Introduction of MAS1
MAS1, encoded by MAS1 gene, is a seven-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor and preferentially couples to the Gq protein. It is a receptor for angiotensin-(1-7) and plays diverse roles in humans physiological activities by angiotensin-(1-7). Studies have shown that the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas pathway plays a crucial role in myocardial remodeling, glucose homeostasis, anti-proliferative, anti-vasodilatory and anti-metastatic. Moreover, ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis can be regarded as a potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes.
| Basic Information of MAS1 | |
| Protein Name | Proto-oncogene Mas |
| Gene Name | MAS1 |
| Aliases | MAS, MGRA |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | P04201 |
| Transmembrane Times | 7 |
| Length (aa) | 325 |
| Sequence |
MDGSNVTSFVVEEPTNISTGRNASVGNAHRQIPIVHWVIMSISPVGFVENGILLWFLCFRMRRN PFTVYITHLSIADISLLFCIFILSIDYALDYELSSGHYYTIVTLSVTFLFGYNTGLYLLTAISV ERCLSVLYPIWYRCHRPKYQSALVCALLWALSCLVTTMEYVMCIDREEESHSRNDCRAVIIFI AILSFLVFTPLMLVSSTILVVKIRKNTWASHSSKLYIVIMVTIIIFLIFAMPMRLLYLLYYEY WSTFGNLHHISLLFSTINSSANPFIYFFVGSSKKKRFKESLKVVLTRAFKDEMQPRRQKDNCNT VTVETVV |
Function of MAS1 Membrane Protein
The activated MAS1 by angiotensin-(1-7) can stimulate the activation of the phospholipase C signaling pathway thereby mediating multiple cellular responses. MAS1 functions as an antagonist of AGTR1 (angiotensin-2 type 1 receptor) despite it promotes AGTR1 expression. It can suppress the activation of AGTR1, resulting in vasodilatation and a decrease in blood pressure. Studies have shown that MAS1 may be involved in multiple processes including hypotension, smooth muscle relaxation, and cardioprotection by mediating the effects of angiotensin-(1-7). Besides, MAS1 as an antagonist of AGTR1 also plays a key role in the progression of tumors through controlling cell proliferation, survival, invasion, angiogenesis, and subsequent metastasis. Studies have shown that MAS1 acts as an inhibitory regulator of types of cancer and possible therapeutic target for malignant tumors, such as breast cancer, bladder cancer. In addition, MAS1 is associated with the inflammation responses via angiotensin-(1-7). The activated MAS1 via angiotensin-(1-7) can suppress inflammation responses by mediating leukocyte recruitment/activation. ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis may be a promising therapeutic target for chronic inflammatory diseases.
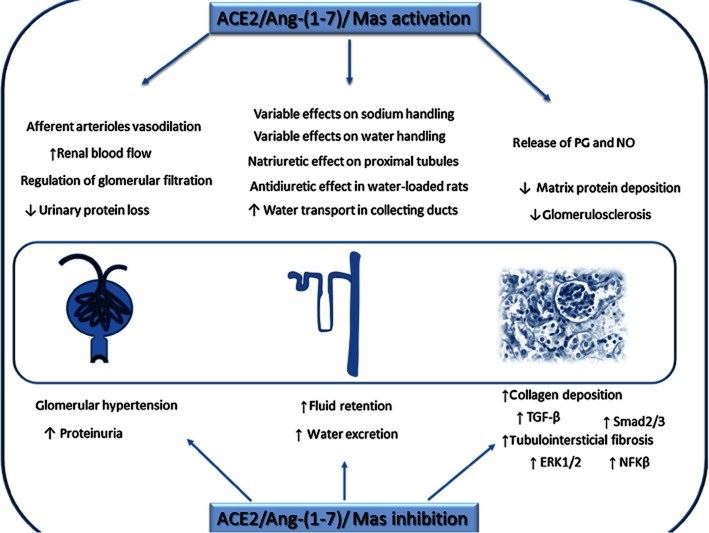 Fig.1 Schematic representation for the role of ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas receptor axis on renal tissue. (Silva, 2013)
Fig.1 Schematic representation for the role of ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas receptor axis on renal tissue. (Silva, 2013)
Application of MAS1 Membrane Protein in Literature
The article shows that angiotensin-(1-7) treatment suppresses lung inflammatory responses and lung fibrosis induced by cigarette smoke (CS) exposure.
The study indicates that a reduced expression of ACE2 and Ang-(1-7) in the placenta by dexamethasone treatment may be responsible for intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and consequent disease programming later in life.
In this review, authors summarize recent findings regarding the physiological and biological roles of the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis in the cardiovascular system and discuss ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis potential as an antihypertensive in functional foods.
The findings reveal that ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-MasR axis may play a protective role in the development of myocardial remodeling, suggesting ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-MasR axis can be regarded as a new target for drug development of cardiac fibrosis.
The study indicates that Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis activity is differentially modulated in the acute and post-acute stages of nerve injury in mice model.
MAS1 Preparation Options
Based on the versatile Magic™ membrane protein production platform, Creative Biolabs can provide many flexible options for soluble and functional target protein, from which you can always find a better match for your particular project. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-MAS1 antibody development services.
As a forward-looking research institute as well as a leading custom service provider in the field of membrane protein, Creative Biolabs has won good reputation among our worldwide customers for successfully accomplishing numerous challenging projects including generation of many functional membrane proteins. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.