Hi-Affi™ hPD-L1/hSIRPα/hCD47 Triple Humanized Mouse Model
Tumor cells escape the immune attack through multiple pathways, including the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and SIRPα/CD47 pathway. The monoclonal antibodies against human SIRPα (hSIRPα) or human CD47 (hCD47) are either toxic or not enough to activate the immune response against tumor cells. Thus, the triple combination of anti-hPD-L1, anti-hSIRPα, and anti-hCD47 antibodies becomes a new strategy for cancer treatment. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hPD-L1/hSIRPα/hCD47 triple humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hPD-L1/hSIRPα/hCD47 Molecule
Human programmed cell death-ligand 1 (hPD-L1), is a type I of transmembrane protein with a size of 40kDa. Its receptor is human programmed cell death protein 1 (hPD-1). The expression of hPD-L1 on various tumor cells can be up-regulated in the tumor environment and the hPD-L1 is associated with immune evasion.
Human signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) is a type of immunoglobulin and a typical inhibitory immune receptor from the SIRP family. It can be selectively expressed on the surface of myeloid cells and nerve cell membranes. Its ligand is human CD47 (hCD47), which is an Ig-like membrane protein. hCD47 exists on the surface of many normal cells, and also resides in various tumor cells.
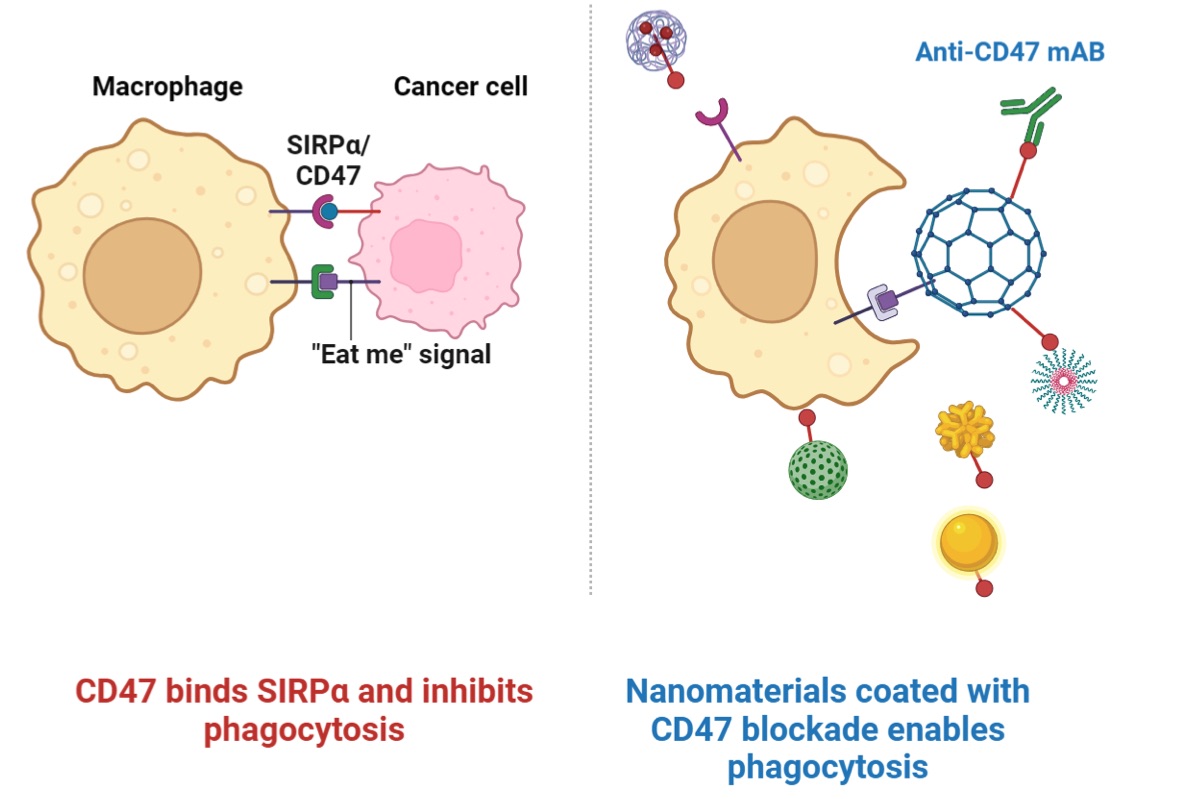 Fig. 1 Pictures showing the interaction between CD47 and SIRP. 1
Fig. 1 Pictures showing the interaction between CD47 and SIRP. 1
hPD-L1/hSIRPα/hCD47 Signal Pathway
The binding of hPD-L1 to its receptor hPD-1 could transmit regulatory signals, which induce the cell death of effector T cells (Teffs) and reduce the apoptosis of regulatory T cells (Tregs). This signal pathway is adopted by tumor cells to assist the escape from immune attack. Under normal circumstances, hSIRPα binds to the surface hCD47 on macrophages to produce a signal of “don’t eat me”. This signal inhibits the activity of macrophages and prevents macrophages from engulfing healthy cells. However, tumor cells use this mechanism to achieve immune evasion. Therefore, hCD47 and hSIRPα are respectively treated as potential targets for tumor immunotherapy. In theory, therapeutics that block the hCD47/hSIRPα signaling pathway can restore the phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages. Whether it is a monoclonal antibody that targets hCD47 or hSIRPα, or a fusion protein, the mechanism of action of these drugs has been proven to include: 1. blocking the hCD47/hSIRPα signal pathway and sending out the signal of “don’t eat me” to macrophages; 2. traditional effect functions caused by the Fc end of the monoclonal antibody, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). If the Fc end causes the ADCC and CDC to act strongly, it will inevitably kill a large number of red blood cells and cause serious toxicity. However, if only relying on the functions by the hCD47/hSIRPα signal pathway, it is not enough to activate a significant anti-tumor response. Therefore, a combined mechanism with anti-hPD-L1 antibody was proposed, at which time only the hCD47/hSIRPα signal pathway was blocked to release the anti-tumor potential of macrophages.
Development of hPD-L1/hSIRPα/hCD47 Triple Humanized Mice
The single drug used for cancer treatment has its limitations, such as the low response rate of anti-hPD-L1 antibody, the toxicity, and poor efficacy of anti-hCD47 or anti- hSIRPα antibodies. Thus, the combinational usage has become the mainstream strategy in clinical cancer treatment. The triple combination of anti-hPD-L1, anti-hCD47, and anti- hSIRPα antibodies has been proposed and under investigation. Creative Biolabs not only provides the well-established Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models, but also the related analysis services. As a recognized CRO company, we have provided professional preclinical R&D services for our global clients and greatly advanced their novel drug development. If you are interested in these humanized mice or have any problems in your study project, please feel free to contact us for further discussions.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Aljabali, Alaa AA, et al. "Nanomaterial-driven precision immunomodulation: a new paradigm in therapeutic interventions." Cancers 16.11 (2024): 2030. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
