This program aims to develop therapeutic monoclonal antibodies against the target – HVEM/TNFRSF14.
HVEM/TNFRSF14 is a bidirectional modulator that regulates T-cell activation in either co-stimulating or co-inhabiting manner, depending on its binding partner. HVEM/TNFRSF14 can act as both ligand or as a receptor. Binding of HVEM/TNFRSF14 to BTLA (IgSF) or CD160 on effector T cells, delivers a coinhibitory signal; alternately, binding to either of two tumor necrosis factor ligands, LIGHT or lymphotoxin-α, delivers the costimulatory signal. Because of its bidirectional role, HVEM/TNFRSF14 has become a promising target in the file of cancer immunotherapy.
HVEM/TNFRSF14
HVEM (Herpes Virus Entry Mediator; TNFRSF14) is a member of the TNFR superfamily and is normally expressed in T cells, B cells, NK cells and antigen-presenting cells. This gene has been proved to be the most frequently mutated genes in germinal lymphomas and has a variable correlation with other prognoses. Multiple studies have shown that:
-
The HVEM/BTLA axis is an immune checkpoint that plays an important role in the blockade of T cell-mediated immune responses.
-
The binding of BTLA to its ligand HVEM, found in melanoma and other cancers, negatively regulates T cell immune responses and allows cancer cells to escape immune surveillance.
-
The HVEM/BTLA/LIGHT pathway is also involved in the regulation of autoimmune responses, which making these proteins promising therapeutic targets for a number of diseases.
-Monoclonal-Antibody-Program-1.png) Fig.1 MOA for HVEM/TNFRSF14 regulates T cell immune responses.1
Fig.1 MOA for HVEM/TNFRSF14 regulates T cell immune responses.1
Published Data
• Induction of in vivo antitumor immunity by anti-HVEM scFv.
• Soluble HVEM (solHVEM) restores BTLA inhibitory signals and kills lymphoma cells.
• HVEM signaling exerts a neurite growth inhibitory effect on nodose neurons.
Indication
HVEM has been suggested to play certain role in cancer biology, because it is widely expressed in a range of hematopoietic cells, including T-cells, B-cells, natural killer cells, monocytes, and immature dendritic cells. HVEM is also expressed in nonhematopoietic cells and tissues including the lung, liver, and kidney. Some indications may related to HVEM are colorectal cancer (CRC), gastric cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, esophageal, and ovarian cancer. Therefore, we intend to develop multiple programs for different indications (not limited to one specific type of tumor), in which HVEM/TNFRSF14 is highly expressed.
Clinical Trials under Progress
To the best of our knowledge, there are only a few studies involving HVEM in cancer biology. The role of HVEM in actual human cancer remains unidentified. In this case, our program will be a pioneer in this field.
With our extensive experience in providing CRO services, we are confident in providing streamlined end-to-end program development. We are committed to developing a complete program, which tarilors to the needs of our partners, from antibody discovery, engineering, optimization, to pre-clinical studies. Periodic progress report will be delivered to our clients for effective, smooth and timely communication.
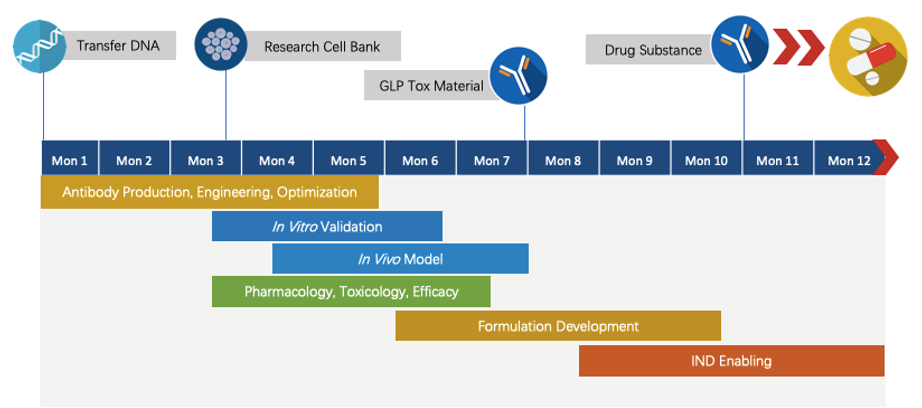
Creative Biolabs is looking for potential partners (including but not limited to major pharma or biotech firms) to develop anti-HVEM/TNFRSF14 therapeutic monoclonal antibody program. Our scientists are dedicated to bringing years of valuable experience to our partner. By using this strategic collaboration, By using this strategic collaborations, we wish to help both sides to proceed with IND and many stages of clinical trials.
If you are interested in our program, please feel free to contact us to learn more
details about the
cooperation. Looking forward to working with you in the near future.



-Monoclonal-Antibody-Program-1.png) Fig.1 MOA for HVEM/TNFRSF14 regulates T cell immune responses.1
Fig.1 MOA for HVEM/TNFRSF14 regulates T cell immune responses.1



 Download our brochure
Download our brochure