NASH Target Development Service for TRAIL-R Inhibitors
Creative Biolabs has successfully constructed a series of innovative and diversified platforms to provide fast and convenient services for our worldwide customers. With over a decade of experience and NASH drug discovery platform, we can totally meet your project requirements and budgets in the NASH treatment services and related researches.
What is TRAIL-R?
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), also known as Apo2L and TNFSF10, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) that selectively induces cell apoptosis through cell surface death receptors (DR). TRAIL receptors (TRAIL-R) are several of those death receptors that mediate apoptosis signaling pathway. They belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. So far, four TRAIL-Rs for TRAIL have been identified: TRAIL-R1 (also named DR 4), TRAIL-R2 (also named DR 5), TRAIL-R3 (also named DR 1), and TRAIL-R4 (also named DR 2). Another TRAIL-binding receptor identified later is osteoprotegerin, which is a soluble receptor initially for binding RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand). RANKL has been reported to be involved in the progression of insulin resistance and other diseases. Generally, among these receptors, both TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 contain a conserved death domain, which are capable of inducing signal apoptosis, while, other three receptors TRAIL-R3, TRAIL-R4 and osteoprotegerin function as decoy receptors or inhibitors with the ability to inhibit TRAIL signaling apoptosis.
TRAIL-R Inhibitors for NASH Treatment
By binding corresponding TRAIL-R, TRAIL acts as a cytokine primarily to regulate programmed cell death pathway and induce cell apoptosis in various tumor cells. Since the 1990s, TRAIL and its receptors mainly have been researched and developed as therapeutic targets of anti-cancer treatment. In recent years, they have also been implicated as potential therapeutic targets in several hepatic diseases, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fatty liver disease.
Investigations demonstrated that TRAIL levels in NASH patients were higher than those in healthy individuals, which were positively correlated with triglyceride levels. TRAIL and TRAIL-R were also upregulated in hepatitis associated steatosis patients. However, in vitro experiments showed that TRAIL deficiency increased the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver, leading to triglyceride accumulation and liver injury. Despite the precise role of TRAIL in NASH still remains to be controversial and needs to be further confirmed, it can be confirmed that TRAIL-R gene deletion can obviously attenuate steatohepatitis and insulin resistance in mice. Therefore, TRAIL-R antagonists or inhibitors stand a good chance to be potential therapeutic candidates for NASH treatment.
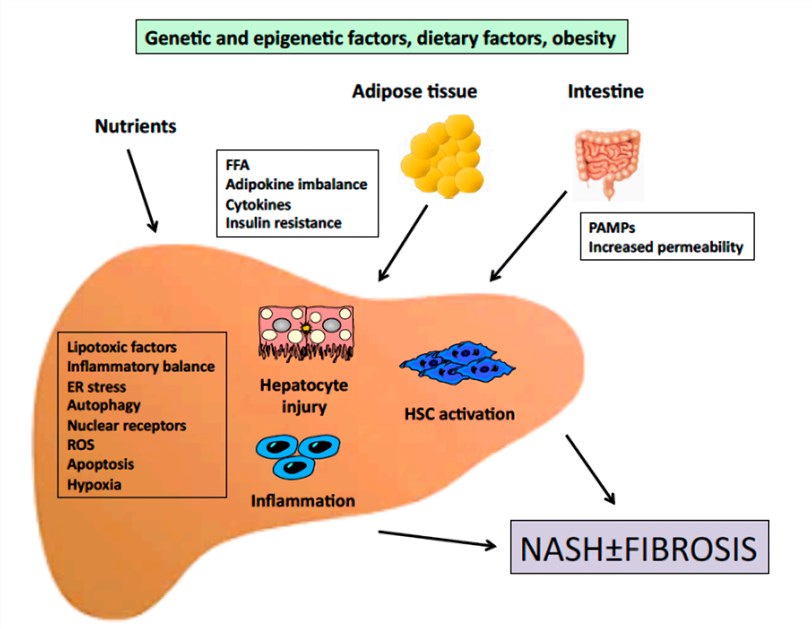 Fig.1 Outline of the pathogenesis of NASH. (Caligiuri, 2016)
Fig.1 Outline of the pathogenesis of NASH. (Caligiuri, 2016)
Creative Biolabs is confident in providing the best and comprehensive NASH treatment services to universal customers based on possessing platforms (e.g. Hit to Lead, Lead Optimization, IND-Enabling, Target Identification, and Validation, Hit identification) as well as abundant experience and expertise in target identification for drug discovery. Our NASH treatment services mainly include but not limited to:
- Biomarkers for NASH Diagnosis
- Target Discovery and Therapeutic Strategies
- Preclinical Models of NASH
Customized NASH treatment services specific to your demands are also within our ability. What you need do is just feel free to contact us or send us an inquiry and tell us your questions.
Reference
- Caligiuri, A.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis of NASH. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016, 17(9): E1575. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
 For Research Use Only.
For Research Use Only.