About This Program
This program aims to develop anti-CD163 therapeutic monoclonal antibody for immuno-oncology.
Rationale when developing program:
-
A high number of CD163+ macrophages in breast cancer is associated with rapid proliferation, poor differentiation, ER-negative, and ductal histological types.
-
In pancreatic cancer, an increasing number of CD163+ macrophages is associated with LN metastasis and poor prognosis.
-
More advanced forms of tumors secrete higher levels of monocyte colony-stimulating factors, IL-10 and/or TGF-β, hence, a large number of CD163+ M2 macrophages production.
In conclusion, M2 macrophages play a role in tumor progression by producing vascular endothelial growth factor and extracellular matrix remodeling proteins, highlighting the logic behind CD163-based cancer immunotherapy.
CD163
CD163, a member of the scavenger receptor cysteine (SRCR) superfamily, is the optimal marker for M2 macrophages. Some functions are highlighted below:
-
By directly participance in the cellular uptake of hemoglobin, CD163 significantly reduces the ability of hemoglobin to participate in the oxidation reaction.
-
CD163 is involved in anti-inflammatory signaling following the bindings of certain forms of haptoglobin, including the initiation of IL-10 responses via Akt signaling. IL-10 is involved in the polarization of macrophages to the M2 (CD163+) phenotype, resulting in a positive feedback loop of IL-10 and CD163 expression.
-
Pro-inflammatory signals, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma, transforming growth factor-beta and lipopolysaccharide, may lead to decreased levels of CD163 expression.
-
CD163 may engage in host defense system by binding to Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
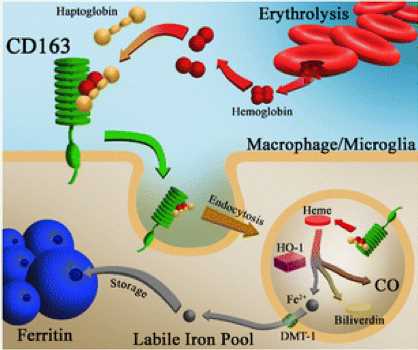 Fig.1 Ghemoglobin-haptoglobin-CD163 pathway in microglia/macrophages.1
Fig.1 Ghemoglobin-haptoglobin-CD163 pathway in microglia/macrophages.1
CD163 in Cancer Studies
Here are some published data about CD163 working as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy.
-
MyCD163+ TAMs at the invasive front is correlated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
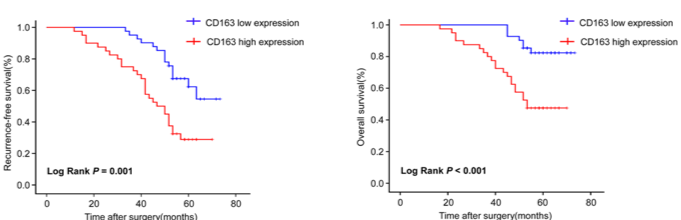 Fig.2 Association of CD163 expression at invasive front with the patients’ recurrence-free survival and overall survival in CRC.2
Fig.2 Association of CD163 expression at invasive front with the patients’ recurrence-free survival and overall survival in CRC.2
-
Survival analysis of CD163 in glioma and glioblastoma.
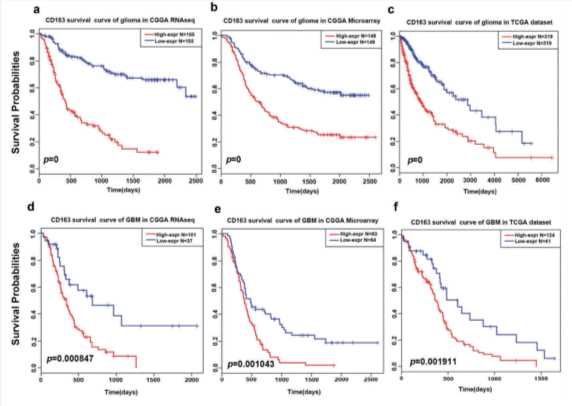 Fig.3 Survival analysis of CD163 in whole grade glioma and glioblastoma.3
Fig.3 Survival analysis of CD163 in whole grade glioma and glioblastoma.3
Ongoing Clinical Trials
-
Currently, to the best of our knowledge, NO anti-CD163 therapeutic monoclonal antibodies are being evaluated in clinical trials.
-
Despite this, CD163 is still a compelling target for cancer immunotherapy. In an effort to optimally leverage CD163-mediated immune response, our antibody development project will focus primarily on the cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
Program Planning and Management
We have extensive knowledge of end-to-end program development. For each program, we are committed to delivering the final complete program to our clients within 1.5 years before entering the IND stage.
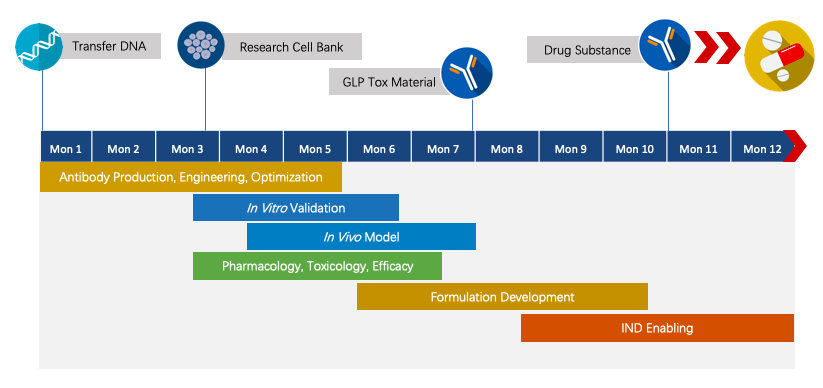 Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
Cooperation
Creative Biolabs is looking for potential partners (include but not limit to major pharma or biotech firms) to develop anti-CD163 Therapeutic Monoclonal antibody program together. Our scientists are dedicated to bringing years of valuable experience to our partner and achieve a meaningful partnership. For any partners interest in our Next-IO™ programs, Creative Biolabs welcomes collaboration.
Here are two ways for your choice, and please contact us for more details.
1) Collaborate with us and co-develop the programs from the discovery phase to IND enabling. Costs will be shared.
2) Become a licensed candidate for our programs.
With our quality control protocol and knowledge of global regulatory requirements, we can help our partners advance their programs with more chance to succeed. Look forward to cooperating with you in the near future.


 Fig.1 Ghemoglobin-haptoglobin-CD163 pathway in microglia/macrophages.1
Fig.1 Ghemoglobin-haptoglobin-CD163 pathway in microglia/macrophages.1
 Fig.2 Association of CD163 expression at invasive front with the patients’ recurrence-free survival and overall survival in CRC.2
Fig.2 Association of CD163 expression at invasive front with the patients’ recurrence-free survival and overall survival in CRC.2
 Fig.3 Survival analysis of CD163 in whole grade glioma and glioblastoma.3
Fig.3 Survival analysis of CD163 in whole grade glioma and glioblastoma.3
 Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
Fig.4 Project pipeline management of therapeutic monoclonal antibody.
 Download our brochure
Download our brochure