Hi-Affi™ Humanized OX40 Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
Immunotherapy recently emerges as a promising therapeutic alternative for clinical treatment of many types of tumors. Of note, increasing attention has been attached to a novel class of targets termed “immune checkpoint”, which represent a group of surface antigens that can regulate/balance immune system stimulation and inhibition. During tumor progression, they are often hijacked by tumor cells as one major mechanism to escape host immune surveillance and elimination. Therefore, antibody drugs targeting immune checkpoints can play powerful roles in the conquering of cancer. Creative Biolabs has successfully developed a set of well-characterized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models in order to offer you the most appropriate platform for evaluating potential tumor immunotherapy.
Stimulation Process of T cells
Stimulation of T cells by antigen undergoes four phases including activation, expansion, contraction, and development of long-lived memory. Naïve Ag-specific T cells proliferate and form a pool of effector T cells after antigen stimulation. When the antigen is removed, the antigen-specific T cells contracts leaving a smaller pool of memory T cells.
OX40 Immune Checkpoint Pathway
OX40 is a co-stimulatory molecule expressed on the surface of activated cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). It has been reported that the interaction of OX40 and OX40L are capable of recruiting TNFR-associated (TRAFs) molecules to the intracellular domain of OX40. TRAF2 and 3 activate either the canonical NF-κB1 pathway or the noncanonical NF-κB2 pathway, both of which are crucial for cell survival.
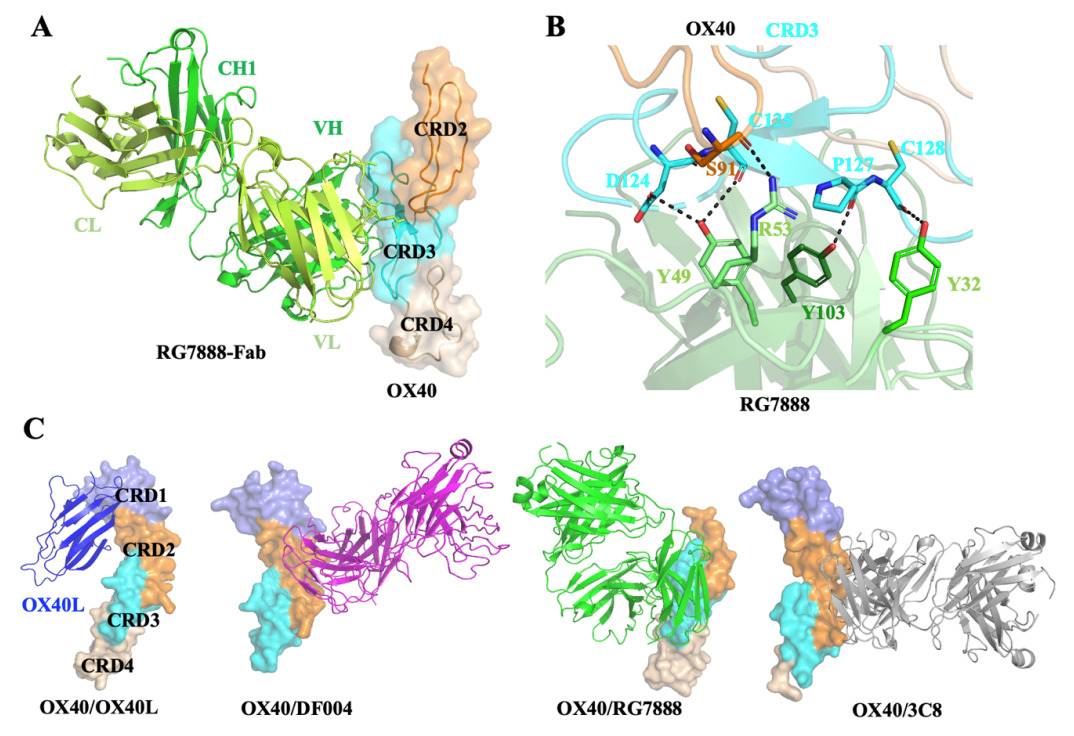 Fig. 1 Structure analysis of the OX40 complexes. 1
Fig. 1 Structure analysis of the OX40 complexes. 1
OX40 signaling can increase cytokine secretion (e.g. IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IFN-γ) by activated CD4 T cells. It has been clearly proved that OX40 signaling can enhance the development of both Th1 and Th2. OX40-stimulated T cells also increase expression of receptors associated with T-cell survival like IL-7Rα (CD127), IL-2Rα (CD25) and IL-12Rβ2.
It is well known that Tregs act to limit the immune response. OX40-OX40L signaling can block the ability of Tregs to suppress T cells and reduces Treg generation. OX40 will further amplify the impact of T-cell activation by inhibiting the immunosuppressive effect of Tregs and limiting their population.
Administration of anti-OX40 increases proliferation of peripheral blood CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, increases responses to recall and naïve reporter Ags, and increases endogenous tumor-specific immune responses. Several agonistic anti-OX40 antibodies are now tested in early phase cancer clinical trials. Accumulating preclinical evidence supports their application value in cancer treatment.
Development of OX40 Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
As is known, the dual roles of OX40 create a tumor microenvironment that is more favorable to the anti-tumor immune response. Our featured model of OX40 knock-in mice provides a powerful tool for in-depth studying the drug efficacy, potency and adverse effects related to OX40. In contrary to conventional immunodeficient mice, it carries not only a human version OX40 but also an intact immune system, thus manifesting as a more relevant, reliable and accurate model. So far, Creative Biolabs has established a full range of Humanized Immune Checkpoint Mouse Models as follows:
Moreover, we are also glad to present our other Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in. Please feel free contact us for more information.
Reference
- Zhang, Jing et al. "Structural Basis of a Novel Agonistic Anti-OX40 Antibody." Biomolecules vol. 12,9 1209. 31 Aug. 2022, doi:10.3390/biom12091209. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using the A, B, and C parts of the original image.
For Research Use Only.
