Biotinylation Service
As a leading global company, Creative Biolabs has established an advanced platform to offer the most comprehensive glycan modification and labeling service. We own a team of experts who have accumulated extensive experience in the biotinylation of diverse glycans. We are pleased to tailor the most appropriate strategies for biotinylation to meet every demand of our customers.
Introduction of Biotinylation
Biotin is widely utilized in biotechnological applications as a labeling reagent or affinity purification tag owing to its extremely high affinity. It was first exploited in immunocytochemical applications in the mid-1970s and has since been commonly used to localize antigens in cells and tissues. Generally, biotinylation is rapid, specific, and unlikely to perturb the natural function of the molecule due to the small size of biotin. The labeled molecule then can be detected in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), dot blot or western blot (WB) methods using streptavidin or avidin probes. Therefore, it is widely used in the study of glycoproteins and glycan-binding proteins.
Biotinylation Service at Creative Biolabs
Since biotinylation is rapid, specific, and is unlikely to perturb the natural function, it is popularly used in the study of interactions. Creative Biolabs has accumulated years of experience in carbohydrate biotinylation service, we are confident in offering high-quality custom biotinylation services according to our customers' specific demands. Different strategies can be employed for biotinylation including but not limited to N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), enzymatic biotinylation with E. coli biotin ligase (BirA), and proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID).
-
NHS
NHS ester-activated biotins are the most popular type of biotinylation reagent. NHS esters react efficiently with primary amino groups (-NH2) in pH 7-9 buffers to form stable amide bonds. Because glycoprotein and other proteins generally contain multiple lysine (K) residues in addition to the N-terminus of each polypeptide, they have multiple primary amines available as targets for labeling with NHS-activated reagents.
-
BirA
BirA binds biotin and ATP and generates the intermediate, biotinoyl-5 -AMP (bioAMP). At low biotin concentrations, bioAMP is transferred to the -NH2 of a lysine in BCCP. Under conditions of high biotin concentration, where all BCCP subunits are biotinylated, bioAMP remains bound to BirA; in vitro the BirA-bioAMP complex has a half-life of ~30 min. In bacteria, the BirA-bioAMP complex binds to a 40-base pair sequence in the biotin biosynthetic operon, resulting in the transcriptional repression of genes encoding enzymes required for biotin biosynthesis.
-
BioID
BioID is a unique method to screen for physiologically relevant protein interactions that occur in living cells. Based on its mechanism of action, BioID is effective when applied to insoluble and membrane-associated proteins, two classes of proteins that may be refractory to screening with conventional approaches. Additional advantages include the ability to identify weak and/or transient interactions, the ability to screen for interactions in a relatively natural cellular setting, and temporal inducibility of biotin labeling. With modifications, BioID is effective in a wide variety of cell types and species.
Advantages of Our Services
-
Experienced experts team.
-
Advanced technology platform.
-
Accurate, efficient, and cost-effective.
-
Perfect after-sales service.
Creative Biolabs is a forward-looking company that has devoted to biotinylation services for many years. Strong scientists team and experienced technical support make us confident in providing the best glycan modification and labeling services to global customers. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Published data
Galectins are associated with cancer, so designing inhibitors against galectins is one of the new strategies for treating cancer. Galectin-3 (Gal-3) plays a key role in tumor development and metastasis, which has a pro-apoptotic effect on specific cell types and has become one of the potential targets for anticancer therapy and cancer diagnosis. In this study, the authors used three recombinant glycosyltransferases to biotinylate two tetrasaccharides (N-acetyllactosamine (LacNAc), N, N-diacetyllactosamine (LacdiNAc)) at the C6 position of terminal galactose and N-acetylgalactosamine, respectively, by enzymatic oxidation and reductive amination. The new polysaccharide carrying this biotin was used as a new ligand for Gal-3. Compared with non-biotinylated polysaccharides, the binding performance of Gal-3 to immobilized biotinylated polysaccharides was improved and even showed higher selectivity. In addition, the authors also bound biotinylated glycans to bovine serum albumin (BSA) of different densities and measured the binding of Gal-3 to fixed and free new glycoproteins by ELISA and surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy (SPR). The results showed that the biotinylated ligand had high binding affinity and inhibition even at low glycosylation density. In summary, this new biotinylated glycoprotein is expected to become a potential candidate for cancer research targeting Gal-3 in the future. It can be further loaded with fluorescent dyes and cytotoxic substances for the development of customized therapeutic and diagnostic preparations.
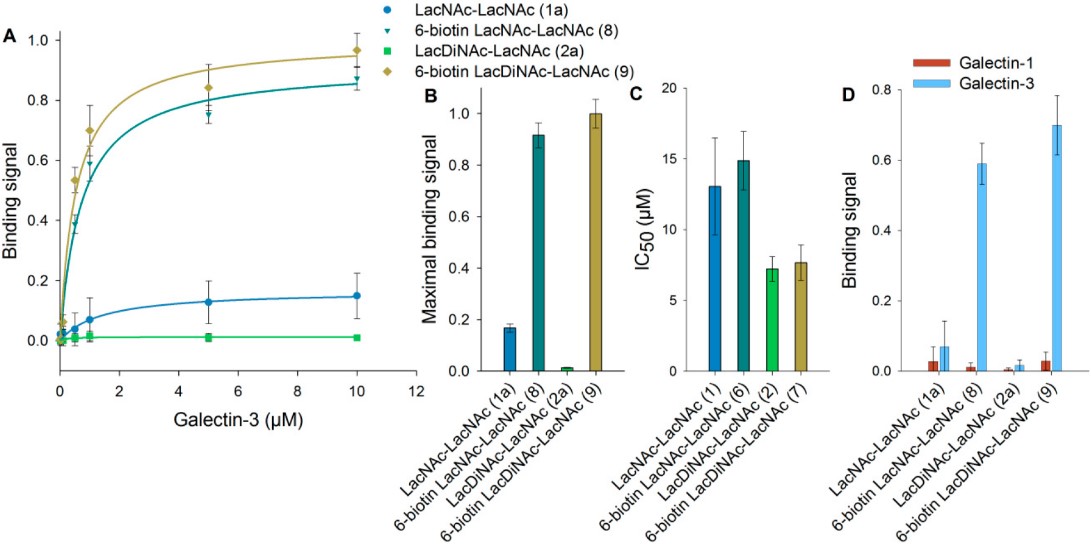 Fig.1 Effects of 6-biotinylated tetrasaccharide on galectin binding and inhibition.1
Fig.1 Effects of 6-biotinylated tetrasaccharide on galectin binding and inhibition.1
FAQs
Q1: Can you work with complex carbohydrates?
A1: Of course! Our expertise extends to complex carbohydrates with diverse glycan types. Our advanced technology and extensive experience in working with and modifying complex carbohydrates ensure precise and efficient biotinylation to your specific requirements.
Q2: I need to perform a specific type of glycosyl biotinylation. What specific customized services can you provide for me?
A2: We provide a variety of customized glycosyl biotinylation services according to your needs, including but not limited to different strategies such as NHS, BirA, BioID, etc. These strategies can select the most appropriate method for biotinylation according to your project requirements.
Q3: Can you biotinylate non-glycan molecules?
A3: Yes, while we specialize in glycan biotinylation, our capabilities include biotinylation of proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules. We can adapt our protocols to a variety of substrates, ensuring efficient and specific molecule biotinylation.
Customer Review
High-quality Biotinylation Results
"The biotinylation service provided by Creative Biolabs is of high quality. They use advanced equipment to ensure accurate and efficient biotin labeling, and the labeled samples also show excellent stability. The quality of their work has greatly facilitated my project research on glycoproteins."
Highly Customizable Service
"One of the most important advantages of choosing Creative Biolabs is their ability to customize the biotinylation strategy. I have specific requirements for my project, and their team customized the biotinylation linking strategy using the NHS ester method, which perfectly matches my experimental conditions."
Reference
-
Böcker, Sophia, and Lothar Elling. "Biotinylated N-acetyllactosamine-and N, N-diacetyllactosamine-based oligosaccharides as novel ligands for human galectin-3." Bioengineering 4.2 (2017): 31. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Effects of 6-biotinylated tetrasaccharide on galectin binding and inhibition.1
Fig.1 Effects of 6-biotinylated tetrasaccharide on galectin binding and inhibition.1

