Hi-Affi™ hCTLA-4/hTIM3 Dual Humanized Mouse Model
Human T cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain 3 (hTIM3) and human cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (hCTLA-4) are both inhibitory receptors in T cells. Novel therapies against hTIM3 and hCTLA-4 as the combined targets might achieve a promising efficacy in cancer treatment and improve patient prognosis. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hCTLA-4/hTIM3 dual humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hCTLA-4/hTIM3 Molecule
hCTLA-4, also called CD152, is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. hCTLA-4 protein is encoded by the hCTLA-4 gene and is located on human chromosome 2 (2q33.2). It is expressed on the surface of activated T cells and is homologous to CD28 (T cell co-activator), both of which can bind to CD80 and CD86 (also called B7-1 and B7-2, respectively) on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). CD28 is responsible for transmitting activation signals and activating T cells; while CTLA-4 is responsible for transmitting inhibition signals to T cells so that T cells will not kill other cells, including tumor cells. hCTLA-4 has a much higher affinity for CD80 and CD86, so it will compete and block the activation of CD28.
hTIM3, also known as HAVCR2, belongs to the hTIM gene family. The hTIM family includes hTIM1, hTIM3, and hTIM4. As a negatively regulated immune checkpoint, hTIM3 exists in different types of immune cells, including effector T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), dendritic cells (DCs), B cells, macrophages, natural killer cells (NKs), and mast cells. hTIM3 is a type I membrane protein consisting of 281 amino acids. It is composed of a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail, a single transmembrane domain, and an extracellular region. hTIM3 has four ligands, including galectin-9 (Gal-9), carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM-1), high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1), and phosphatidylserine (PS). Gal-9 is the first ligand recognized. It is a carbohydrate-binding protein that specifically recognizes the N-linked sugar chain structure in the variable region (IgV) of hTIM3 immunoglobulin. hTIM3/Gal-9 suppresses anti-tumor immunity by negatively regulating T cell immunity.
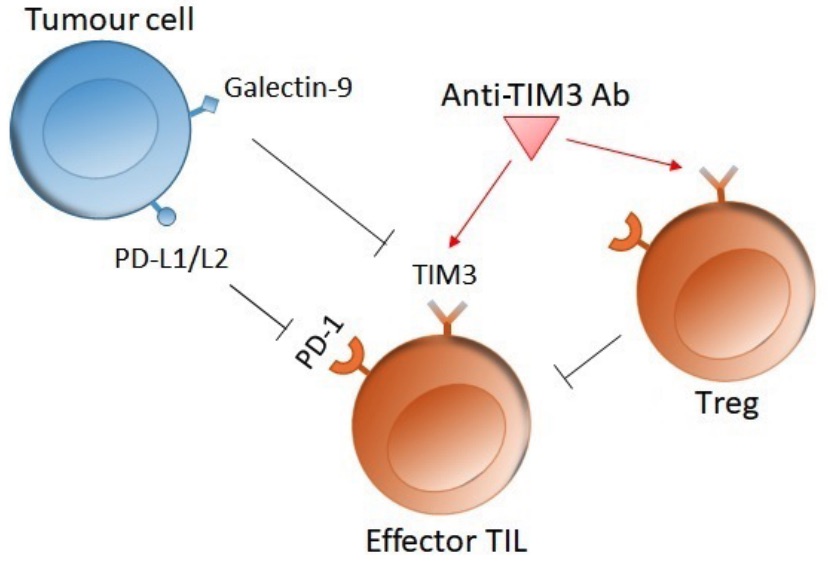 Fig. 1 The interaction between Tim3 on an effector T cell and galectin-9 on a tumour cell inhibits the immune response by inducing apoptosis in the T cell. 1
Fig. 1 The interaction between Tim3 on an effector T cell and galectin-9 on a tumour cell inhibits the immune response by inducing apoptosis in the T cell. 1
hCTLA-4/hTIM3 Signal Pathway
In resting naive T cells, hCTLA-4 is primarily located intracellularly. The stimulation signal generated by the combination of TCR and CD28: B7 induces ectopic hCTLA-4 onto the cell surface through exocytosis of vesicles containing hCTLA-4. Through hCTLA-4: B7 competitive binding, it generates negative regulatory signals and prevents full activation of T cells by inhibiting IL-2 production and cell cycle progression. hCTLA-4 is also involved in other immune control pathways. Tregs constitutively express hCTLA-4, which is also important for Tregs function. Studies have suggested that a mechanism by which Tregs control effector T cells is the down-regulation of B7 ligands on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), resulting in reduced CD28 co-stimulation.
hTIM3 suppresses anti-tumor immunity by mediating T cell depletion. hTIM3 positive CD8+ T cells have impaired Stat5 and p38 signaling pathways. Blocking the hTIM3 pathway can enhance the immune function of tumor cells and promote the production of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) by T cells. In both in vivo and in vitro models, the population of hTIM3 positive CD8+ T cells was positively correlated with the expression of PD-1. hTIM3 is constitutively expressed on natural immune cells and has the effect of suppressing natural anti-tumor immunity. hTIM3 can inhibit the effects of IL-2 and other cytokines. PD-1 and hTIM3 positive CD8+ T cells produce lower IFN-γ than hTIM3 negative CD8+ T cells. Anti-hTIM3 antibodies can also increase the IFN-γ of peripheral NKs.
Development of hCTLA-4/hTIM3 Dual Humanized Mice
hTIM3 and hCTLA-4 are both immunosuppressive receptors in T cells and have been recognized as important targets in cancer treatment. Moreover, hTIM3 plays an important role in the anti-tumor immune response mediated by natural immune cells. Thus, blocking both hCTLA-4 and hTIM3 could be a promising clinical therapy and has been exploited in clinical trials. With advanced technology, a professional R&D team, Creative Biolabs provides years of preclinical CRO services for our global clients. We have assisted our clients in their drug development using our stable and verified Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models. If you are interested in these models, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Friedlaender, Alex, Alfredo Addeo, and Giuseppe Banna. "New emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy: the role of TIM3." ESMO open 4 (2019): e000497. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
