Phage display is an in vitro screening technique for identifying binding ligands for proteins and other macromolecules. This technology has also proved to be a powerful tool for isolating ligands for drug discovery. As one of the well-recognized experts in phage display technology, Creative Biolabs provides professional phage display service to help our customers discovering novel drugs.
With the rapid development of sequencing technology (such as the next generation sequencing, NGS), the genome sequences of many microorganisms have been known. This highly accelerates discovering new potential targets for drugs. However, the biochemical activities of many of these new targets are not known, which making it difficult to develop HTS assays for them. With the development of phage display, it overcomes the disadvantages of traditional biochemical activity-based HTS screening. Those peptides in targets can be used as “surrogate ligands” in competition assays for screening of targets of unknown function with small-molecule libraries. It allows screening previous unavailable targets by traditional HTS-compatible assay methods.
Creative Biolabs standardizes the protocols of affinity selection of phage-displayed peptides (Figure 1).
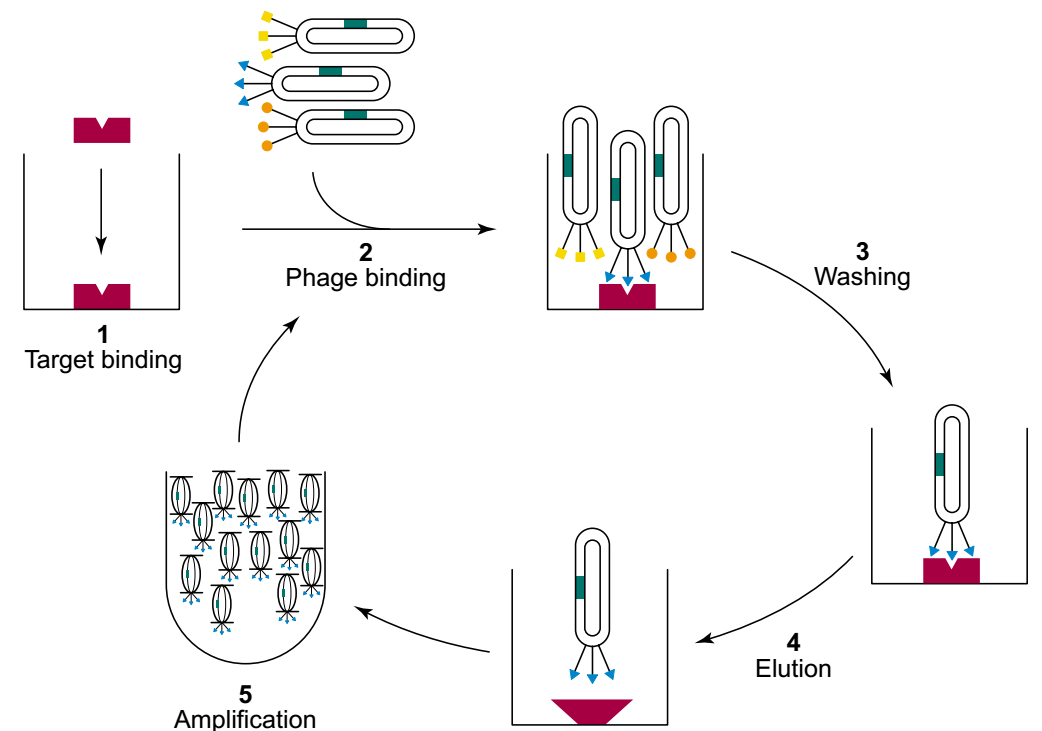 Figure 1. The process for affinity selection of phage-displayed peptides. (Dale J. Christensen et al. 2001)
Figure 1. The process for affinity selection of phage-displayed peptides. (Dale J. Christensen et al. 2001)
The typical protocol includes:
-
Construction of a library of variants of polypeptides fused to a bacteriophage coat protein. This step creates a physical linkage between phenotype and genotype. It allows affinity selection from the combinatorial library of those phage particles displaying peptides that bind to a target of interest while reserving the genetic identity.
-
Immobilization of the target on the surface of beads or the wells of a microtiter plate.
-
Phages from the library are incubated with the immobilized target to allow affinity selection of phage-displayed peptides with binding target proteins.
-
The plate is washed to remove unbound phages, and the bound phages are eluted from the plate by denaturation of the target protein.
-
The eluted phages are incubated with E. coli host cells to allow for infection and amplification of the subpopulation of phage displaying peptides with affinity for the target.
-
The amplified phages are used for additional cycles of selection until only phage displaying specific, tight-binding peptides remain.
-
Individual phage is isolated, the DNA sequence encoding the displayed peptide is determined, and the peptide sequence is deduced.
Phage display technology can be adapted into a high-throughput format based on radioactive, luminescence or fluorescence detection. Except for extracellular ligand-binding assay, we also provide intracellular expression of the peptide surrogate ligand for validation of peptides. In this assay, peptides identified by phage display can inhibit the function of target proteins inside a bacterial cell.
For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
Reference
-
Chistensen D J, Gottlin E B, Benson R E. (2001). “Phage display for target-based antibacterial drug discovery”. Drug Discovery Today 6(14):721-727.
For Research Use Only.
Copyright © 2024 Creative Biolabs.
 Figure 1. The process for affinity selection of phage-displayed peptides. (Dale J. Christensen et al. 2001)
Figure 1. The process for affinity selection of phage-displayed peptides. (Dale J. Christensen et al. 2001)