NASH Target Development Service for Lipase Inhibitor
One of the important pathological features of NASH is excessive fatty accumulation in the liver. Lipases are the key enzymes which catalyze the hydrolysis of lipids and reduce the dietary fat delivery to the liver from the gut. Hence, lipases are promising drug targets for NASH treatment. Creative Biolabs is very proud of providing the first-class target screening, structural characterization, and functional profiling services for identification of potential drug targets.
Introduction of Lipase
Lipases are a subclass of the esterases. They function as enzymes to catalyze the hydrolysis of lipids. Hence they play an essential role in digestion, transporting and processing of dietary lipids such as triglycerides, fats, oils in most living organisms. Besides, some lipases are even present in certain viruses. Candida albicans (C. albicans) has a large number of different lipases which may be responsible for the persistence and virulence of C. albicans in human tissue. The activities of lipases are limited in special compartments within cells or extracellular spaces. For example, lysosomal lipase is limited in lysosome while pancreatic lipases are secreted into extracellular spaces. Lipases have been implicated to be involved in diverse biological processes such as metabolism of dietary triglycerides, cell signaling, and inflammation. Furthermore, studies have also reported lipases are involved in the pathological process of NASH via the increase of the dietary fat delivery to the liver from the gut.
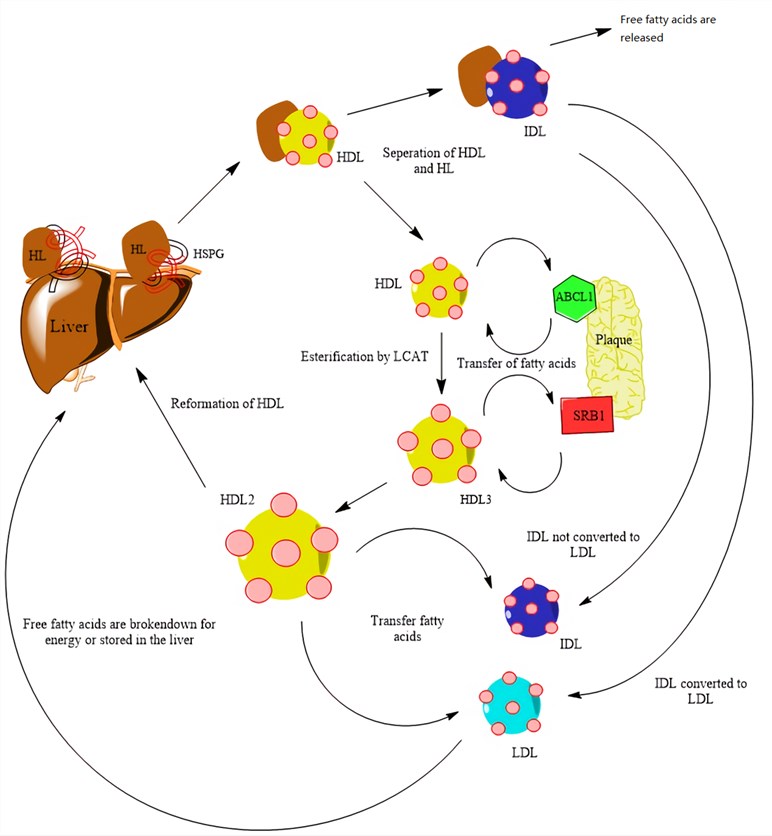 Fig.1 The function of hepatic lipase in regulating the formation and degradation of plaque (lipid pools). Distributed under Open Access License CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 The function of hepatic lipase in regulating the formation and degradation of plaque (lipid pools). Distributed under Open Access License CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Lipase Inhibitor Applied for NASH Treatment
Excessive triacylglycerol (TG) accumulation is the distinctive feature of obesity. In the liver, sustained TG accretion leads to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), eventually progressing to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. Lipase inhibitors are a class of substances that inhibit the activity of lipases. In the intestine, lipase inhibitors bind to lipase enzymes and reduce the enzyme activities, thus preventing the hydrolysis of dietary triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids. In other words, lipase inhibitors can reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of dietary fat. Hence, lipase inhibitors are mostly used for weight loss. Additionally, lipase inhibitors such as orlistat are also the effective therapeutic agents for NASH through decreasing free fatty-acid flux into the liver and improving insulin sensitivity.
Creative Biolabs has extensive experience and comprehensive knowledge of disease target discovery for a broad range of project objectives. We are capable of offering high-quality target construction and custom target screening services to precisely meet different purposes of projects. Our service lists cover antibody development (e.g. Phage Display & Antibody Library Services, Antibody Analysis Services, Antibody Engineering Services) or the one-stop service of drug discovery. We believe that our services will assist you to discover the most effective targets and promote the development of NASH therapeutic drugs. If you are interested in our services, please don’t hesitate and feel free to contact us for more details.
 For Research Use Only.
For Research Use Only.