Inosine Modification Service
Introduction
Inosine a natural nucleoside analog is a versatile modification in therapeutic oligonucleotides with flexible base-pairing enhancing target binding and reducing off-target effects it mitigates immune activation boosting biocompatibility key benefits include enhanced stability via 2'-O-methyl or phosphorothioate backbones improved specificity through promiscuous pairing and reduced toxicity our two decades of experience delivers end-to-end solutions custom synthesis analytical services and preclinical validation to accelerate gene therapy.
With two decades of experience, we offer end-to-end solutions including custom synthesis of site-specific inosine-modified oligonucleotides analytical services via HPLC and mass spectrometry and preclinical validation to accelerate gene therapy programs
[Contact Our Experts for Tailored Solutions]
Inosine
Basic Properties
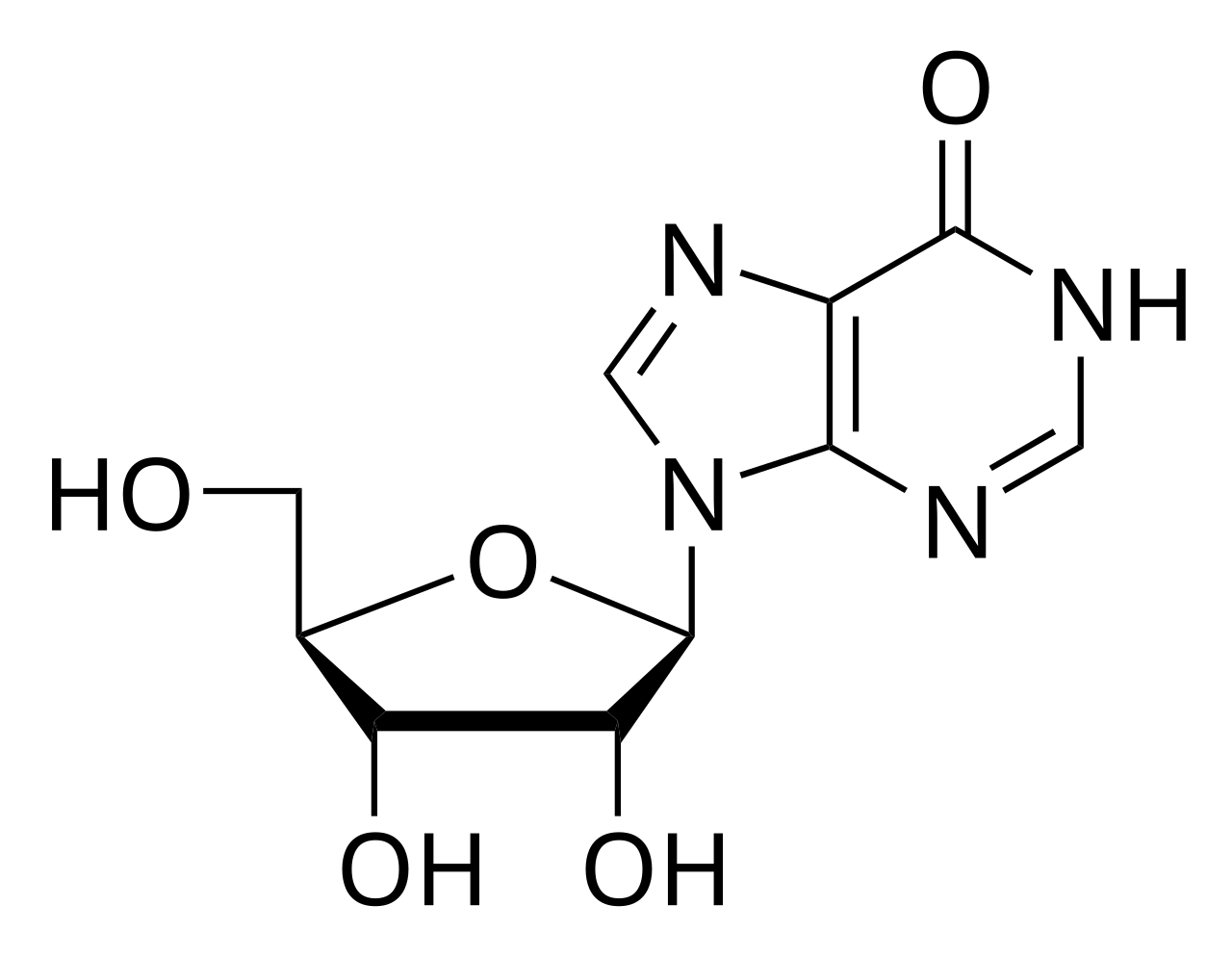 Fig.1 The chemical structural formula of inosine.Distributed under the public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 The chemical structural formula of inosine.Distributed under the public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Inosine a purine analog substitutes guanine in oligonucleotide sequences forming non canonical base pairs such as inosine cytosine or inosine adenine This substitution mimics natural RNA editing processes while introducing structural versatility that enhances the molecule's ability to adapt to target sequences. In oligonucleotide modifications, inosine is usually introduced in a chemically modified form to optimize its performance. Common types include:
- Inosine: It is directly embedded in oligonucleotide sequences as a substitute for guanine, and its flexible pairing property is utilized to enhance the binding specificity with target RNA and reduce off-target effects.
- 2' -modified inosine: By introducing modifications (such as 2'-O-methyl, 2' -fluorinated, etc.) at the ribose 2' position of inosine, the stability of oligonucleotides is further enhanced, resisting nuclease degradation while retaining their base pairing flexibility.
- Phosphate skeleton modified inosine: By combining skeleton modifications such as PS, it alters the chemical stability of oligonucleotides and their interaction with proteins, reduces immunogenicity, and prolongs the half-life in vivo. It is suitable for systemic administration of therapeutic oligonucleotides.
Key Advantages
- Enhanced Stability
Inosine reduces nuclease degradation via altered base-pairing dynamics, tripling serum half-life vs unmodified sequences for longer therapeutic effects.
- Improved Specificity
Minimizes off-target interactions through selective binding, critical for targeting splice variants or SNPs were minor mismatches risk efficacy.
- Reduced Immunogenicity
Shows lower innate immune activation than sulfur-based modifications like phosphorothioate, ideal for systemic delivery requiring minimal immune responses.
Design Considerations
- Position Specific Substitution
Strategic placement such as in seed regions of siRNA balances stability and activity ensuring modifications boost performance without disrupting essential functions
- Hybrid Modification Strategies
Combining inosine with 2'-O-methyl or phosphorothioate groups optimizes pharmacokinetics leveraging the strengths of each modification to enhance overall efficacy
Workflow
-
Step 1: Sequence Design & Optimization
Submit your target sequence such as mRNA for ASO or siRNA and our experts will optimize inosine placement using advanced predictive algorithms and in silico specificity screening This process ensures each inosine is positioned to enhance stability and target binding while minimizing off target interactions laying a strong foundation for effective oligonucleotide performance
-
Step 2: Precision Synthesis
Automated solid phase synthesis integrates inosine phosphoramidites under strictly controlled inert conditions each step achieving coupling efficiency above 98% to ensure consistent incorporation of inosine residues This precision minimizes diastereomer formation resulting in a uniform product that meets the highest standards for structural integrity
-
Step 3: Rigorous QC & Characterization
Purity is assessed via HPLC with standards set above 95% pure and confirmed by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry Functionality is validated through nuclease resistance tests including serum stability assays and target binding evaluations using techniques like SPR or Tm analysis ensuring the modified oligonucleotides perform as expected in biological systems
-
Step 4: Timely Delivery
Final products arrive as lyophilized oligonucleotides alongside a comprehensive analytical report detailing synthesis parameters purity results and functional validation data delivered within 4 to 8 weeks to keep your research or development timeline on track
Request a Customized Project Timeline
What We Can Offer?
Tailored Design Expertise
Proprietary algorithms predict optimal inosine sites to maximize efficacy enhancing stability and target binding while minimizing off-target interactions
GMP-Compliant Synthesis
State-of-the-art GMP facilities ensure batch-to-batch consistency across scales from mg to kg supporting seamless preclinical to clinical transitions
Rapid Turnaround
Expedited services meet preclinical urgency with streamlined processes delivering high-quality oligonucleotides on tight timelines
Regulatory Support
Detailed documentation aids IND/CTA submissions including stability toxicity and manufacturing data to ease regulatory reviews
[Legare Our Cutting-Edge Oligonucleotide Platform – Schedule a Consultation]
Customer Reviews

FAQs
Q1: How do you ensure the accuracy and consistency of inosine batch placement?
A: We use validated inosine phosphate reagents and automated solid-phase synthesis, monitored by real-time high-performance liquid chromatography, to ensure efficient conjugation. After synthesis, MALDI-TOF and LC-MS/MS confirm accurate modification sites, with batch-to-batch variation remaining below 1%. For scaled-up production, our GMP-compliant processes maintain consistent placement parameters, from nmol to gram scales.
Q2: Could you provide data on how inosine modification affects functional performance (for example, binding affinity, stability)?
A: Yes. For each project, we offer tailor-made validation: SPR to measure target binding affinity, serum stability assays to determine half-life, and off-target binding screens to quantify non-specific interactions.
Q3: Does inosine modification interfere with downstream processes such as fluorescence labeling or LNP packaging?
A: Inosine modification is compatible with common downstream steps. Terminal inosine residues (5' or 3') avoid steric hindrance during NHS ester labeling, while internal inosine enhances LNP encapsulation through mild charge interactions. For your specific workflow, we recommend 3'-inosine for diagnostic probes or internal inosine and PS backbones for LNP-delivered therapeutics.
Q4: How do you address issues such as reduced binding affinity or unexpected immunogenicity after modification?
A: We restore affinity by adjusting inosine spacing or combining inosine with other modifications. For immunogenicity, we optimize inosine insertion density and provide TLR activation assays. We offer one free small-batch resynthesis for verified issues to minimize project delays.
[Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project]
