Case Study of Hybridoma
Background:
Target A is a member of immune checkpoint proteins, which is primarily expressed on the plasma membrane of many T cell subsets and NK cells. It is a type I transmembrane protein with co-inhibitory immune modulatory effects. Expression of target A can be upregulated by tumor cells, thus weakening NK cell killing efficiency. It has been proved that target A’s inhibition of NK cytotoxicity is correlated with many types of tumor growth and progression.
Case design:
➢ Immunogen design & preparation
As the target A is a multi-pass membrane protein with a large extracellular domain, which is responsible for its key biological functions, we chose to synthesize the extracellular loop as surrogate immunogen. The resulting recombinant protein showed adequate binding activities with its natural ligand, indicating that this surrogate antigen can represent the structural and functional properties of the original molecule.
➢ Immunization scheme design & conduction
Considering the small MW and high similarity between human and mouse sequence, a unique water-soluble adjuvant was used to enhance immunogenicity. Three CAMouse™ models of adequate age were used, and the whole process was designed accordance with conventional mouse immunization scheme. Besides, we prepared 5-10 CAMouse™ models of different strains/genetic backgrounds, in case the initial immunization outcome failed to be satisfactory. For every single antigen, we guarantee our clients that good immune responses will be achieved (serum dilution at 1: 8000, Elisa OD450 > 1.0 or serum titer> 512,000) using the transgenic CAMouse™ models.
The results of post-immune titer measurement were shown as follow: after routine 3-time immunization of three CAMouse™ models, the 2# mouse revealed the highest titer of up to 1:512,000, which we decided to use for downstream studies.
Table 1. Titering results after the booster immunization
| Dilution | A490 | |||||
| Coating: Target A | Coating: Control | |||||
| Mouse 1 | Mouse 2 | Mouse 3 | Mouse 1 | Mouse 2 | Mouse 3 | |
| 1:200 | 1.993 | 1.878 | 1.715 | 0.077 | 0.082 | 0.097 |
| 1:400 | 1.840 | 1.817 | 1.485 | 0.061 | 0.064 | 0.068 |
| 1:800 | 1.448 | 1.672 | 1.232 | 0.061 | 0.062 | 0.068 |
| 1:1600 | 1.114 | 1.389 | 0.953 | 0.057 | 0.061 | 0.065 |
| 1:3200 | 0.801 | 1.039 | 0.658 | 0.054 | 0.056 | 0.057 |
| 1:6400 | 0.564 | 0.725 | 0.459 | 0.060 | 0.063 | 0.063 |
| 1:12800 | 0.356 | 0.484 | 0.304 | 0.062 | 0.061 | 0.062 |
| 1:25600 | 0.259 | 0.396 | 0.218 | 0.069 | 0.067 | 0.073 |
| 1:51200 | 0.190 | 0.201 | 0.150 | 0.067 | 0.093 | 0.086 |
| 1:102400 | 0.119 | 0.144 | 0.108 | 0.060 | 0.075 | 0.060 |
| 1:204800 | 0.099 | 0.108 | 0.092 | 0.062 | 0.079 | 0.066 |
| 1:409600 | 0.086 | 0.091 | 0.078 | 0.064 | 0.077 | 0.061 |
| 1:819200 | 0.081 | 0.077 | 0.071 | 0.057 | 0.072 | 0.062 |
| 1:1638400 | 0.079 | 0.078 | 0.075 | 0.064 | 0.079 | 0.064 |
| Blank | 0.072 | 0.074 | 0.079 | 0.063 | 0.080 | 0.062 |
| Negative | 0.089 | 0.079 | 0.081 | 0.078 | 0.087 | 0.083 |
[Green]: titer
a. blank: PBS
b. negative: pre-immunized sera (1:1000)
c. Coating: target A or control, 0.5 ug/well
d. 1st Ab: antisera
e. 2nd Ab: HRP-goat anti-mouse IgG (Fcr)
➢ Cell fusion & antibody screening
Spleen of the mouse with highest titer was extracted and spleen cells were fused with myeloma cells to form hybridomas. Featured fusion agent was used to achieve optimal fusion efficiency. After that, large population of hybridoma cell clones were harvested for subsequent screenings. We have versatile function-based screening approaches, including high-throughput strategies. In this case, the antigen of interest was easy to obtain and highly soluble. Therefore, we chose to conduct a 2-round ELISA for antibody screening using hybridoma supernatants. The limiting dilution method guarantees the hybridoma cell clones as completely monoclonal clones. Typically, we can identify more than 10% stable positive clones from all the fused cells.
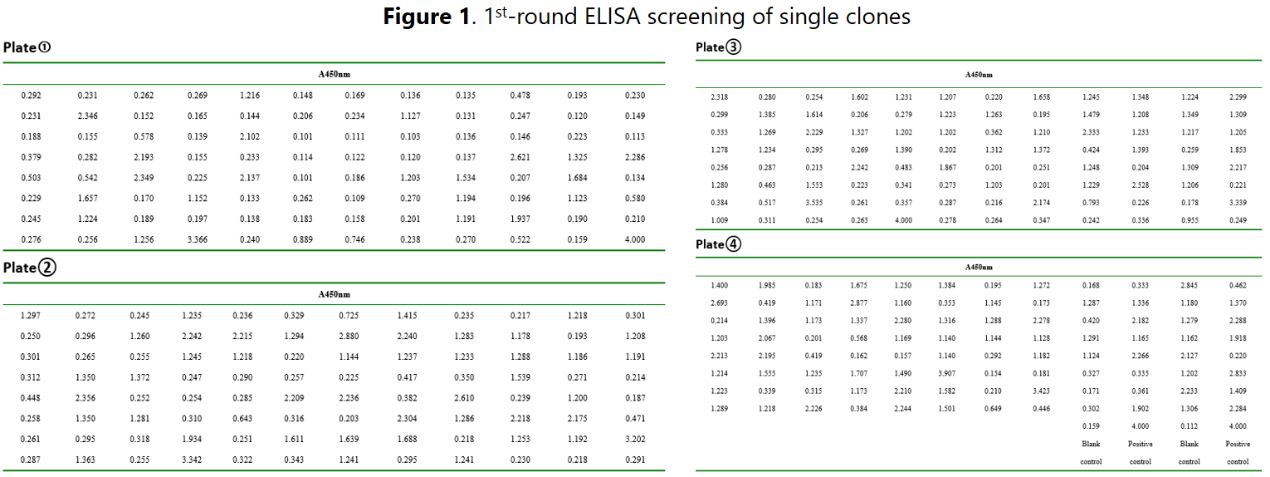
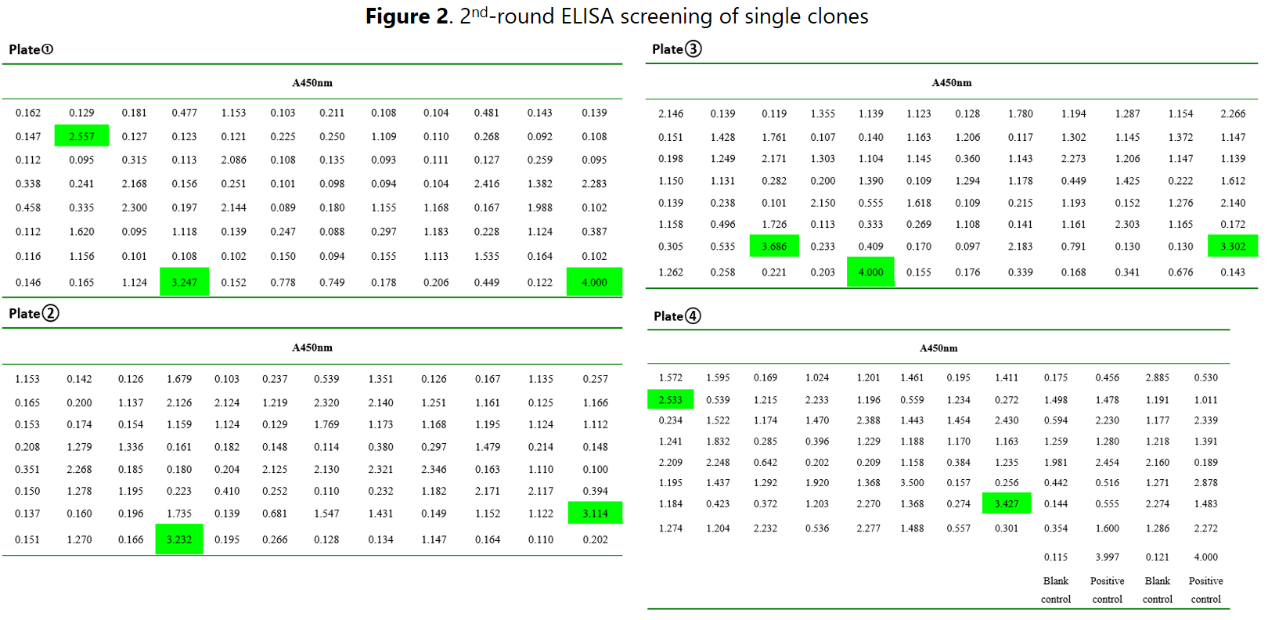
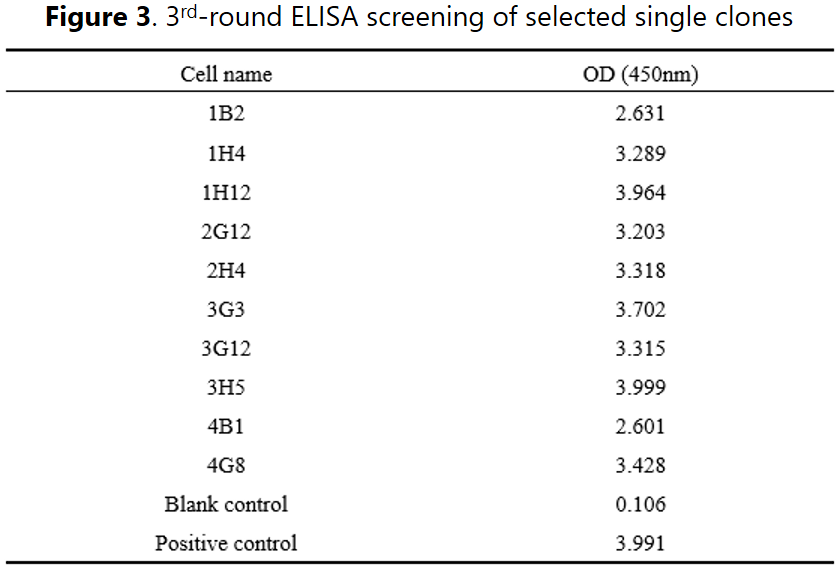
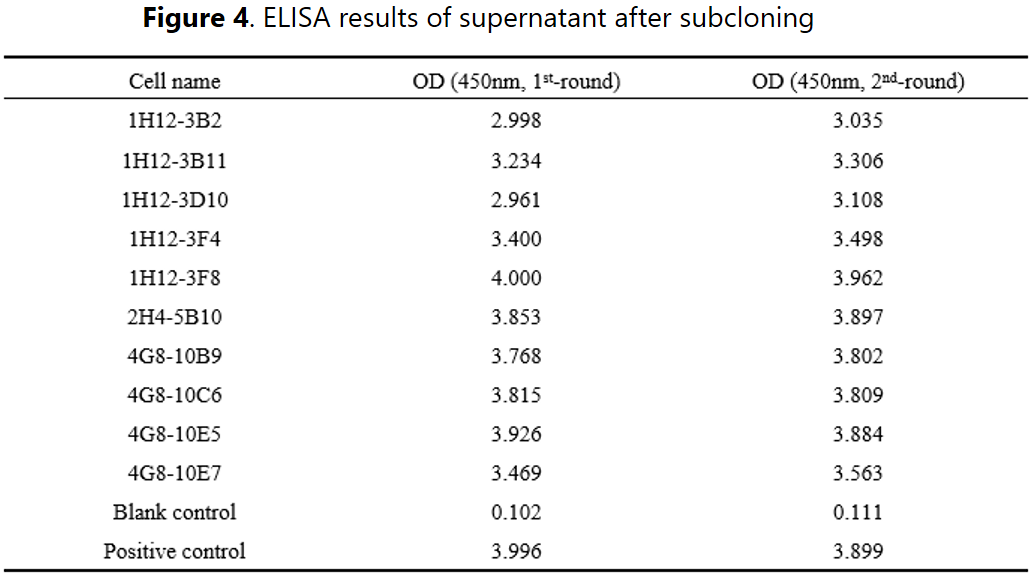
After two rounds of ELISA screening, 10 clones were identified to be suitable for limited dilution to establish subclones for subsequent screening. A 3rd-round ELISA analysis to confirm the positivity.

➢ Subcloning & validation
Selected positive clones were subjected to the subcloning stage for further binding validations. A total of 10 subclone strains were derived from the selected clones and a 2-round ELISA results confirmed the positive binding activities. In addition, other function-based approaches can also be applied to isolate binders with adequate properties, e.g. internalization, IHC, neutralization, etc.
➢ Antibody mRNA sequencing
Afterwards, antibody sequences will be obtained via hybridoma mRNA sequencing. Our robust sequencing platform can reveal full-length antibody sequences in 2-3 weeks. With sequence analysis, we can sort out the unique clones and proceed to recombinant expression stage. Meanwhile, positive hybridoma clones will be frozen for long-term storage.
➢ Antibody production and purification
For downstream binding & function validations (in vitro / in vivo), scaling-up production of antibody candidates with high purity will be needed. We have extensive experience in recombinant antibody expression (scFv/Fab/IgG) using a variety of systems. Both transient and stable transfection in a variety of featured host cell options are available. Of note, we also provide GMP-grade manufacture strain establishment service upon request.
Conclusions:
In this case, we designed and tailored proposals to obtain fully human antibody against target A by the transgenic CAMouse™ model. Equipped with skillful teams and world-leading resources, we conducted the all-round antibody production experiment from upstream immunogen design to the downstream antibody purification. Our unique adjuvant, featured myeloma cells, special fusion agent, etc., will help to enable higher success rate in each single step.
Please note: we only produce antibodies for research purposes. Our products and services cannot be used directly on humans.

