Glycoprotein Pharmaceuticals: Scientific and Regulatory Considerations
Many protein pharmaceuticals being developed for human use are glycoproteins, with oligosaccharides covalently attached to the polypeptide side chains. Increasing evidence suggests that oligosaccharides can play an important role in glycoprotein function. In evaluating the therapeutic effect and safety of a glycoprotein pharmaceutical, the intrinsic properties of the oligosaccharides, as well as their modulating effect on the protein, must be considered.
General Properties of Glycoproteins: Microheterogeneity
Although glycosylation is a common protein-modification process in eukaryotic cells, the range of structures for protein-liked glycans is exceeding large, and the biological significance of this heterogeneity is not well understood. Glycosylation can affect solubility, resistance to proteolytic attack and thermal inactivation, quaternary structure, activity, targeting, antigenicity, and functional activity half-life of the protein concerned.
Most glycoproteins are structurally heterogeneous. Heterogeneity is the rule rather than the exception with many biological products. This has led to the concept of “glycoforms”. Glycoforms frequently have different physical and chemical properties leading to potential functional diversity.
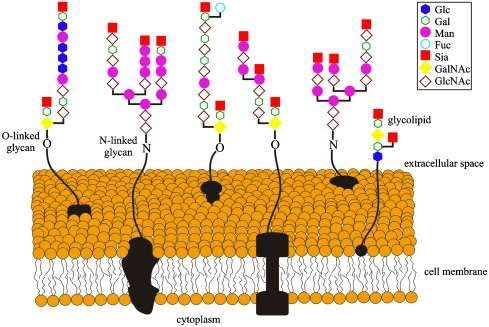 Fig.1 Showing carbohydrate heterogeneity found on cell surface glycoproteins and glycolipids.1
Fig.1 Showing carbohydrate heterogeneity found on cell surface glycoproteins and glycolipids.1
Effect of Glycosylation on Immune Characteristics and Pharmacokinetics
The absence of glycosylation for human proteins produced in E. coli may reveal new antigenic sites or may cause altered immunogenicity due to the tendency of glycosyl proteins to aggregate. Although pharmaceutical glycoproteins produced in heterologous mammalian cells may differ from their natural counterparts for detailed oligosaccharide structures, experience to the date indicated that, in general, immune responses due to microheterogeneity of glycan structures are not a major concern. Proteins without appropriate carbohydrate moieties may have altered pharmacokinetics. Reliable quantitative analysis of sialic acid will be an important aspect of quality control for glycoprotein pharmaceuticals.
Regulatory Concerns
There is an impressive list of protein drugs derived from cloned genes currently being used or evaluated in humans, or soon to be available for clinical trials. The list includes insulin, human growth hormone, various cytokines, albumin, clotting factors, monoclonal antibodies, and the surface antigens of hepatitis, herpes, and AIDS viruses. National control authorities and international organizations have responded by developing a series of regulatory documents. Glycoprotein pharmaceuticals are also subject to conventional regulatory issues applying to all biological products. Even though many glycoprotein pharmaceuticals will be produced by mammalian cells that can properly glycosylate, and can oxidatively form the correct disulfide bonds and allow the glycoproteins to be secreted, mammalian cells may contain viruses, host-cell components that may be antigenic in humans, or potentially oncogenic DNA.
The issue of glycoprotein microheterogeneity presents a challenge to industry and regulators alike. The concern is not only how microheterogeneity is generated, but also how to develop analytical approaches for detecting it and evaluating its significance about the safety and efficacy of the product. Both in vitro and in vivo bioassays for appropriate properties of the material are essential to confirm that the same material is being made in each batch. The extent, frequency, and methods of animal testing must be determined on a case-by-case basis to establish pharmacokinetics, including tissue distribution and clearance mechanisms of a glycoprotein pharmaceutical. In the final analysis, however, only carefully designed clinical trials and long-term surveillance can provide answers to the relevance of heterogeneity to the safety and efficacy of glycoprotein pharmaceuticals.
Creative Biolabs is specialized in glycoprotein development and production. We are fully equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and an experienced team of key personnel. We provide our customers with custom glycoprotein services. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more.
Reference
-
Kankia, H. I. "Immunomodulatory effects of carbohydrates and advanced glycation end products." Biotechnology and Molecular Biology Reviews 10.1 (2015): 1-11. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Showing carbohydrate heterogeneity found on cell surface glycoproteins and glycolipids.1
Fig.1 Showing carbohydrate heterogeneity found on cell surface glycoproteins and glycolipids.1

