Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
Background Significance Services Features FAQs
Exosome is a kind of membrane coated nanoparticles or particles, which can protect its internal contents from the influence of external proteases and other enzymes, which provides a new solution for the analysis of phosphorylated proteins. Based on the advanced proteomics analysis platform, Creative Biolabs launches exosome phosphorylation proteomics analysis service.
Background of Protein phosphorylation
Protein phosphorylation is one of the most important and extensive molecular regulatory mechanisms controlling almost all aspects of cell function. The state of phosphorylation events can provide clues about the state of disease. However, few phosphoproteins have been developed as disease markers. Because of the invasive nature of tissue biopsy and the high dynamic of protein phosphorylation in typical long and complex biopsies, the detection of phosphoproteins in tissues is facing great challenges.
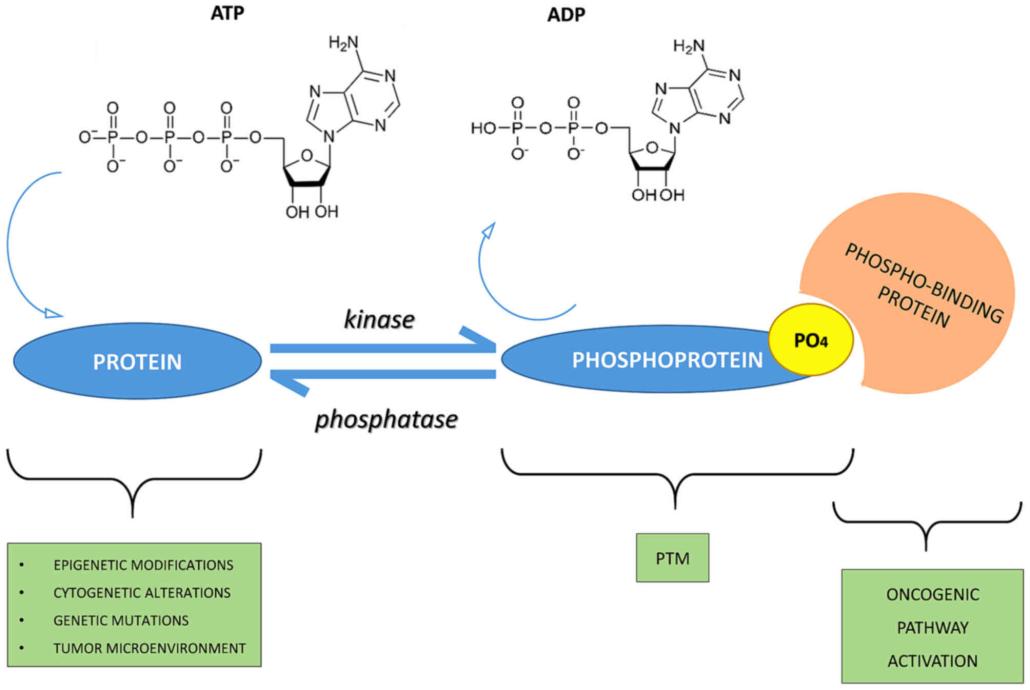 Fig.1 Phospho-signaling networks. (Ardito, 2017)
Fig.1 Phospho-signaling networks. (Ardito, 2017)
Significance of Proteomic Analysis of Exosomal Phosphorylation
With the discovery of exosomes and more and more studies, the above problems have found solutions. The vesicular properties of exosomes make them highly stable in biological fluids for a long time, and make it possible to develop phosphorylated proteins for medical diagnosis in electric vehicles. The ability to detect genome output (active proteins, especially phosphorylated proteins) can provide more direct and real-time information about biological physiological functions and disease progression, particularly in cancer.
Our Phosphorylation Proteomics Service for Exosome
At present, we have the ability to isolate and identify phosphoproteins from exosomes, and adopt the immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) enrichment strategy to efficiently increase the number of S, T, Y phosphorylated peptides. At the same time, based on Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) technology, we can collect all signals within the scanning range of mass spectrum without bias, so as to effectively solve the problem of qualitative and quantitative phosphorylation modification.
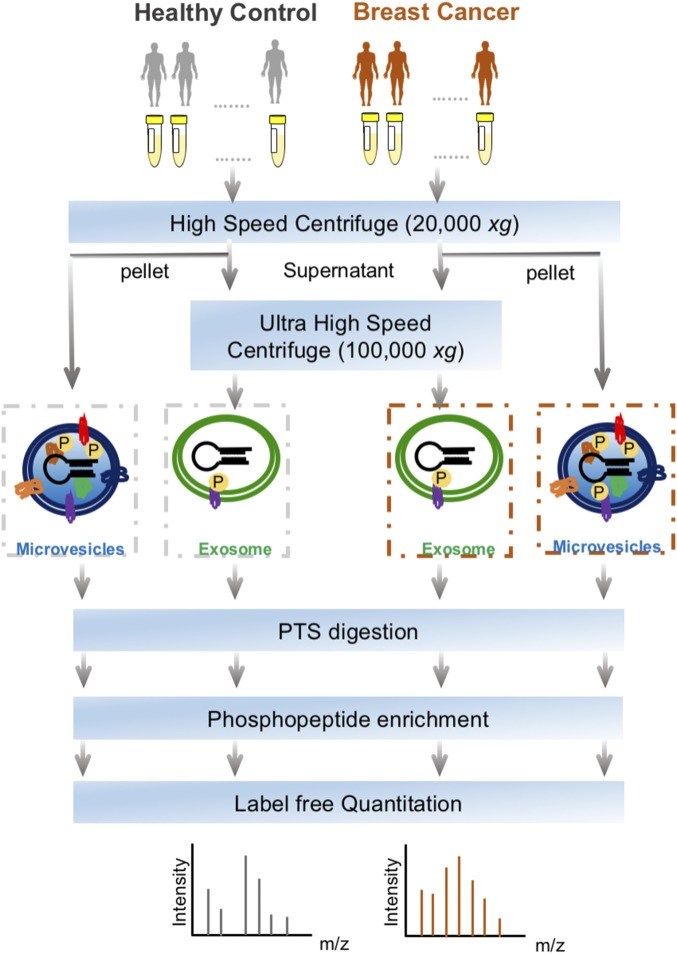 Fig.2 The workflow for exosomes phosphoproteomics of plasma samples from patients with breast cancer and healthy controls. (Chen, 2017)
Fig.2 The workflow for exosomes phosphoproteomics of plasma samples from patients with breast cancer and healthy controls. (Chen, 2017)
Technical Advantages
-
Full scan mode: DIA mode, greatly reducing the interference of high abundance, comprehensively collecting high and low abundance signals, increasing the data coverage by nearly 40%;
-
Ultra-high reproducibility and stability: the repetition rate of large sample identification increased by nearly 40%, and the quantitative precision increased by nearly one time;
-
Ultra-high quantitative accuracy: the quantitative ability is close to the gold standard multiple reaction monitoring (MRM, also known as Selective Reaction Monitoring-SRM) targeting technology.
Creative Biolabs is the research object of exosomes and is committed to providing one-stop service for exosomes research. Through our phosphorylated proteomics analysis service, the development of exosomal phosphoprotein as a potential disease marker is just around the corner. If you are interested in our service, please contact us for more information.
References
-
Ardito, F., et al. The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy. International journal of molecular medicine. 2017, 40(2): 271-280.
-
Chen, I. H., et al. Phosphoproteins in extracellular vesicles as candidate markers for breast cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2017, 114(12): 3175-3180.
FAQs
What is phosphorylated exosomal proteomic detection, and why is it important in drug development research?
Phosphorylated exosomal proteomic detection involves identifying and quantifying phosphorylated proteins within exosomes. This service is vital in drug development as phosphorylation plays key roles in signaling pathways, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic target identification.
How are phosphorylated proteins within exosomes detected and analyzed?
Phosphorylated proteins in exosomes are detected using advanced proteomic techniques such as mass spectrometry coupled with phosphoprotein enrichment methods. This enables comprehensive profiling and quantification of phosphorylation events, revealing insights into exosome-mediated signaling pathways and disease processes.
What types of phosphorylated proteins can be identified through this service?
Phosphorylated exosomal proteomic detection allows for the identification of a wide range of phosphorylated proteins involved in various cellular processes, including cell signaling, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. These proteins serve as potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets in drug development research.
Can this service be customized for specific research objectives or sample types?
Yes, our phosphorylated exosomal proteomic detection service offers customization options to address specific research objectives or sample requirements. Whether it's investigating signaling pathways, comparing disease states, or analyzing different sample types, we tailor our approach to meet your research needs.
How can phosphorylated exosomal proteomic detection services support drug development projects?
Our services provide valuable insights into exosome-mediated signaling events and disease mechanisms, aiding in the identification of potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers. By elucidating phosphorylation patterns within exosomes, we accelerate the discovery and development of novel drugs and personalized treatments.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Phospho-signaling networks. (Ardito, 2017)
Fig.1 Phospho-signaling networks. (Ardito, 2017)
 Fig.2 The workflow for exosomes phosphoproteomics of plasma samples from patients with breast cancer and healthy controls. (Chen, 2017)
Fig.2 The workflow for exosomes phosphoproteomics of plasma samples from patients with breast cancer and healthy controls. (Chen, 2017)








