Radial Arm Maze
The radial arm maze is a commonly used task to assess two types of memory: reference memory and working memory. Working memory corresponds to a critical cognitive domain required for the representation of objects or places during goal-directed behavior. Alternatively, reference memory is required for temporally stable representations of those objects or places. Creative Biolabs utilizes the radial arm maze paradigms to assess these two types of memory in rodents.
Introduction of the Radial Arm Maze
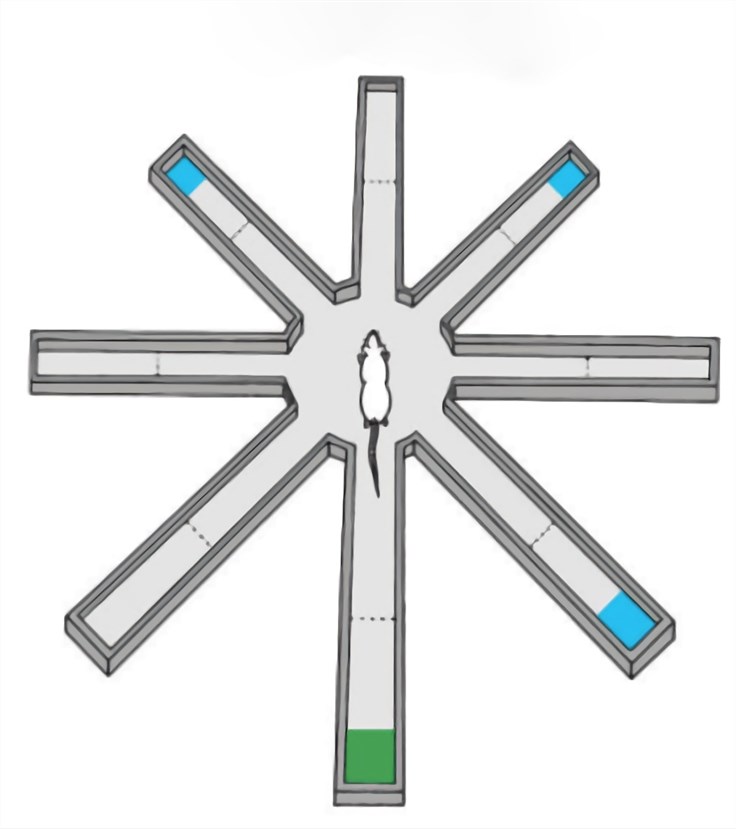 Fig. 1 Radial Arm Maze (Baker et al. 2015)1, 3
Fig. 1 Radial Arm Maze (Baker et al. 2015)1, 3
The radial arm maze was developed by Olton and Samuelson in 1976 to measure the special learning and memory in rats. Now it has been widely used in other rodents like mice. The radial arm maze apparatus consists of eight horizontal arms placed radially around a central platform above the floor. Animals are placed on the central platform and allowed to explore the maze for reinforcers (baits) placed at the end of each arm. Each testing session lasts until all eight arms have been entered or 10 min has passed since the start of the test.
Commonly used measurements for the analysis of the rodent performance are the number of errors in each session (entering an arm that has been visited previously is counted as an error) and the number of entries until the first error occurs. The failure to only visit the arms of the maze containing the reward is regarded as reference memory error while re-entry into the arms is regarded as a working memory error.
Features of the Radial Arm Maze
- This test distinguishes between motor impairment and spatial learning if the animal has motor problems it can still choose an arm.
- These tasks require pretraining, as rats are not predisposed to spontaneous maze running, which significantly increases the time needed to complete an experiment and can interfere with time-sensitive longitudinal designs.
- The animals must be mildly food-deprived to be motivated to look for baited arms, which may be a problem in some cases (e.g. in aged rats which need full food supplies to stay healthy).
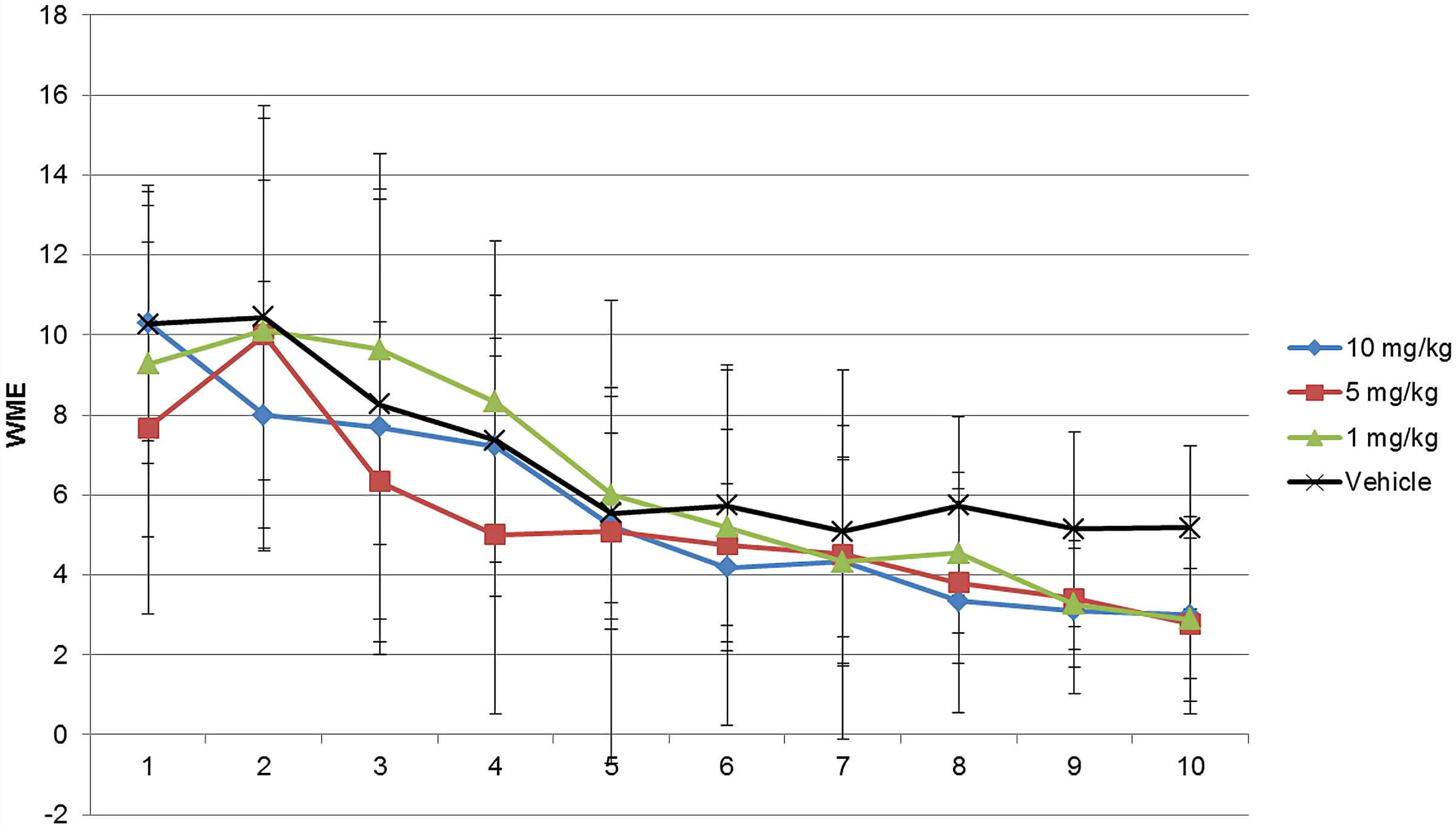 Fig.2 Working memory error (WME) assessment of modafinil in the radial maze for 10 days. (Karabacak et al. 2015)2, 3
Fig.2 Working memory error (WME) assessment of modafinil in the radial maze for 10 days. (Karabacak et al. 2015)2, 3
Creative Biolabs also conducts other behavioral tests for memory and cognitive function assessment in rodents:
- Morris Water Task
- Y Maze
- Novel Object Recognition Task
- Passive Avoidance Test
- Fear Conditioning Test
Creative Biolabs provides highly customized behavioral tests to suit specific scientific needs of our clients. Moreover, new behavioral tests of cognition are constantly developed and validated.
As an undisputed specialist in neurological disease drug development, Creative Biolabs has an extensive range of rodent neurological disease models, which are widely used for drug efficacy studies combined with different behavioral tests. If you are interested, click the links for more detailed description.
For more information, please contact us or send us an inquiry.
References
- Baker, P. M.; et al. Ongoing behavioral state information signaled in the lateral habenula guides choice flexibility in freely moving rats[J]. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2015, 9(2):1-7.
- Karabacak, Y.; et al. The effect of modafinil on the rat dopamine transporter and dopamine receptors D1–D3 paralleling cognitive enhancement in the radial arm maze[J]. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2015, 9:215.
- under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
