Glycoprotein-based Vaccine Development Service
Equipped with top-class scientific experts and integrating state-of-the-art technologies as well as substantial experience in the field of glycoprotein development, Creative Biolabs employs several highly efficient glyco-engineered platforms and chemical or (chemo) enzymatic methods for the development of glycoprotein vaccine candidate. We are fully competent and dedicated to serving as your one-stop-shop for glycoprotein vaccine candidate development and characterizations.
Examples of Glycoprotein-based Vaccine Development
Glycoprotein candidates for hepatitis C virus (HCV) vaccine development.
HCV infection remains a major public health issue with some 185 million individuals infected with HCV worldwide. Although the introduction of several direct‑acting antiviral agents, there is an urgent need for an effective prophylactic HCV vaccine. HCV envelope glycoproteins E1 and E2 form a heterodimer on the surface of HCV. E2 interacts directly with cellular receptors CD81 and scavenger receptor class B member 1 to mediate viral entry. E2 is an optimal candidate for HCV vaccine development because it possesses most neutralizing antibody-recognized epitopes. Therefore, a number of HCV vaccine candidates based on E2 have been developed.
Glycoprotein candidates for cytomegalovirus (CMV) vaccine development.
Development of a vaccine against human CMV infection is a major public health priority. So far, the most widely studied vaccine is a subunit vaccine based on the viral envelope glycoprotein B (gB). CMV gB is synthesized as a polypeptide with 906- or 907-aa in length that undergoes extensive posttranslational modification, including glycosylation at N- and O-linked sites. gB remains an important component of all CMV vaccines currently in development.
Glycoprotein candidates for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine development.
Human RSV is the main cause of severe lower respiratory tract infections among infants and young children worldwide. Great efforts on the development of RSV vaccine have been done to bring safe and effective vaccines to the market. Subunit-based vaccines are considered for important target group. The viral envelope glycoproteins, the fusion (F) protein and the attachment glycoprotein (G) protein, are involved in virus entry into the target cell. G protein is the receptor-binding protein, while F protein has membrane fusion activity. Both proteins have been shown to elicit virus-neutralizing antibodies. Clearly, antibodies directed to G protein interfere with binding of RSV virions to cellular receptors, while antibodies directed to F protein inhibit viral membrane fusion. Therefore, F protein and G protein are promising antigens in the development of a subunit vaccine against RSV.
Technologies for Glycoprotein Vaccine Candidates Development at Creative Biolabs
Glycoprotein by glyco-engineered platforms
The ability to modify, manipulate and incorporate in a site-specific way glycosidic residues on proteins is widely accepted as one of the most important challenges. Glycosylation of protein by the natural cell is a prevalent post-translational modification (PTM) that results in complex mixtures of constructs with different glycoforms. With proven experience in glycoscience, Creative Biolabs has established glyco-engineered mammalian cell expression system, glyco-engineered pichia pastoris expression system and glyco-engineered plant-based expression system for the development of glycoprotein vaccine candidates.
Site-specific glycosylation of proteins by chemical or (chemo)enzymatic strategies
Glycoforms produced in vivo are difficult to purify and characterize and different glycoforms can have different biological functions. Chemical site-specific glycosylation methods can resolve issues of homogeneous glycoprotein vaccine candidates. Site-specific strategies allow for the synthesis of defined glycoproteins with a precisely controlled epitope. With Ph.D. level scientists and substantial experience in employing chemical and (chemo)enzymatic strategies for site-specific glycosylation of proteins, we ensure high-purity homogeneous glycoprotein vaccine candidates which are obtained by highly efficient and simple operation under mild conditions.
Synthetic glycoprotein
Creative Biolabs has accumulated extensive experience in custom glycoprotein synthesis through glycoprotein remodelling, native chemical ligation (NCL), expressed protein ligation (EPL), Staudinger ligation or sugar-assisted ligation. We have developed a highly specialized platform as well as various comprehensive and innovative protocols for the synthesis of well-defined glycoprotein vaccine candidates up to 150 amino acids in length.
Highlights
-
Highly efficient in vivo glyco-engineered expression platforms
-
In vitro chemical and chemoenzymatic strategy
-
Powered by a proven, first-in-class technology
-
High flexibility and cost-effectiveness
As a leading specialist in in glycoscience, Creative Biolabs excels at the glycodesign and the development of glycoprotein. We offer custom glycoprotein vaccine candidate development according to our clients’ needs and delivered in a timely manner. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly send us an inquiry.
Published data
Novel coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which mainly attacks the respiratory system and is transmitted through aerosols, especially in poorly ventilated environments. The disease can cause mild or severe pneumonia symptoms in humans. The spike (S) glycoprotein on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 is a trimeric structure on the surface of the virus. This glycoprotein can recognize and connect to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on the host cell, promote the virus to enter the host cell, and spread within the cell. However, the body's immune system also recognizes the S glycoprotein, which triggers the body's self-protection. Therefore, the S glycoprotein is currently the main target for the development of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Many vaccines that have been marketed or are in advanced clinical trials are mostly developed according to the complete SARS-CoV-2 virus, the full-length S protein, the highly immunogenic RBD region, or the RNA encoding the S protein. Many of these vaccines have shown high efficacy and protection. However, COVID-19 will have many new variants, which may pose challenges to existing vaccines. To effectively control the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists need to adopt multiple strategies to redesign or adjust SARS-CoV-2 antigens to develop and optimize vaccines to better adapt to changes in the external environment.
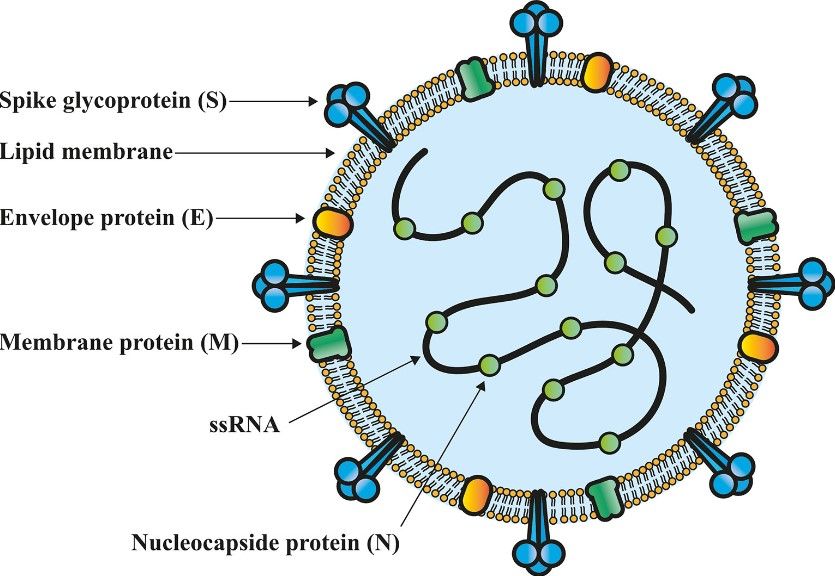 Fig.1 The structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion.1
Fig.1 The structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion.1
FAQs
Q1: What are the advantages of glycoprotein-based vaccines over traditional vaccines?
A1: Glycoproteins contain specific epitopes that are recognized by the immune system, resulting in a more specific and effective immune response. Glycosylation improves the stability, solubility, and half-life of vaccines, thereby enhancing immunogenicity. Moreover, glycoprotein vaccines are customized to target novel pathogen strains by changing the glycosylation pattern or protein sequence.
Q2: What technologies does Creative Biolabs use in its glycoengineered plant expression system?
A2: Creative Biolabs uses some key technologies in its glycoengineered plant expression system. We develop transgenic plants that express desired glycoproteins using engineered glycosylation pathways. High levels of glycoproteins are expressed in plant tissues using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation.
Q3: How does Creative Biolabs ensure high purity and homogeneous glycoprotein vaccine candidates?
A3: We ensure high-quality glycoprotein vaccine candidates through the following:
-
State-of-the-art expression systems: We use glycoengineered mammalian, yeast, and plant systems to produce glycoproteins.
-
Chemical and chemoenzymatic strategies: We utilize precise chemical or chemoenzymatic methods to ensure site-specific glycosylation and uniform glycoforms.
-
Advanced purification techniques: We employ advanced chromatography and purification methods to isolate glycoproteins.
-
Quality control: We implement stringent quality control measures, including mass spectrometry and glycan analysis, to verify the homogeneity and purity of glycoproteins.
Customer Review
Comprehensive Project Management
"Creative Biolabs provided comprehensive project management support. From initial design to final delivery, their team excelled at every stage, allowing us to obtain a high-quality glycoprotein vaccine candidate in a short period. Highly recommend them for vaccine development services."
Substantial Advancement of Research Results
"Working with Creative Biolabs not only enabled us to obtain high-quality glycoprotein vaccine candidates but also deepened our understanding of the field of glycoscience. Their expertise and technical support significantly promoted our research progress."
Reference
-
Martínez-Flores, Daniel, et al. "SARS-CoV-2 vaccines based on the spike glycoprotein and implications of new viral variants." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2021): 701501. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 The structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion.1
Fig.1 The structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion.1

