About This Program
This program aims to develop anti-CD155 therapeutic monoclonal antibody for immuno-oncology.
CCD155 is reported to be expressed in many tumor cells and activated DCs. It affects cell adhesion, migration, differentiation, proliferation, survival, and metastasis. Another important function of CD155 is immunization regulation. These data fully indicate that CD155 may be involved in cancer progression and could be a promising next generation of cancer immunotherapy.
CD155
CD155 is the fifth member of the nectin-like family and acts as a receptor for poliovirus; therefore, CD155 is also known as necl-5 or PVR. As an immunoglobulin-like adhesion molecule, CD155 is involved in cell movement, natural killing, and T cell-mediated immunity.
Highlights of CD155 for cancer treatment:
-
CD155 molecules have domains similar to pectin and play a key role in cell adhesion and polarization.
-
As the ligand for both costimulatory receptor CD226 and coinhibitory receptor TIGIT on natural killer and T cells, CD155 seems to play a dual role in the community.
-
CD155 is barely or weakly expressed in various normal human tissues but frequently overexpressed in human malignant tumors.
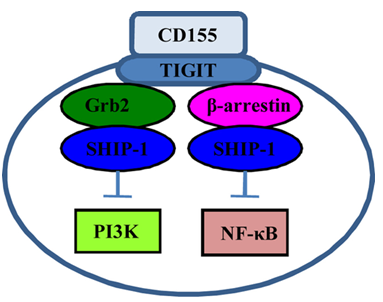 Fig.1 Signaling initiated by CD155‐TIGIT ligation.1
Fig.1 Signaling initiated by CD155‐TIGIT ligation.1
CD155 in Cancer Studies
A newly identified target, only a few studies have investigated the immune‑regulatory effect of CD155 antibody in the tumor microenvironment. Here are some published data about CD155 molecule as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy.
-
High CD155 expression was significantly associated with poor overall survival in SCLC patients.
-
Deletion of tumor CD155 decreases tumor growth and metastasis.
Indication
According to published data, CD155 can be found ubiquitous in several human tissues, including brain, liver, ileum, white blood cells, placenta, and lungs. Compared to serum from healthy donors, CD155 is reported to be highly expressed from that of patients with breast cancer, gynecological diseases, gastrointestinal cancer, and lung cancer. In addition, available evidence indicates high levels of CD155 expression in human cancer tissues. CD155 has been shown to be widely expressed in several skeletal and soft tissue sarcoma cell populations.
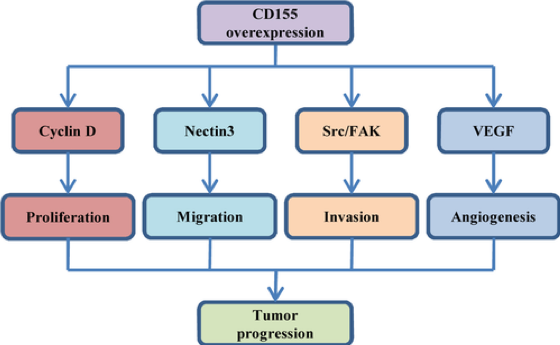 Fig.2 The role of CD155 in tumor development and its underlying molecular mechanisms.2
Fig.2 The role of CD155 in tumor development and its underlying molecular mechanisms.2
We plan to develop multiple mAb programs that apply to different indications (not limited to one specific tumor type), of which CD155 is highly expressed.
Clinical Trials under Progress
To our knowledge, there are NO ongoing clinical trials of anti-CD155 therapeutic monoclonal antibody. Our program will be a pioneer in the development of CD155 antibody.
Program Plan
We have extensive knowledge of end-to-end program development. For each program, we are committed to delivering the final complete program to our clients within 1.5 years prior to entering the IND stage.
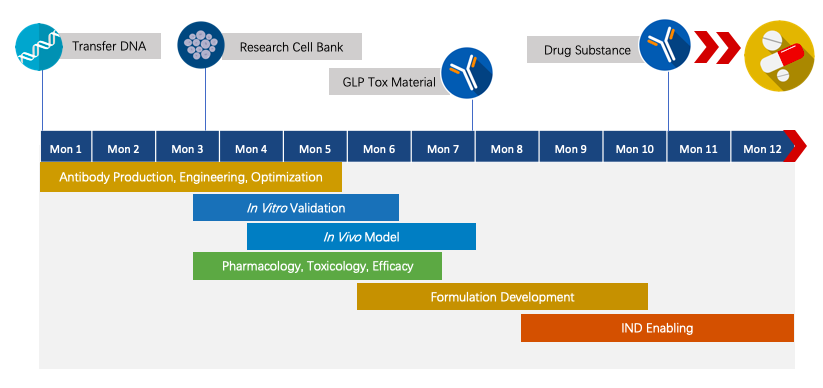 Fig.3 The timeline of Next-IOᵀᴹ programs.
Fig.3 The timeline of Next-IOᵀᴹ programs.
Cooperation
Creative Biolabs is looking for potential partners (include but not limit to major pharma or biotech firms) to develop anti-CD155 therapeutic monoclonal antibody program together. Our scientists are dedicated to bringing together years of valuable experience to our partner and achieve a meaningful partnership. By doing so, we wish to help both parties to proceed with IND and many stages of clinical trials beyond.
If you are interested, please feel free to contact us so that we can discuss the program and other possible opportunities for cooperation. Look forward to working with you in the near future.


 Fig.1 Signaling initiated by CD155‐TIGIT ligation.1
Fig.1 Signaling initiated by CD155‐TIGIT ligation.1
 Fig.2 The role of CD155 in tumor development and its underlying molecular mechanisms.2
Fig.2 The role of CD155 in tumor development and its underlying molecular mechanisms.2
 Fig.3 The timeline of Next-IOᵀᴹ programs.
Fig.3 The timeline of Next-IOᵀᴹ programs.
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure