Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type I Diabetes (T1D) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers specialized Type I Diabetes animal models that replicate key aspects of the disease, including autoimmune-mediated beta-cell destruction and insulin deficiency. These models are ideal for preclinical studies, drug testing, and therapeutic evaluation. Our services include comprehensive support, from model development to data analysis, to accelerate your research and therapeutic discoveries.
Introduction
Type I diabetes (T1D) is a chronic autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This leads to an absolute insulin deficiency, disrupting the body's ability to regulate blood glucose levels. Unlike Type II diabetes, which is more associated with insulin resistance and obesity, Type I diabetes primarily affects children, adolescents, and young adults. The exact cause of the immune system's attack is unclear, but it is believed to involve genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, such as viral infections. Symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Without proper insulin treatment, T1D can lead to life-threatening complications like diabetic ketoacidosis, cardiovascular disease, and nerve damage. Management of the disease requires lifelong insulin therapy, careful monitoring of blood glucose levels, and lifestyle modifications. Despite significant advances in treatment options, including insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors, there is currently no cure for Type I diabetes.
Disease Models and Applications
The streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Type I diabetes model is a widely used animal model for studying the pathophysiology and therapeutic interventions of Type I diabetes. STZ, a glucosamine-nitrosourea compound, selectively induces beta-cell destruction in the pancreas by generating reactive oxygen species, leading to insulin deficiency. The model is typically established by injecting STZ into rodents, resulting in the progressive development of hyperglycemia and insulin dependence, mimicking the key features of human Type I diabetes. This model provides valuable insights into immune-mediated beta-cell destruction, insulin dysfunction, and the effects of hyperglycemia on various organs. The main advantages of the STZ-induced model include its cost-effectiveness, reproducibility, and the ability to study the disease progression over a short period. However, there are some limitations: the model may not fully replicate the autoimmune component of human Type I diabetes, as STZ-induced beta-cell damage is chemically induced rather than immune-mediated. Additionally, the model may exhibit variability in the onset and severity of diabetes, depending on the STZ dosage and animal strain used, potentially affecting the consistency of research outcomes. Despite these limitations, it remains a valuable tool for preclinical drug testing and exploring potential therapies for Type I diabetes.
- Simulates: The Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Type I Diabetes Model simulates Type I diabetes, a condition where the immune system destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. In this model, STZ induces beta-cell toxicity and selective destruction, resulting in hyperglycemia and a need for exogenous insulin. This model helps mimic the onset and progression of insulin-dependent diabetes in animals, providing insights into the disease's pathophysiology and its complications.
- Evaluates Drugs: This model is used to evaluate drugs targeting insulin replacement, beta-cell regeneration, and immune modulation. It is particularly useful for testing insulin formulations, novel insulin therapies, anti-inflammatory agents, and drugs aimed at preserving beta-cell function. Additionally, the STZ model is suitable for evaluating drugs that prevent or treat complications of diabetes, such as neuropathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular issues. It also aids in screening potential immunomodulatory therapies for halting autoimmune beta-cell destruction.
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:
- General observations: Blood glucose levels, body weight, mortality rate, behavior, and food/water intake.
- Immunohistochemistry: Infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in pancreatic tissues.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Expression levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IFN-γ.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: Blood glucose levels, insulin secretion, HbA1c, and pancreatic enzyme levels.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT-qPCR and Western blot techniques for assessing β-cell function, apoptosis markers, and immune-related pathways.
- Histopathological analysis: Examination of pancreatic tissues for signs of insulitis, β-cell destruction, and fibrosis.
In addition to the established STZ-induced Type 1 Diabetes model, our expertise extends to the development of other diabetes models, such as high-fat diet-induced diabetes or genetic models, to meet the specific needs of your research. Our scientific team is ready to provide guidance on experimental design, model selection, and data analysis to ensure the best outcomes for your project.
Related Services
In addition to the streptozotocin (STZ)-induced Type I diabetes model, we also offer a range of other diabetes models induced by different methods. Each model offers unique insights into the pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications, allowing for comprehensive drug testing and therapeutic evaluation.
- Non-Obese Type I Diabetes Mouse Model
- Alloxan induced Type I Diabetes Model
- db/db Type II Diabetes Mouse Model
- Intrauterine Growth Retardation (IUGR)-Diabetic Model
- STZ-NA induced Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Type II Diabetes Rat Model
- High-Fat Diet & Streptozotocin (STZ) induced Type II Diabetes Model
- Combined Spleen & Partial Pancreas Resection & Glucocorticoid induced Type II Diabetes Model
Advantages
- Customized Solutions: We provide tailored experimental designs to meet the unique needs of each research project.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: We use state-of-the-art technologies for accurate data collection, including cytokine profiling, gene expression analysis, and histopathological assessments.
- Full-Spectrum Support: From model selection and experimental design to data analysis and reporting, we offer comprehensive services to support your project at every stage.
- Reliable and Reproducible Results: We prioritize scientific rigor, ensuring that our models deliver consistent, reproducible, and high-quality results for publication or regulatory approval.
- Flexible and Cost-Effective: We offer competitive pricing and flexible solutions that fit within your research budget.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
Q: How long does it take for STZ to induce diabetes in mice?
A: Diabetes typically develops within 1–2 weeks after the administration of STZ, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
-
Q: Can this model be used to study drug efficacy for Type 1 Diabetes?
A: Yes, the STZ model is ideal for evaluating the efficacy of drugs aimed at improving β-cell function, reducing inflammation, or restoring insulin production.
-
Q: Are there other models available for studying Type 1 Diabetes?
A: Yes, in addition to the STZ model, we also offer genetic models like the Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) mouse model and other chemical induction models for diabetes research.
-
Q: What measurements can be used to assess the progression of diabetes in STZ models?
A: Key measurements include blood glucose levels, insulin secretion, histological analysis of pancreatic tissue, and immune cell infiltration.
Published Data
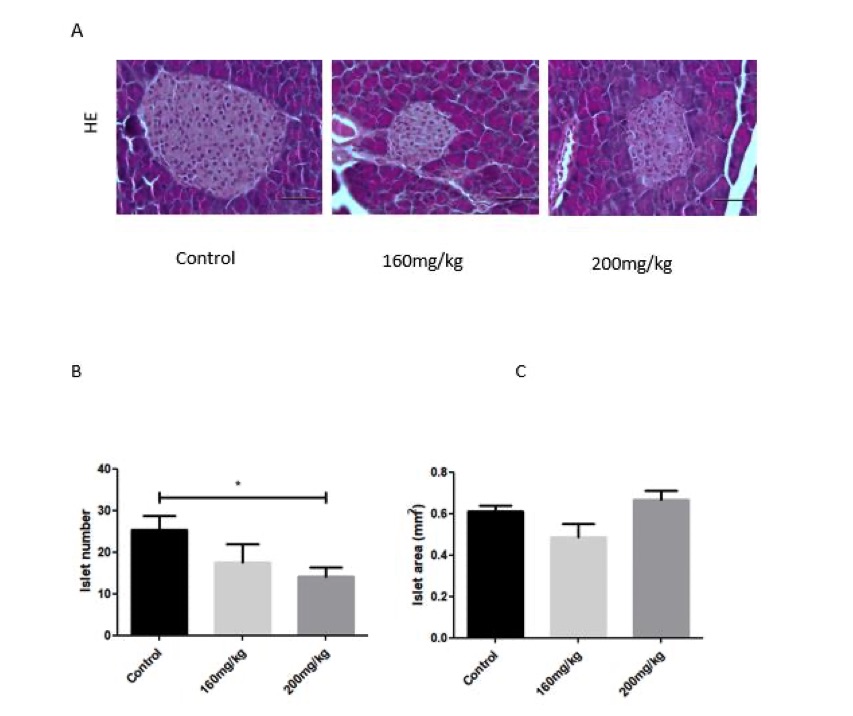 Fig. 1 Pancreatic islet morphology in the pancreas of STZ-induced diabetic mice.1
Fig. 1 Pancreatic islet morphology in the pancreas of STZ-induced diabetic mice.1
STZ-induced diabetic mice exhibited impairments in pancreatic islets. No significant differences were observed in the islet area between control and STZ-treated mice in groups receiving less than 300 mg/kg of STZ (Figure 1C). However, H&E and insulin staining revealed a reduction in the pancreatic islet area in STZ-treated mice compared to control mice (Figure 1A, B). The reduction in the number of islets did not exceed 30% (Figure 1B). These findings suggest that while STZ treatment caused some degree of islet damage, the effect on islet number and area was relatively modest at the tested doses.
Reference
- Wszola, Michal et al. "Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in a Mouse Model (BALB/c) Is Not an Effective Model for Research on Transplantation Procedures in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes." Biomedicines vol. 9,12 1790. 29 Nov. 2021, DOI:10.3390/biomedicines9121790. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
