Morris Water Task
Morris water task is a test widely used and established by behavioral physiologist and pharmacologist to evaluate and compare learning and memory in rodents. Creative Biolabs performs this test to assess the effects of test compounds on both learning and memory. By recording the escape latency (time to find the hidden platform form the starting point) and time spent in the target quadrant studying, we can assess their ability to learn and remember the location of the platform.
Introduction of the Morris Water Task
The Morris water task has become a gold standard task for special learning and memory. It is based on the rodent's (rats or mice) aversion to the water environment. The apparatus consists of a water-filled pool with a hidden escape platform beneath the surface of the water. When the animal is released into the water, it will swim around the pool to look for the platform to escape from the water. The platform offers no local cues to direct the escape behavior of the animal. The only spatial cues are mainly the visual cues exterior of the tank.
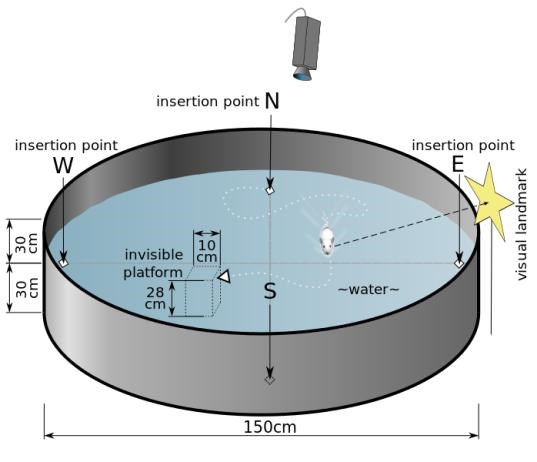
The crux of the task is that the animal is released from four different sites, so that an egocentric response (‘straight ahead and then a gentle left turn') will not help to find the platform in more than one of the starting locations. Before the testing session starts, animals are trained for 3-5 days with 3-5 daily trials. After the escape latency to the hidden platform reaches a plateau, the spatial memory is separately assessed in a probe trial without the platform, which is usually done 24 h after the last acquisition trial. Moreover, the swim pattern is monitored by a video-tracking system and the time in the target quadrant or the former platform area is calculated.
Features of the Morris Water Task
- The beauty of the task is that the water prevents the animals from using their proprioception (number of steps) to assess the traversed distance and forces them to rely on visual landmarks of the environment.
- Both learning and retrieval processes can be evaluated through the use of training as well as a probe or transfer trials.
- Non-mnemonic behaviors or strategies can be described, and motor or motivational insufficiencies can be recognized through the use of video tracking strategies.
- Visible platform tests can recognize gross visual deficiencies that might confound interpretation of results obtained from standard Morris water task testing.
- Both learning and re-learning experiments can be done by changing the position of the platform.
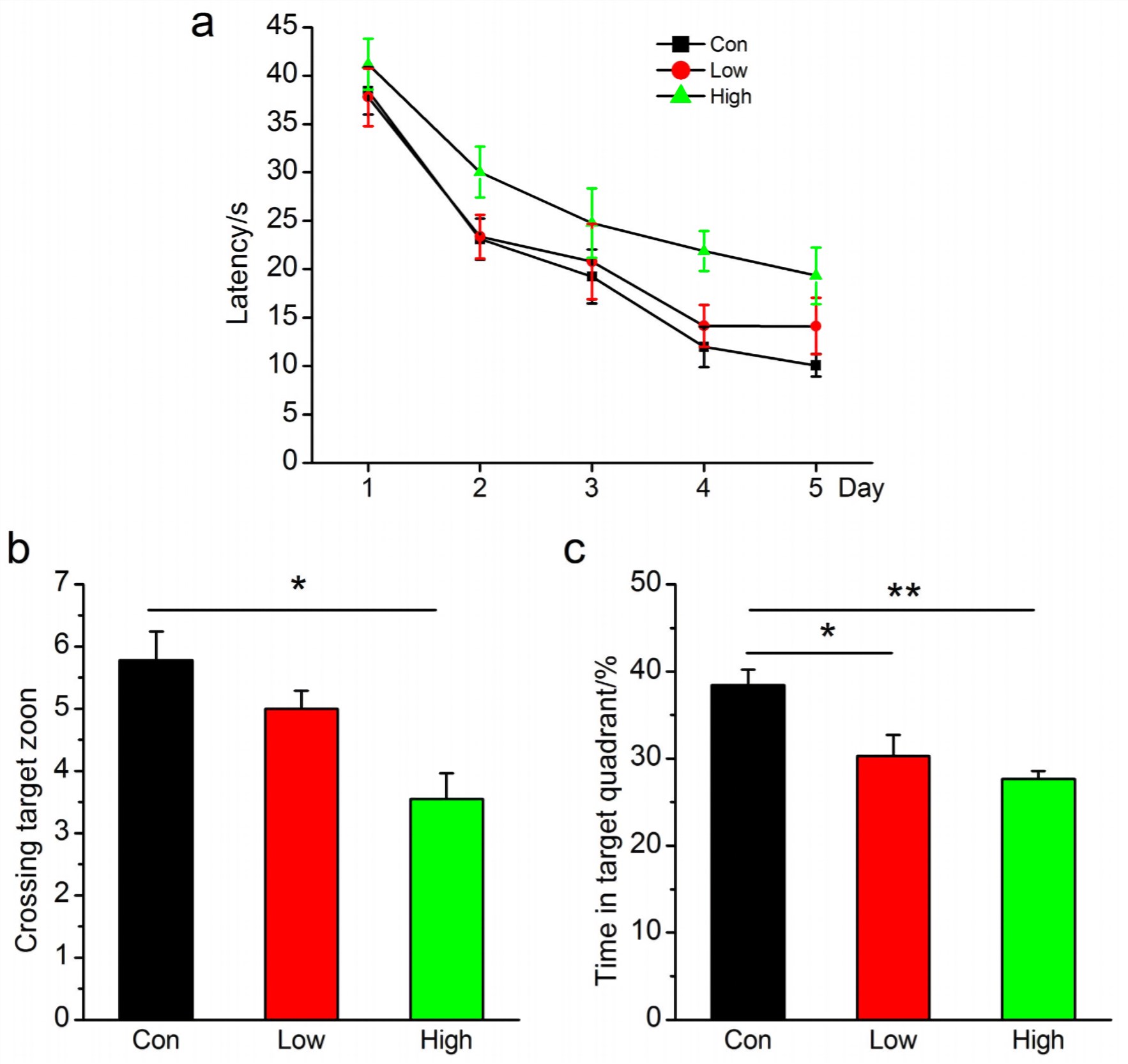 Fig.1 NO2 inhalation deteriorates spatial learning and memory in C57BL/6J mice. (a) Learning curve for 5 days of invisible training to find the hidden platform in the Morris water maze. (b) The number of times crossing the target zone. (c) Percentages of time stayed in the target quadrant. (Wei et al. 2016)1, 2
Fig.1 NO2 inhalation deteriorates spatial learning and memory in C57BL/6J mice. (a) Learning curve for 5 days of invisible training to find the hidden platform in the Morris water maze. (b) The number of times crossing the target zone. (c) Percentages of time stayed in the target quadrant. (Wei et al. 2016)1, 2
Creative Biolabs also conducts other behavioral tests for cognition and memory assessment in rodents:
Creative Biolabs provides highly customized behavioral tests to suit specific scientific needs of our clients. Moreover, new behavioral tests of cognition are constantly developed and validated.
As an undisputed specialist in neurological disease drug development, Creative Biolabs has an extensive range of rodent neurological disease models, which are widely used for drug efficacy studies combined with different behavioral tests. If you are interested, click the links for more detailed description.
For more information, please contact us or send us an inquiry.
References
- Wei, Y.; et al. NO2 inhalation promotes Alzheimer's disease-like progression: cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin e2 modulation and monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition-targeted medication. Scientific Reports. 2016, 6, 22429.
- under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
