Creative Biolabs has focused on drug discovery for a long time and developed a comprehensive functional analysis platform. Our team can provide customized digital imaging services using atomic force microscopy to meet all your demands.
As the rapid development of drug discovery, approaches of digital imaging plays an essential role in this process. One of which, atomic force microscopy, widely known as AFM, is a technique developed to examine the whole and three-dimensional glory surface of both hard and soft artificial materials regardless of opaqueness or conductivity. What's more, AFM is an essential method for researching biological samples, such as cells, tissues, and biomolecules, on account of its ability to image surfaces under liquids. In addition, the cantilever cusp enables to be applied to visioning live cells with atomic resolution and burrowing into single molecular events in active cells under physiological states. At present, AFM is the unique approach that straightly offers mechanical, structural, and functional information at high resolution.
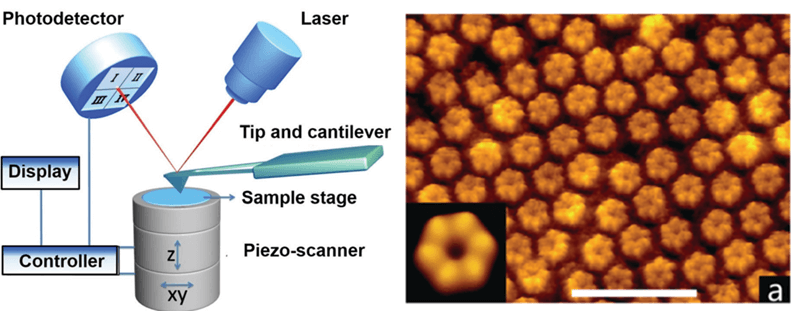 Figure1. Schematic diagram of atomic force microscopy and high-resolution AFM image of proteins. (Shan 2015)
Figure1. Schematic diagram of atomic force microscopy and high-resolution AFM image of proteins. (Shan 2015)
The majority of conventional approaches used to study these structures need cell drying, such as electron microscopy and X-rays, which probably come to terms of the accuracy of the analysis through denaturing the surfaces. While, the particular character of AFM makes it highly outstanding for biological applications of living cell imaging and unitary molecule force spectroscopy, offering mechanical, structural, and functional information. There are several operation modes of AFM, including contact mode imaging, tapping mode imaging, and dynamic force spectroscopy mode.
Specific AFM Applications to Microbiology
AFM is the only technique that directly provides structural, mechanical, and functional information at a high resolution of cells under physiological conditions. In comparison to electron microscopy, which requires cell fixation and drying, AFM offers the possibility of acquiring high-resolution data in living specimens in real time.
In cellular biology, AFM applies to differentiate normal cells and cancer cells on a hardness of cells and to appraise interactions between a particular cell and its adjacent cells in a competitive culture system. In more progressive versions, currents enable to be gone through the tip to detect the electrical conductivity or transport of the underlying surface.
Creative Biolabs has professional and experienced scientists hammering at drug discovery. Our scientists are confident in performing high-quality digital imaging services using atomic force microscopy to satisfy every client's scientific research or clinical requirements.
Creative Biolabs provides other various drug discovery services. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
References
-
Shan (2015). “The structure and function of cell membranes examined by atomic force microscopy and single-molecule force spectroscopy”. Chemical Society Reviews 44(11): 3617-3638.
-
Meyer (1988). “Novel optical approach to atomic force microscopy”. Applied physics letters 53(12), 1045-1047.
-
Henderson (1992). “Actin filament dynamics in living glial cells imaged by atomic force microscopy”. Science 257(5078): 1944-1946.
-
Nishida (2008). “Photothermal excitation and laser Doppler velocimetry of higher cantilever vibration modes for dynamic atomic force microscopy in liquid”. Review of scientific instruments 79(12): 123703.
For Research Use Only.
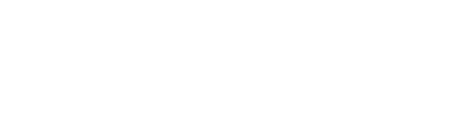
 Figure1. Schematic diagram of atomic force microscopy and high-resolution AFM image of proteins. (Shan 2015)
Figure1. Schematic diagram of atomic force microscopy and high-resolution AFM image of proteins. (Shan 2015)