Exosome Cargo Post-loading Service
Further benefits can be achieved by loading molecules of interest on unmodified exosomes. The payload of exosomes and therapeutic products is one of the biggest challenges in this field. Among them, the loading of cargos after exosome isolation, that is, the post-loading strategy, has been widely used.
Introduction of Post-loading Strategy
After isolating the exosomes, it is a more common strategy to load exosomes with therapeutic products. This is not only because of the simplicity of the process, but also due to the loading efficiency is higher than the pre-loading method. The post-loading method can be further divided into passive and active loading. Passive loading refers to the incubation of exosomes with therapeutic cargo so that they can be passively loaded into exosomes. Active loading requires some type of destruction of the exosomal membrane, which is usually achieved by electroporation or the addition of surfactants.
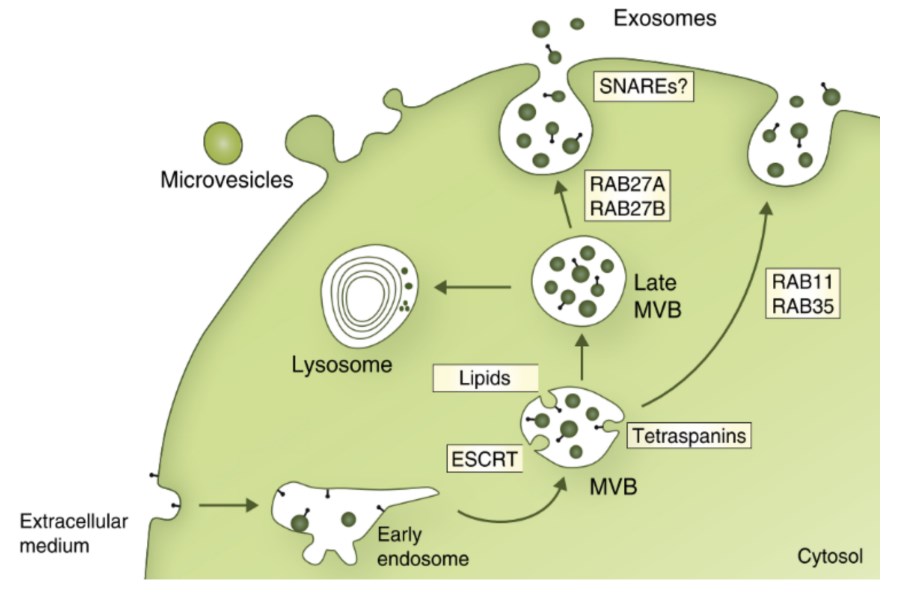 Fig.1 Several machineries involved in the biogenesis of exosomes. (Rodrigues, 2020)
Fig.1 Several machineries involved in the biogenesis of exosomes. (Rodrigues, 2020)
Post-Loading Methods
-
Incubation
The isolated and purified exosomes are incubated with the cargos to be loaded. Due to the concentration gradient, the cargos will diffuse into the exosomes.
-
Electroporation
In electroporation, the exosomes are placed in a conductive solution and an electric field is applied. The applied current rearranges the phospholipid bilayer of exosomes, thereby forming small pores in the membrane. The presence of these pores causes the diffusion of drugs and/or nucleotides into the interior of the exosomes. Generally, electroporation is the primary method of choice for encapsulating nucleotides.
-
Sonication
This technique uses ultrasonic frequencies to agitate the particles in the suspension. The exosomes are mixed with the cargos, and the probe sonicator induces the plasma membrane deformation of the nanovesicles. When the membrane deforms, the drug diffuses inside the exosomes.
-
Freeze/Thaw Cycles
In this method, the exosomes are incubated with the cargos. Then, they were quickly frozen at -80 ℃ and thawed at room temperature. Repeat the cycle several times and in each cycle, the plasma membrane is destroyed, allowing the drug molecules to diffuse in the exosomes.
-
Saponin Assisted Incubation
In this method, exosomes are incubated with cargos and saponin. Compared with simple incubation, this increase in permeability makes the loading of hydrophilic molecules easier.
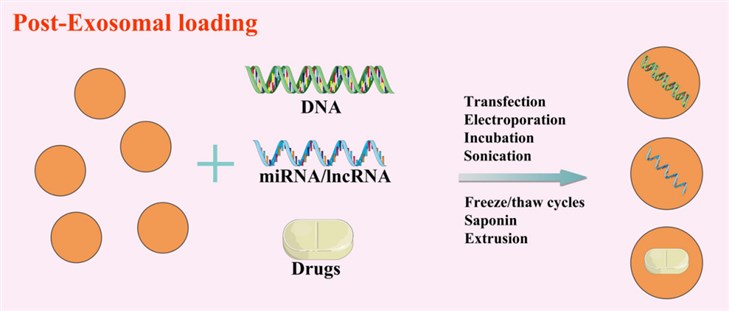 Fig.2 Exosomes can be modified by post-loading methods. (Xu, 2020)
Fig.2 Exosomes can be modified by post-loading methods. (Xu, 2020)
What Can We Do?
Among many post-loading strategies, the use of active loading is a more efficient means. At present, for the post-loading strategy of exosomes, Creative Biolabs provides methods of electroporation or chemical reagent transfection. Our technical advantages are:
-
Mature technology platform and professional staffing;
-
There are no restrictions on cell types, and the cargo loading rate can be calculated and evaluated;
-
Short development cycle and low cost.
The source of exosomes and cargo loading methods are important factors that affect their use as drug carriers. Creative Biolabs has been making efforts to provide diverse and high-end exosome research services. At present, there are many ways for loading cargos in exosomes, and our researchers have been looking for new and improved methods in addition to the existing technical means. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Rodrigues, P., et al. An Overview of Exosomes in Cancer Therapy: A Small Solution to a Big Problem. Processes. 2020, 8(12): 1561.
-
Xu, M., et al. Recent advancements in the loading and modification of therapeutic exosomes. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology. 2020, 8.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Several machineries involved in the biogenesis of exosomes. (Rodrigues, 2020)
Fig.1 Several machineries involved in the biogenesis of exosomes. (Rodrigues, 2020)
 Fig.2 Exosomes can be modified by post-loading methods. (Xu, 2020)
Fig.2 Exosomes can be modified by post-loading methods. (Xu, 2020)








