Hi-Affi™ Humanized CD40 Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
The TNFR (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor) superfamily members are considered as appealing candidates for the development of targeted immunotherapies. Recently, a great attention has been focused upon a member of TNFR superfamily, CD40 (also known as TNFRSF5). It is demonstrated that agonistic CD40 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) allow a new option of immunotherapies, which has the potential to induce anti-cancer immunity by various mechanisms. As a world leader in the industry of drug discovery, Creative Biolabs has developed a Hi-Affi™ platform including a series of well-established human immune checkpoint KI mouse models, which can provide you this humanized CD40 immune checkpoint knock-in mice with extensive experience and legendary transgenic techniques.
CD40 Immune Checkpoint Pathway
CD40 (cluster of differentiation 40) is one of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family member, which is also known as TNFRSF5. CD40 is expressed on antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as B cells, dendritic cells (DC), and monocytes as well as many non-immune cells and various type of cancer cells.
CD40L (CD154), the trimeric ligand of CD40, is expressed on the surface of CD4+ T cells. When binding to CD40 on the antigen presenting cells (APCs), the CD40-CD40L complex plays a vital role in the “helper” T-cell function to activate APCs to prime CD8+ T cells, which has been demonstrated to be essential in regulating various kinds of immune and inflammatory responses including T cell-dependent immunoglobulin class switching, memory B cell development, and germinal center formation.
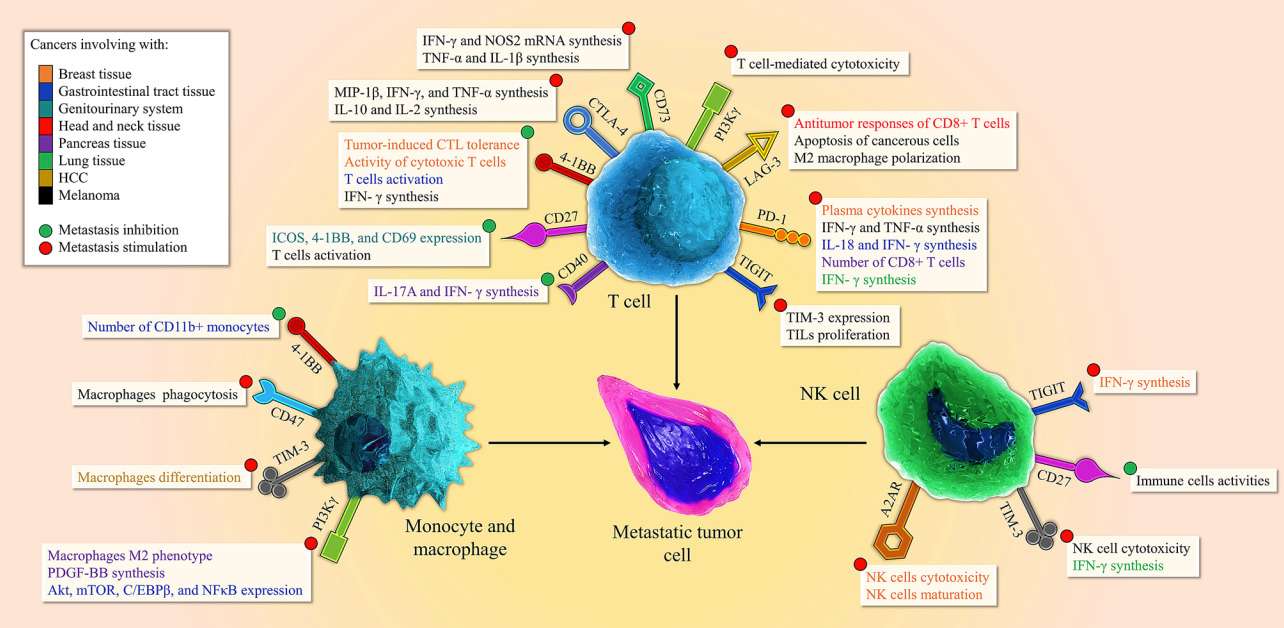 Fig. 1 Diverse roles of the immune checkpoint in T cell, NK cell, monocyte, and macrophage. 1
Fig. 1 Diverse roles of the immune checkpoint in T cell, NK cell, monocyte, and macrophage. 1
CD40 & CD40L immune checkpoint pathway affects the immune system in the following four ways: 1) "activates" or "matures" antigen-presenting cells (APCs, mainly macrophages and dendritic cells) to express co-stimulatory molecules including B7 (CD80 and CD86, both ligands for CD28), ICAM-1 (CD54), and CD44; 2) induces macrophages and dendritic cells to make interleukin-12 (IL-12), IL-18, and other cytokines; 3) CD40L-expressing CD4+ T cells are generally required for the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) against tumors and virus-infected cells; 4) promotes the differentiation of activated B cells and, with few exceptions, is required for the "class switch" from IgM to IgG production.
Some studies have described that CD40 expression on certain tumor cell types has been implicated in pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative activity, suggesting a potential use of this target in anticancer treatment. In vitro studies of agonistic CD40 mAb induced APC activation and maturation, and recombinant CD40L increased the ability of APCs to cross-prime naïve T-cells to tumor antigens. Furthermore, agonistic CD40 mAb has been demonstrated to activate APC and promote anti-tumor T cell response, while fostering cytotoxic myeloid cells with the potential to control cancer in the absence of T-cell immunity.
Development of Humanized CD40 Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
As the development of onco-immunology, a range of CD40-targeting therapies have been developed, including both agonistic mAbs and recombinant ligands. What's more, phase I clinical trials of agonistic CD40 mAb alone as well as combined with traditional therapies, have shown great potential in a variety of solid tumors. And further studies of the CD40-targeting method in combination with other immune-targeting therapies are now getting of significant importance. Creative Biolabs, who always focus on the research spotlight of anti-tumor novel drug discovery, has successfully established an array of well-characterized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models, including CD40. Our experienced scientists focused on humanized mouse models are willing to assist you in your studies of anti-tumor immunotherapies. What's more, we also established comprehensive in vitro immunomodulation assessment service using various approaches. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Safarzadeh, Ali et al. "Varied functions of immune checkpoints during cancer metastasis." Cancer immunology, immunotherapy: CII vol. 70,3 (2021): 569-588. doi:10.1007/s00262-020-02717-2. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
