Oligonucleotide-Aptamer Conjugation Service
Introduction
Our Oligonucleotide-aptamer Conjugation service overcomes precise delivery, off-target, and specificity challenges via advanced conjugation, combining aptamers' targeting with oligonucleotides' therapeutic potential. We provide tailored conjugates for drug delivery, gene therapy, and diagnostics, with characterized products, analytical reports, and expert guidance.
Oligonucleotide-aptamer conjugation represents a groundbreaking approach in modern molecular medicine. Aptamers are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that fold into unique three-dimensional structures, allowing them to bind to specific targets with high affinity. When covalently linked to therapeutic oligonucleotides, these conjugates create highly specific delivery systems. This synergy enhances the precision of drug delivery, minimizes off-target effects.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
Oligonucleotide-aptamer Conjugation
Aptamers are short nucleic acids that bind specific targets (molecules, cells, tissues) via unique 3D folding, with high specificity and affinity. Common types include:
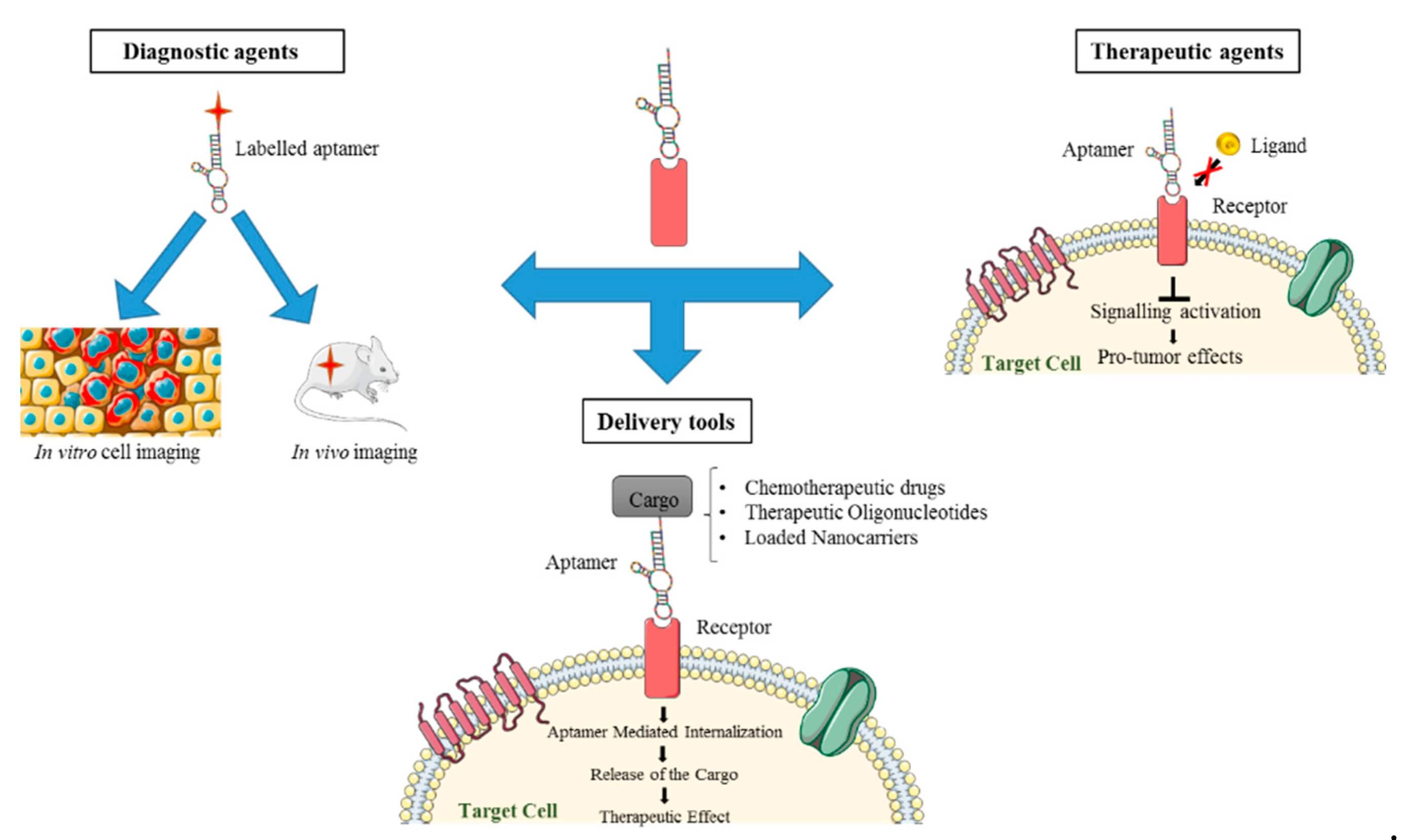 Fig.1 The extensive role of Aptamers in the medical field.1
Fig.1 The extensive role of Aptamers in the medical field.1
- DNA aptamers: They are highly stable (resistant to nuclease degradation), easy to chemically modify, the most commonly used aptamers, suitable for in vivo and in vitro targeted binding (e.g., tumor markers, coagulation factors).
- RNA aptamers: They have flexible folding and strong binding specificity but poor stability (easily degraded by RNase), requiring chemical modifications (e.g., 2'-fluorine) for enhancement. Often used to target proteins or small molecules.
- Modified aptamers: Chemical modifications (thiophosphates, methylation, PEG) optimize stability, half-life, and binding affinity for diverse applications.
- Targeted aptamers: Classified by target type, including:
- Protein-targeting aptamers (such as targeting tumor-related proteins like HER2 and VEGF);
- Small molecule targeted aptamers (such as targeted drug molecules, toxins, metal ions);
- Cell-targeted aptamers (such as targeting specific tumor cells and surface markers of immune cells).
The application of aptamers as carriers
- Aptamers as Carriers for siRNAs
Aptamers carry siRNA, using specific binding to targets (e.g., tumor antigens) for precise delivery. This combines siRNA's efficient gene-silencing with aptamers' targeting to reduce off-target effects, boosting RNA interference therapy's safety and efficacy, widely used in cancer precision treatment.
- Aptamers as Carriers of microRNAs
Aptamers can carry miRNAs for targeted delivery, directing them to diseased cells (e.g., inflammatory or cancer cells) via their targeting ability. miRNAs regulate multiple genes in cell processes; this delivery restores gene regulatory balance by supplementing missing or inhibiting overexpressed miRNAs, offering new therapies for genetic diseases, tumors, etc.
- Aptamers as Carriers for shRNAs
shRNA continuously expresses siRNA for long-term gene silencing. Aptamers, as their carriers, use specific recognition of target cell surface receptors to mediate efficient shRNA entry, reducing impact on normal cells. Suitable for long-term gene regulation, such as chronic disease or persistent viral infection treatment research.
- Aptamers as Carriers for ASOs
ASOs regulate target mRNA splicing/degradation via base pairing. Aptamers, as their carriers, boost targeted delivery efficiency. Their conjugation protects ASOs from nuclease degradation, prolongs half-life, enhances lesion-site enrichment via specific cell binding, and optimizes therapeutic effects in genetic and neurodegenerative diseases.
Workflow
-
Required Starting Materials
- Target Information: Detailed specs of the biological target (e.g., protein, cell surface marker, receptor), including sequence, binding sites, or relevant cell lines.
- Oligonucleotide Sequence: Full sequence and desired modifications of the therapeutic/diagnostic oligonucleotide for conjugation.
- Aptamer Sequence: Full sequence of the aptamer, plus known secondary structures or critical binding domains. Aptamer discovery services are available if not identified.
-
Conjugation
Common strategies use bifunctional linkers reacting with aptamer/oligonucleotide functional groups (amino, thiol, azide) introduced during synthesis, forming stable chimeras. Aptamers guide oligonucleotides to targets, enabling localized action and reducing systemic exposure.
-
Synthesis
Aptamers and oligonucleotides are typically synthesized via automated solid-phase phosphoramidite chemistry, enabling precise sequential nucleotide addition and custom sequences with site-specific modifications (providing reactive handles for conjugation). Both components are rigorously purified pre-conjugation.
-
Purification
Post-conjugation, crude mixtures contain desired conjugates, unreacted materials, and by-products. Purification (vital for function and safety) uses HPLC and FPLC, separating via size, charge, or hydrophobicity differences. Purified conjugate homogeneity ensures reproducible results.
-
Quality Control
Rigorous QC is vital for oligonucleotide-aptamer conjugation. Each batch undergoes tests: mass spectrometry (molecular weight, sequence integrity), gel electrophoresis (size, integrity), UV-Vis spectrophotometry (concentration), target binding assays (SPR, ELISA), and cellular uptake studies. This ensures high-quality, characterized conjugates.
What We Can Offer
High-Purity Conjugate Synthesis
Advanced phosphoramidite chemistry for precise synthesis of components, followed by efficient coupling.
Rigorous Purification Protocols
State-of-the-art HPLC and FPLC for exceptional purity/homogeneity, critical for downstream studies.
Comprehensive Quality Control
Multi-faceted validation (mass spectrometry, gel electrophoresis, functional assays) to confirm identity, purity, and specificity.
Support for Diverse Applications
Expertise in conjugates for drug delivery, gene therapy, diagnostics, and imaging, covering broad research needs.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Customer Reviews

FAQs
How do oligonucleotide-aptamer conjugates enhance therapeutic efficacy?
A: These conjugates significantly boost efficacy by enabling highly specific, targeted delivery of oligonucleotide payloads to diseased cells or tissues. This precision minimizes off-target effects, reduces systemic toxicity, and allows lower effective doses, ultimately driving superior therapeutic outcomes.
What are the advantages of aptamers over antibodies for targeted delivery?
A: Aptamers offer several distinct advantages, including smaller size (leading to better tissue penetration), lower immunogenicity, higher thermal and chemical stability, and easier, more cost-effective chemical synthesis and modification. They also offer greater flexibility in conjugation chemistry.
Can Creative Biolabs assist with aptamer discovery if I don't have a pre-existing aptamer?
A: While our primary service focuses on conjugation, we understand that aptamer discovery is a crucial upstream step. We can discuss your needs and guide you toward appropriate solutions for aptamer identification, or potentially integrate with partners who specialize in aptamer selection.
Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project
Reference
- Rotoli, Deborah, et al. "Advances in oligonucleotide aptamers for NSCLC targeting." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21.17 (2020): 6075. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21176075. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
