Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) is a generic term for glycol polymers with a relative molecular mass of 200-8000 and above, with the chemical structure of HO-(CH2CH2)n-OH. PEG is FDA-approved for in vivo use due to its non-toxicity, non-immunogenicity, precise molecular weight, high purity, and low polydispersity.
In order to ensure the specificity of the PEGylation, a methyl group is usually added to protect the alcohol hydroxyl group at one of its termini, turning it into methoxy PEG (mPEG). This modification allows for better control and precision in the PEGylation process. Moreover, the low bioactivity of the hydroxyl group at the raw end of polyethylene glycol makes it challenging to achieve stable binding with substrates. Consequently, the scope of modification for proteins, peptides, and other drugs becomes relatively narrow. Functionalized groups, such as N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), amino, carboxyl, aldehyde, and p-toluenesulfonic acid salts, have been widely used for the modification of mPEG. These functionalized mPEG derivatives provide a broader range of possibilities for the modification and enhancement of various biomolecules and drugs.
PEGylated technology couples PEG with the modified drugs through covalent bonding. This innovative approach aims to enhance the physicochemical properties and biological activity of the compounds. PEGylation has found extensive applications in various areas including proteins (peptides), enzymes, antibodies, and small molecules. Creative Biolabs offers different methods of PEGylation depending on the molecular structure, weight and physicochemical properties of the modified compounds.
Lysine is usually present in high quantities on the surface of proteins. When protein modification is carried out using ε-NH2 of lysine as the target, a series of PEG chains with different lengths can be formed, resulting in a product that is a mixture of PEGylated isomers.
Site-specific PEGylation is achieved through the optimized selection of coupling modes, PEG crosslinkers and reacting conditions (like pH), etc. The products obtained from this conjugation are homogeneous, with fewer isomers, better retention of activity, and greatly reduced immunogenicity. we offer the following site-specific PEGylation methods.
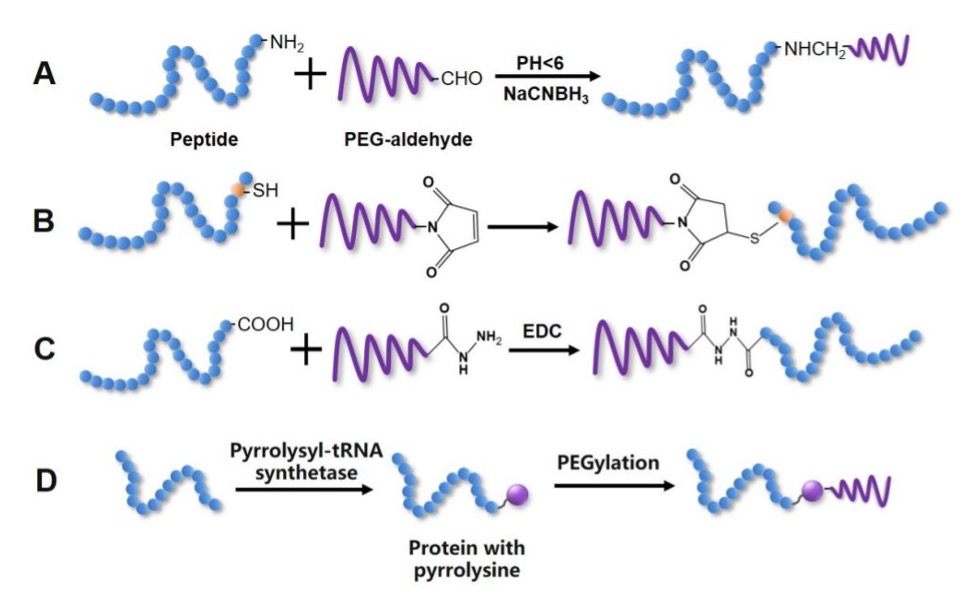 Fig 1. Strategies for site-specific PEGylation.
Fig 1. Strategies for site-specific PEGylation.
At Creative Biolabs, quality is our top priority. We adhere to strict quality control measures to ensure that your PEGylated compounds meet the highest standards of excellence. More importantly, our professional team can provide custom conjugation services according to your specific objectives. We look forward to providing you with an exceptional experience. If you are interested in our services, please contact us.
References
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.