Hi-Affi™ hICOS/hICOSL Dual Humanized Mouse Model
Human ICOS (hICOS) and its ligand human ICOSL (hICOSL) are a pair of costimulatory molecules regulating the immune response. Anti-hICOS agonist antibody or anti-hICOSL antibody could promote the anti-tumor activity and inhibit the tumor evasion. Thus, blocking the hICOS/hICOSL signal pathway provides a new thought for cancer treatment. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hICOS/hICOSL dual humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hICOS/hICOSL Molecule
hICOS is also called CD278. hICOS is homologous to CD28 and CTLA-4, belonging to the CD28 family. The hICOS gene is located on human chromosome 2q33, adjacent to CD28 and CTLA-4. hICOS is a homodimer composed of two subunits and belongs to type I transmembrane protein. It consists of a cytoplasmic region, an IgV domain, and a transmembrane region. The cytoplasmic region contains a TMFM motif and can bind to PI3K kinase. The extracellular region contains a V-like Ig functional region, in which the FDPPF motif is a structure that binds to the corresponding ligand hICOSL. The expression of hICOS is inductive, limited to activated T cells and memory T cells.
hICOSL is also known as B7-H2 or GL50. It has high homology to B7-1/B7-2 and thus is classified as the B7 family. It is a type I transmembrane protein composed of 309 amino acids. The extracellular region includes the IgV and IgC regions. The intracellular segment of this molecule is spliced to form different isomers according to different physiological environments and the state of the cell itself. It resides on B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), and macrophages. Besides, it has been found on hematoma (such as acute lymphocytic leukemia, myeloma) and solid tumors (such as colorectal, gastric, liver, prostate, mast cell cancer, and melanoma).
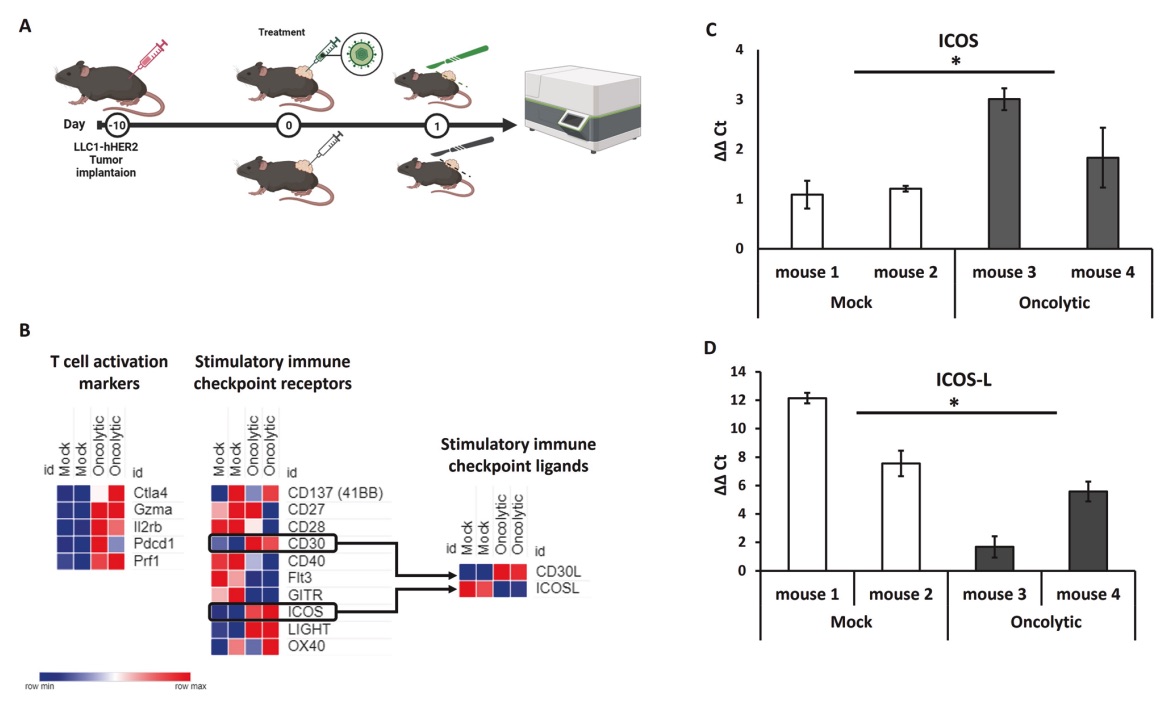 Fig. 1 Analysis of tumor microenvironment perturbation after OV treatment. 1
Fig. 1 Analysis of tumor microenvironment perturbation after OV treatment. 1
hICOS/hICOSL Signal Pathway
hICOS and its ligand hICOSL can produce a series of effects related to immune response. The hICOS/hICOSL signaling pathway can also promote the expression of CD40L on T cells, and CD40/CD40L signaling pathways can further promote the maturation and survival of B cells. hICOSL secreted by B cells can mediate the atypical NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby regulating the differentiation of T helper cells (Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells). The hICOS/hICOSL signaling pathway can promote the secretion of Th1 and Th2 related cytokines INF-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10. This signaling pathway can not only promote the expression of Th2-polarization-related cytokines, but also upregulate Th2-related transcription factors NFATc1 and c-Maf. Studies have found the significantly reduced concentrations of IL-10 and IL-4 and the increased number of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the mouse melanoma model after blocking the ICOS/ICOSL signaling pathway. For tumor cells expressing hICOSL, the high concentration of Th2 cytokines and Tregs around them may play a role in promoting tumor growth, which may constitute one of the mechanisms of tumor immune escape.
Development of hICOS/hICOSL Dual Humanized Mice
hICOS has a wide range of functions to regulate the immune response and has attracted widespread attention. The hICOSL expressed on tumor cells could promote the function of Tregs via binding to hICOS. Blocking the hICOS/hICOSL crosstalk between tumor cells and T cells is important for activating the immune response. Many studies have been taken to investigate the efficacy of the anti-hICOS agonist antibody and anti-hICOSL antibody. Creative Biolabs provides multiple kinds of well-established Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models, including the hICOS/hICOSL dual humanized mice. With many years of CRO services, we have accumulated much experience in preclinical drug development using our humanized mice. If you have any questions about these mice or have problems in your research, please feel free to contact us for further discussions.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Finizio, A., et al. "Integrating system biology and intratumor gene therapy by trans-complementing the appropriate co-stimulatory molecule as payload in oncolytic herpes virus." Cancer Gene Therapy 31.9 (2024): 1335-1343. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
