Introduction of GPR85
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 85 (GPR85, SREB2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR85 gene. Among the related pathways of GPR85 are Peptide ligand-binding receptors. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include G-protein coupled receptor activity. An important paralog of this gene is GPR173. The SREB (Super Conserved Receptor Expressed in Brain) family - SREB1 (GPR27), SREB2 (GPR85), and SREB3 (GPR173) - is a particular subfamily of the GPCRs. They share 52-63% amino-acid identity and have lower homology to other GPCR subfamilies. The unique characteristic of the SREB family is the high conservation of the amino-acid sequence across species. SREB2, located on Chromosome 7q31, is an orphan GPCR of 7.5 kB that generates nine transcripts encoding for four proteins through alternative splicing.
| Basic Information of GPR85 | |
| Protein Name | Probable G-protein coupled receptor 85 |
| Gene Name | GPR85 |
| Aliases | Super conserved receptor expressed in brain 2, SREB2 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | P60893 |
| Transmembrane Times | 7 |
| Length (aa) | 370 |
| Sequence | MANYSHAADNILQNLSPLTAFLKLTSLGFIIGVSVVGNLLISILLVKDKTLHRAPYYFLLDLCCSDILRSAICFPFVFNSVKNGSTWTYGTLTCKVIAFLGVLSCFHTAFMLFCISVTRYLAIAHHRFYTKRLTFWTCLAVICMVWTLSVAMAFPPVLDVGTYSFIREEDQCTFQHRSFRANDSLGFMLLLALILLATQLVYLKLIFFVHDRRKMKPVQFVAAVSQNWTFHGPGASGQAAANWLAGFGRGPTPPTLLGIRQNANTTGRRRLLVLDEFKMEKRISRMFYIMTFLFLTLWGPYLVACYWRVFARGPVVPGGFLTAAVWMSFAQAGINPFVCIFSNRELRRCFSTTLLYCRKSRLPREPYCVI |
Function of GPR85 Membrane Protein
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of membrane surface receptors, essential for signal transduction in central nervous system, and a preferred therapeutic target for psychiatric and neurological disorders. More recently, a possible role of GPR85 in autism and possibly attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, Tourette’s syndrome and intellectual disability has emerged. Thus, it is conceivable that genetic variation in GPR85 might contribute to a spectrum of neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders, analogous to other genetic risk factors associated with risk for schizophrenia. Two single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in GPR85 are nominally associated with schizophrenia risk.
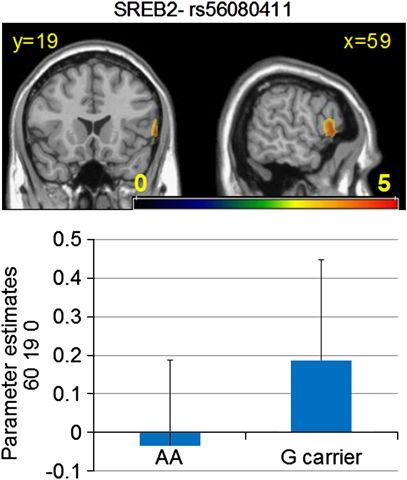 Fig.1 SREB2-genotype effects on BOLD response during the PICT task. (Radulescu, 2013)
Fig.1 SREB2-genotype effects on BOLD response during the PICT task. (Radulescu, 2013)
Application of GPR85 Membrane Protein in Literature
The article reveals that genetic variants in GPR85 have been associated with risk for schizophrenia. Trends in the same direction were present for GPR85 in the right occipital cortex and right fusiform gyrus.
The article indicates that SREB2 is a negative regulator of adult neurogenesis and consequential cognitive functions. Inhibition of SREB2 function may be a novel approach to enhance hippocampal adult neurogenesis and cognitive abilities to ameliorate core symptoms of psychiatric patients.
Authors in this group found that GPR85 influences brain size. GPR85 may be a potential risk factor for psychiatric disorders and its pathway can be used as a target for psychiatric therapy.
This article focuses on the possible link between SREB family and neural plasticity. SREB2 mRNA was expressed in neurons throughout the brain and the most abundant expression was detected in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in all species examined.
This article reports that GPR85 is associated with postsynaptic density protein (PSD)-95 linked with NLGN in the brain. GPR85 carrying the mutations detected in ASD patients disturbs dendrite formation.
GPR85 Preparation Options
To obtain the soluble and functional target protein, the versatile Magic™ membrane protein production platform in Creative Biolabs enables many flexible options, from which you can always find a better match for your particular project. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-GPR85 antibody development services.
As a leading service provider, Creative Biolabs is proud to present our professional service in membrane protein preparation and help you with the research of membrane proteins. Please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.