Large Scale Oligonucleotide Production Service
Introduction
Large Scale Oligonucleotide Production, via cGMP-compliant manufacturing (advanced synthesis, purification, strict QC), accelerates therapeutics. Creative Biolabs supplies multi-gram to kilogram purified DNA/RNA oligonucleotides, aiding discovery-to-clinical transitions with reliable batches. With 7 FDA-approved oligonucleotide drugs and ~100 in trials, demand grows, driving advances in scalable, high-quality manufacturing, optimizing traditional methods, and exploring enzymatic approaches.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
Workflow
Gene Design and Synthesis Considerations
Before oligonucleotide synthesis, meticulous gene design is critical, especially for complex projects. It optimizes sequences for expression, stability, and functionality. Our experts assist with codon optimization, removing unwanted secondary structures, and integrating regulatory elements/restriction sites. This upfront work ensures that synthesized oligonucleotides maximize downstream utility and reduce bottlenecks/rework.
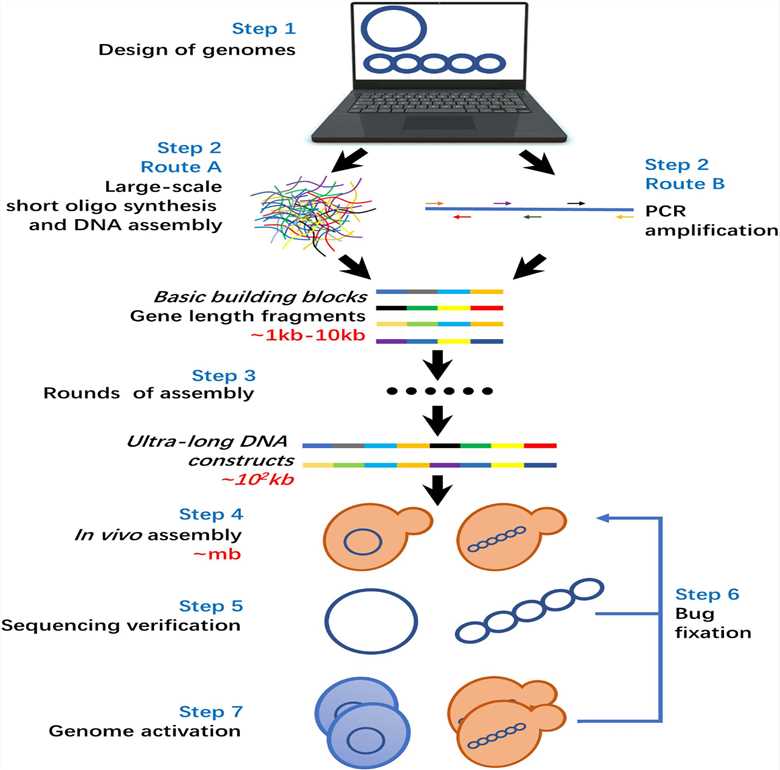 Fig.1 The general workflow of de novo whole genome synthesis.1
Fig.1 The general workflow of de novo whole genome synthesis.1
Synthesis
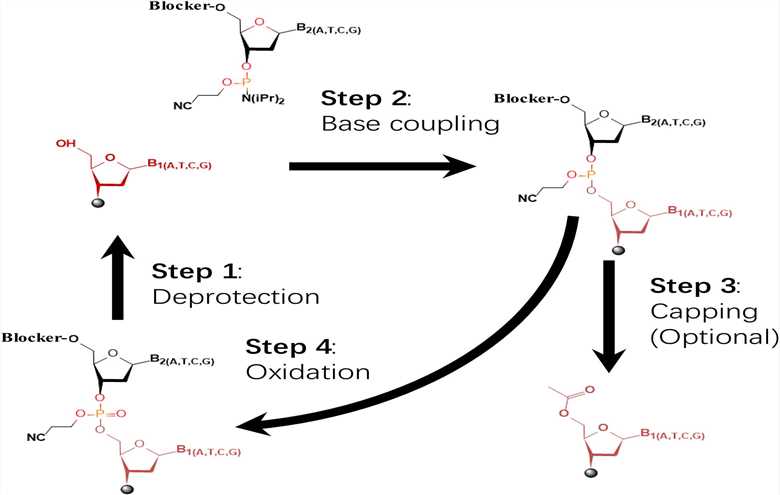 Fig.2 The four main four-step phosphoramidite chemical method is widely used in oligonucleotide synthesis.1
Fig.2 The four main four-step phosphoramidite chemical method is widely used in oligonucleotide synthesis.1
The core of oligonucleotide manufacturing is solid-phase synthesis, an iterative process where phosphoramidite monomers are added sequentially to a solid support. Each cycle involves four critical chemical reactions:
- Detritylation: Removal of the 5'-protecting group (DMT) to expose the 5'-hydroxyl group for the next coupling. This step requires careful control of contact time to prevent depurination, especially at larger scales.
- Coupling: Formation of a phosphite triester bond between the incoming phosphoramidite monomer and the exposed 5'-hydroxyl group on the growing oligonucleotide chain.
- Oxidation/Thiolation: Oxidation of the phosphite triester to a more stable phosphotriester (for phosphodiester linkages) or thiolation to form a phosphorothioate linkage.
- Capping: Acetylation of any unreacted 5'-hydroxyl groups to prevent the formation of truncated sequences, ensuring high full-length product purity.
The choice of solid support (e.g., silica-based CPG, high-loaded porous polystyrene like NittoPhase HL) and the design of the synthesizer are crucial for efficient large-scale production, impacting loading capacity, mechanical stability, and chemical compatibility.
Tab.1 Oligonucleotide synthesis techniques based on different methods.
| Classification | Methods | Core principles and steps |
|---|---|---|
| A method based on Phosphoramidite chemistry | Solid-phase phosphoramidite Method |
Four-step synthetic cycle:
|
| Column oligonucleotide synthesis | Synthesis is carried out in independent columns, and reagent pumping is used to achieve iterative addition of nucleotides. | |
| Chip-type oligonucleotide synthesis | Based on phosphoramidite chemistry, parallel synthesis is carried out on the silicon surface through photocontrolled, electrochemical, or inkjet printing methods. | |
| Emerging enzymatic synthesis methods | Template-independent polymerase |
|
| Template-dependent polymerase |
|
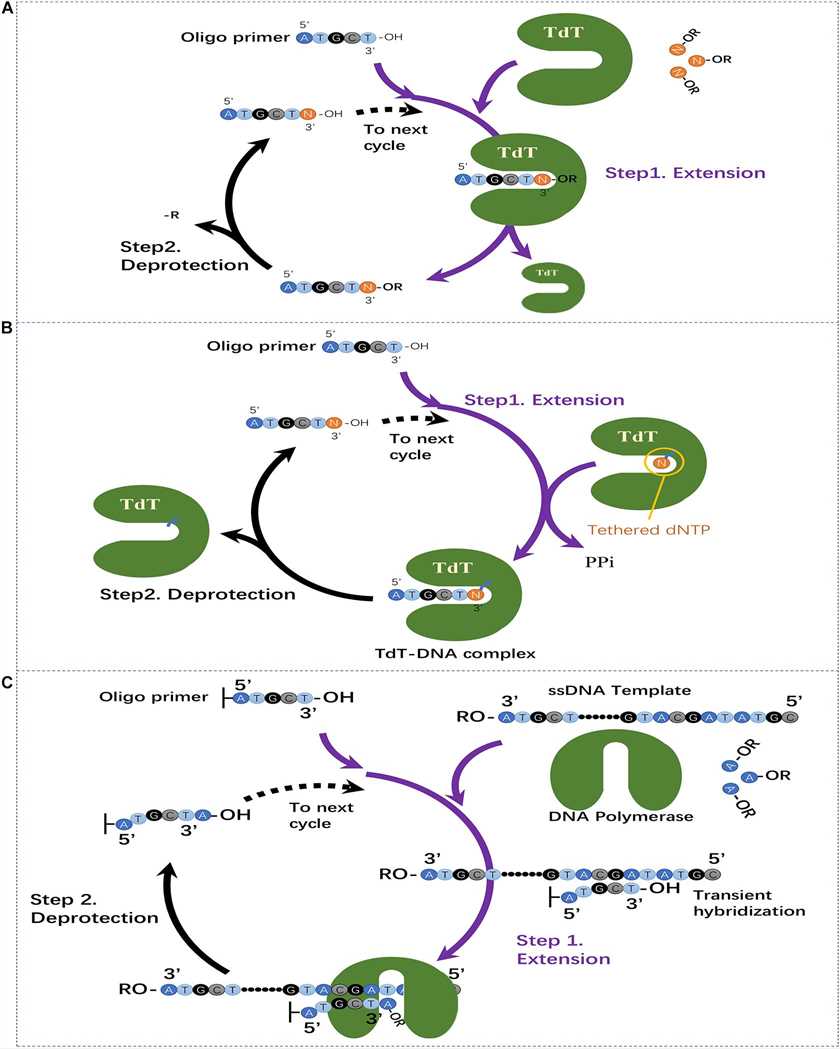 Fig.3 The currently developed enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis method.1
Fig.3 The currently developed enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis method.1
Purification
- Chromatographic Methods: AEX (charge-based, removes short sequences/counter ions) and IP-RP (hydrophobicity-based, discriminates neutral lipophilic impurities) are widely used.
- Resin Selection and Process Parameters: Critical choices include resin (e.g., Q Sepharose, Oligo-RP) and optimized eluents, flow rates, and temperature. RNA purification often needs elevated temperatures (with controlled heat transfer to avoid degradation).
Quality Control
Rigorous QC is integrated throughout the entire manufacturing process, from raw material inspection to final product release. Key QC aspects include:
- Raw Material Purity: Ensuring the highest possible purity of phosphoramidites and other reagents is foundational to high-quality synthetic oligonucleotides.
- In-Process Controls (IPCs): Monitoring key parameters at each stage (e.g., detritylation efficiency, coupling yields, pH during C&D, temperature profiles during purification) ensures batch reliability. Small-scale modeling is essential to predict and optimize these parameters for large-scale operations.
-
Final Product Analysis: Comprehensive analytical testing of the lyophilized oligonucleotide includes:
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): To confirm the molecular weight and sequence integrity.
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): To determine purity and identify impurities.
- Capillary Electrophoresis (CE): For additional purity and size analysis.
- Spectrophotometric Analysis: To determine concentration.
- Endotoxin Testing: Critical for therapeutic applications to ensure safety.
- Bioburden Testing: To assess microbial contamination.
What we can offer
Precision Degeneracy Control
Exact control over oligonucleotide degeneracy for precise targeting of desired residues or variations.
Flexible Synthesis Scales
Custom degenerate oligos from mg to g, tailored to experimental scale for cost-effectiveness and material availability across research phases.
Advanced Purification Strategies
Sophisticated chromatography ensures high purity, minimizing truncated/non-specific products that compromise results.
Rigorous Quality Assurance
Each batch undergoes QC (mass spectrometry, HPLC) to verify integrity, purity, and degenerate position distribution for reliable performance.
Expert Consultation and Design Support
Seasoned specialists guide from design to delivery, aiding sequence optimization and modification selection.
[Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today]
FAQs
What scale of oligonucleotide production can Creative Biolabs accommodate?
Creative Biolabs is equipped to handle a wide range of production scales, from multi-gram quantities suitable for advanced preclinical studies to kilogram-scale batches required for large-scale clinical trials and commercial supply. Our flexible manufacturing platforms are designed to meet your specific project needs. Feel free to discuss your target quantity with our team for a tailored solution.
How do you ensure the purity and quality of large-scale oligonucleotides?
We prioritize purity and quality via high-purity raw materials, optimized synthesis, advanced purification (AEX/IP-RP HPLC), and rigorous in-process/final QC. Each batch undergoes MS and HPLC testing to meet specifications.
How does Creative Biolabs manage the transition from small-scale development to large-scale manufacturing?
We use small-scale modeling to predict and optimize key process parameters (synthesis support bed height, heat transfer, purification temperature, etc.) before scaling up, minimizing risks, ensuring process robustness, and consistent quality across scales.
Creative Biolabs is manufacturing to advance your therapeutic programs. Our expertise covers the entire production lifecycle, from synthesis to lyophilization, backed by rigorous QC and industry best practices.
[Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project]
Reference
- Song, Li-Fu, et al. "Large-scale de novo oligonucleotide synthesis for whole-genome synthesis and data storage: challenges and opportunities." Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 9 (2021): 689797. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.689797. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
