Hi-Affi™ Humanized SIRPα Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
The great success of cancer immunotherapy has inspired tremendous interest in identifying new immunotherapeutic targets. Nowadays, most of the therapies have focused on stimulating the adaptive immune system to attack cancer, including agents targeting CTLA-4, the PD-1/PD-L1 axis, etc. However, macrophages and other myeloid immune cells offer much promise as effectors of cancer immunotherapy. The CD47/signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) axis is a crucial regulator of myeloid cell activation and serves a broader role as a myeloid-specific immune checkpoint. Creative Biolabs has successfully launched an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty transgenic SIRPα immune checkpoint knock-in mice for our clients all over the world.
SIRPα Immune Checkpoint Pathway
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, including those targeting CTLA-4/B7 and the PD-1/PD- L1 inhibitory pathways, are now available for clinical use in cancer patients, with other novel checkpoint inhibitors being currently in development. Most of these have the purpose to promote adaptive T cell-mediated immunity against tumor. Recently, another checkpoint which acts to potentiate the activity of innate immune cells towards cancer has attracted great attention. This innate immune checkpoint is composed of what has become known as the ‘don't-eat-me' signal CD47, which is a protein generally expressed on normal cells and often overexpressed on cancer cells, and its counter-receptor, the myeloid inhibitory immunoreceptor SIRPα.
Signal regulatory proteins (SIRP) are a multigene family of immuno-receptors encoded in humans by a cluster of genes on chromosome 20p13. Basically, the family encompasses five members with variable levels of amino acid sequence homology, including SIRPα, SIRPβ1, SIRPγ, SIRPβ2, and SIRPδ. The major ligand identified for SIRPα in humans, pigs, and rodents, is the surface glycoprotein CD47, originally known as integrin-associated protein. SIRPα is expressed on all myeloid cells (monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, myeloid dendritic cells) and also on neuronal cells in the central nervous system, while CD47 is expressed on all normal cells in the body.
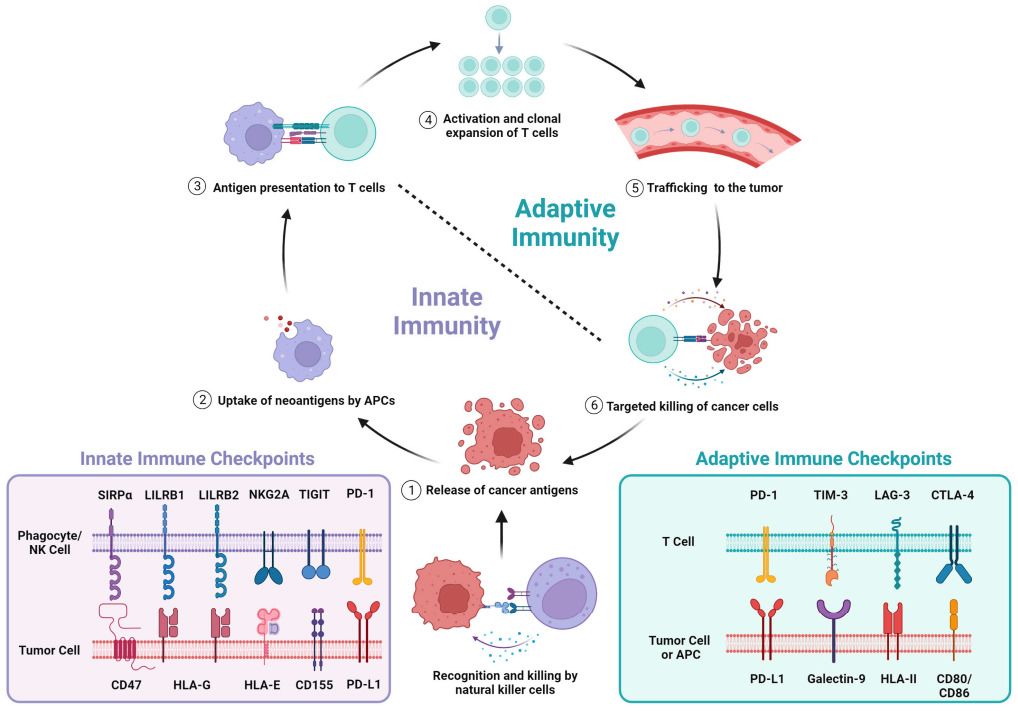 Fig. 1 Immune checkpoints govern the cancer immunity cycle. 1
Fig. 1 Immune checkpoints govern the cancer immunity cycle. 1
Development of Humanized SIRPα Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
In a wide variety of preclinical models, therapies that block the CD47/SIRPα axis stimulate phagocytosis of cancer cells in vitro and anti-tumor immune responses in vivo. Nowadays, many therapeutics targeting the CD47/SIRPα axis are under preclinical and clinical investigation. As a crucial regulator of macrophage phagocytosis and activation, the potential applications of CD47/SIRPα blocking therapies extend beyond human cancer. They may also be utilized for the treatment of infectious disease, conditioning for stem cell transplant, and many other clinical indications. With years of experience, Creative Biolabs has successfully established a series of well-characterized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models, especially for SIRPα. Our scientists focused on humanized mouse models are pleased to assist you in your studies of anti-tumor immunotherapies. What's more, we also established comprehensive in vitro immunomodulation assessment service using various approaches. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Lau, Asa P Y et al. "CD47: The Next Frontier in Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer." Cancersvol. 15,21 5229. 31 Oct. 2023, doi:10.3390/cancers15215229. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
