DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA Chimera Modification Service
Introduction
DNA/2'-O-methyl RNA chimeric oligonucleotides blend DNA and 2'-O-methyl RNA to balance target specificity and nuclease resistance, leveraging DNA's stability and modified RNA's enzymatic resilience, ideal for gene silencing and therapies. They overcome unmodified oligos' degradation and off-target issues, enhancing delivery and durability. We offer tailored design, synthesis, stability profiling, and functional validation. With 20+ years' expertise, we accelerate gene-modulation programs.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA Chimera Modification
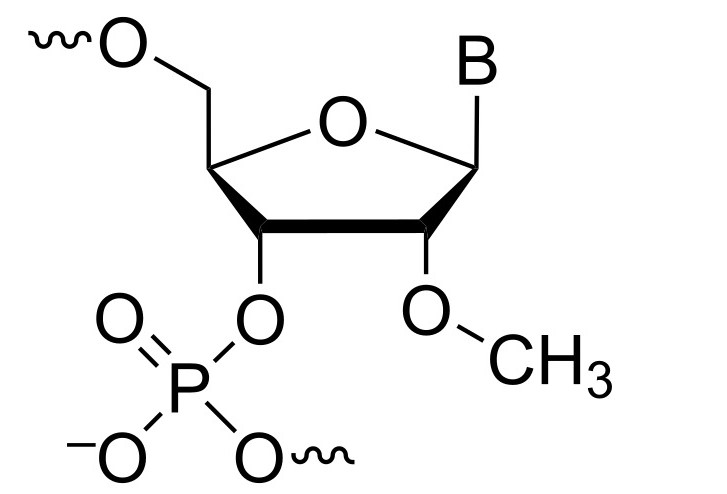 Fig.1 Structure of 2'-O-Methyl RNA.1
Fig.1 Structure of 2'-O-Methyl RNA.1
Structural characteristics
In DNA/2'-O-methyl RNA chimeras, the 2'-O-methyl RNA segment has a typical C3'-endo conformation, with its 2'-O-methyl group pointing to the double strand's minor groove. In the central RNA/DNA hybrid, DNA residues (except the middle thymidine) also adopt C3'-endo, giving an overall structure close to a typical A-type double strand.
Chemical properties
2'-O-methyl modification boosts RNA stability by reducing susceptibility to alkaline hydrolysis, nuclease cleavage, and oxidation, via altering 2'-hydroxyl hydrogen bonding and inhibiting nucleophilicity. It also increases Tm and stability of hybrid duplexes with complementary RNA versus DNA sequences.
Biological functions
DNA/2'-O-methyl RNA chimeras act via the RNAi pathway: For example, asymmetric 18-base-pair med-siRNAs (alternating DNA/2'-O-methyl RNA) bind Ago 2, cleave target mRNA efficiently, and reduce target protein expression.
The synergistic combination of 2'-O-Methyl RNA and phosphorothioate linkages creates highly stable and potent chimeric oligonucleotides. This dual modification strategy is particularly advantageous for:
- Antisense Therapy: Enhancing the stability and efficacy of antisense oligonucleotides designed to modulate gene expression by binding to target mRNA.
- miRNA Modulation: Improving the stability and activity of oligonucleotides used to inhibit or mimic microRNAs.
- Gene Silencing: Providing a durable and effective tool for silencing specific genes implicated in disease.
- Genetic Disorder Therapies: As exemplified by research into Duchenne muscular dystrophy, where such chimeras are explored for inducing exon skipping to restore functional protein production.
Workflow
-
Sequence Design & Modification Mapping
The DNA/2'-O-methyl RNA chimeric sequence was designed using algorithms to avoid off-target risks, optimize the position of modifications in the gene sequence, enhance the recruitment of RNase H, eliminate CpG sequences or TLR activation sequences that may cause side effects, and reduce immunogenicity while ensure specificity.
-
Solid-Phase Synthesis
We achieved a coupling efficiency of over 99.5% by using amide phosphorus chemistry and an auto-synthesizer. This high precision reduces the formation of incomplete sequences and truncated impurities. Our unique synthetic method enables the smooth integration of DNA/2'-O-methyl RNA chimeras, supporting complex chimeric designs with precise modification patterns.
-
Purification & QC
Employ UHPLC for size-exclusion purification, followed by MS to confirm mass accuracy. PAGE analysis ensures diastereomer impurities <5%, critical for maintaining consistent biological activity. Endotoxin levels are controlled (<0.1 EU/mg) for in vivo applications.
-
Functional Validation
Nuclease Stability: Incubate with serum nucleases to quantify half-life improvements over unmodified oligonucleotides.
Thermodynamic Profiling: Differential scanning calorimetry measures Tm shifts, ensuring optimal duplex stability for target engagement.
-
Timeline & Deliverables
Research-Grade: 4-8 weeks, including design iterations and basic validation.
GMP-Grade: 10-14 weeks, with full compliance documentation.
Outputs: Lyophilized products with >95% purity, stability profiles, HPLC/MS reports, and application-specific optimization guides.
What We Can Offer
Customized Design & Synthesis
Tailored oligonucleotide design/synthesis to meet unique sequence/modification needs, ensuring optimal performance for specific applications.
Enhanced Stability & Nuclease Resistance
Produces chimeras with improved enzymatic degradation resistance, extending half-life and efficacy in biological systems.
Superior Target Affinity
Modifications boost binding affinity to target mRNA, enabling more potent and specific therapeutic effects.
Advanced Polymerase Engineering
Uses cutting-edge polymerase engineering for efficient enzymatic synthesis of long 2'-O-Methyl RNA and MOE-RNA oligomers, overcoming traditional limitations.
Support for Diverse Applications
Solutions for antisense therapy, miRNA modulation, gene silencing, and development of novel nucleic acid catalysts (2'OMezymes) and aptamers.
[Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today]
Customer Reviews

FAQs
Q: How does the design of DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA chimeras influence siRNA activity, and what structural factors balance efficiency and off-target effects?
A: Placing 2'-O-Methyl RNA in the guide strand's seed region (positions 2-8) preserves Ago2 loading for efficient silencing while reducing off-target mRNA binding. Limiting modifications in the passenger strand avoids disrupting strand separation, balancing potency and specificity.
Q: What are the optimal storage conditions for DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA chimeras, and why are they critical?
A: Store at -80°C in RNase-free Tris-EDTA (pH 8.0); avoid >3 freeze-thaw cycles. Low temperature and neutral pH prevent 2'-O-Methyl group hydrolysis, while minimizing cycles preserves structural integrity and functional activity.
Q: What strategies mitigate immune activation in DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA chimera design, and how do they interact with innate immune receptors?
A: Designs exclude CpG motifs (TLR9 triggers) and use UNA spacers in TLR7/8-binding regions. 2'-O-Methyl modifications further reduce TLR recognition by altering backbone flexibility, lowering IFN-α secretion by ~60% without losing therapeutic function.
[Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project]
Reference
- Liczner, Christopher, et al. "Beyond ribose and phosphate: selected nucleic acid modifications for structure–function investigations and therapeutic applications." Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 17.1 (2021): 908-931. DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.17.76. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, the picture was cropped.
