Biolabs has successfully launched, commercialized and optimized an exclusive Hi-Affi™ therapeutic antibody discovery platform. Of note, as increasing attention has been attached to a novel class of target termed “immune checkpoint”, there evolves a new trend of antibodies aiming at modulating immune system functions, aka immunotherapy antibodies. With leading transgenic techniques and years' of expertise, Creative Biolabs now provides specialty humanized immune checkpoint knock-in mice to facilitate diverse immunotherapy development for our worldwide clients, particularly CTLA-4.
CTLA-4 Prevents T-Cell Activation
CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a homolog of the immune co-stimulatory protein CD28. It is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on the surface of T cells. Of the immune checkpoint proteins identified to date, CTLA-4 is one of the best-understood checkpoint pathways.
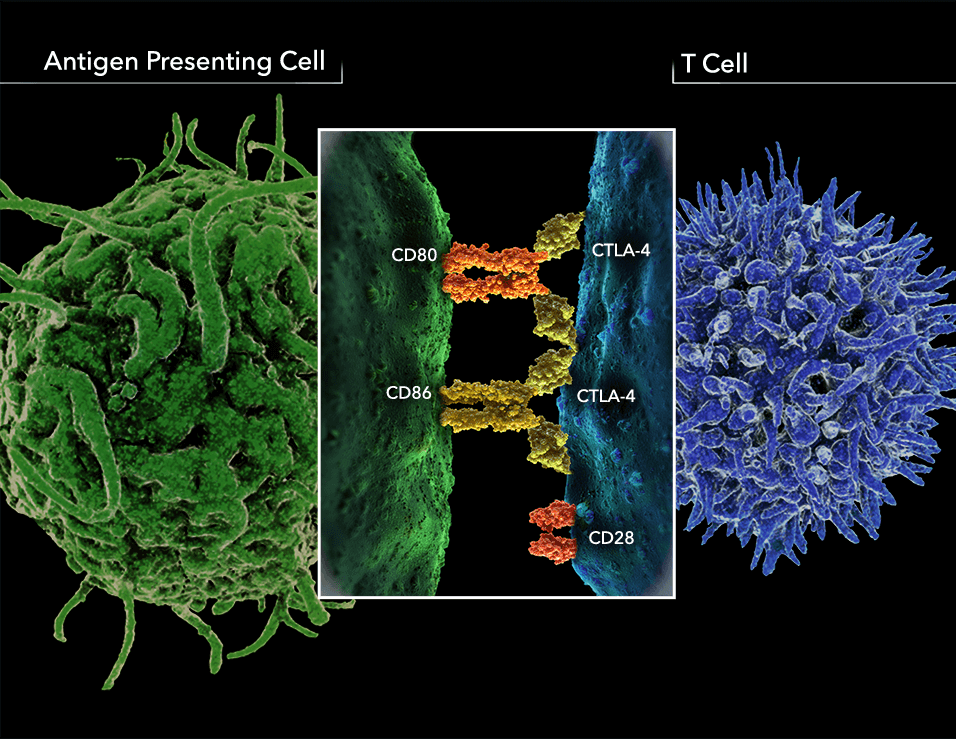 Fig.1 CTLA-4 is a co-inhibitory receptor of CD28.
Fig.1 CTLA-4 is a co-inhibitory receptor of CD28.
In the normal immune response, T-cell activation is initiated by exposure to antigens. Although tumors express antigens that are recognizable by the immune system, antigen presentation alone is not sufficient to induce immune responses. A second signal is required for T-cell activation to stimulating or inhibiting the process. The cell surface molecule CD28 provides positive modulatory signals to an immune response by binding to CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) proteins on antigen presenting cells (APCs). Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) competes with CD28 for binding these B7 proteins with approximately 20 times greater affinity and provides negative modulatory signals in the early stages of an immune response.
Immune checkpoints such as CTLA-4 play an important role in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity when the immune system is overactive. Tumor cells activate the CTLA-4 pathway to suppress the initiation of anti-tumor immune response. Therefore, several CTLA-4 checkpoint inhibitor antibody drugs are currently developed for the treatment of cancers. In patients with advanced metastatic melanoma, anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody therapy has been associated with a 10%-21% response rate.

Development of CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
Introducing human checkpoint KI mice model allows researchers to study drugs that only recognize the human version of the checkpoint molecule. In this regard, KI mice offer the possibility to study checkpoint blockers targeting human checkpoints which provide more accurate prediction of drug's efficacy as well as possible side effects (like autoimmune, pro-inflammation) before clinical trials. Creative Biolabs has developed a serial of well-established human immune checkpoint KI mouse models, including CTLA-4 KI mouse model, to test drugs that target human immune checkpoint molecules. In addition, we also provide multiple other Humanized Mouse Models for selection:
Meanwhile, we can also provide a broad range of immune checkpoint mouse models, including but not limited to:
Our diligent scientists are always ready to deliver professional services 24/7. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
For Research Use Only.
