NASH Target Development Service for NF-κB Inhibitors
Some evidence found that NF-кB activation can lead to development of NASH and its progression to fibrosis, thus it can be a potential target for NASH therapeutic. Creative Biolabs is a world leader of service provider in the field of target identification for drug discovery. Based on our years of experience and advanced platform, we are confident in offering the best and most suitable NF-кB inhibitors for the NASH treatment.
Introduction of NF-κB
Activation of the dimeric transcription factor nuclear factor (NF)-кB is essential for the development of inflammation in various conditions. NF-кB homodimers and heterodimers are formed by association of five members of the Rel family that can be activated upon assembly of a kinase complex formed by two catalytic subunits, IKK1 (IKKa) and IKK2 (IKKb), and a regulatory subunit, IKKc (NEMO). The IKK kinase complex phosphorylates a class of inhibitory proteins, termed as IkB, inducing their degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, and allowing NF-кB dimers to migrate to the nucleus and modulate transcription. Proinflammatory stimuli, such as tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), preferentially activate IKK2, causing accumulation of p65:p50 heterodimers. This "canonical pathway" is paralleled by a "non-canonical pathway" where IKK1 is the primary kinase, and different Rel dimers can be activated. The non-canonical NF-кB pathway is less tightly connected to inflammation and it may even involve in resolution of inflammation.
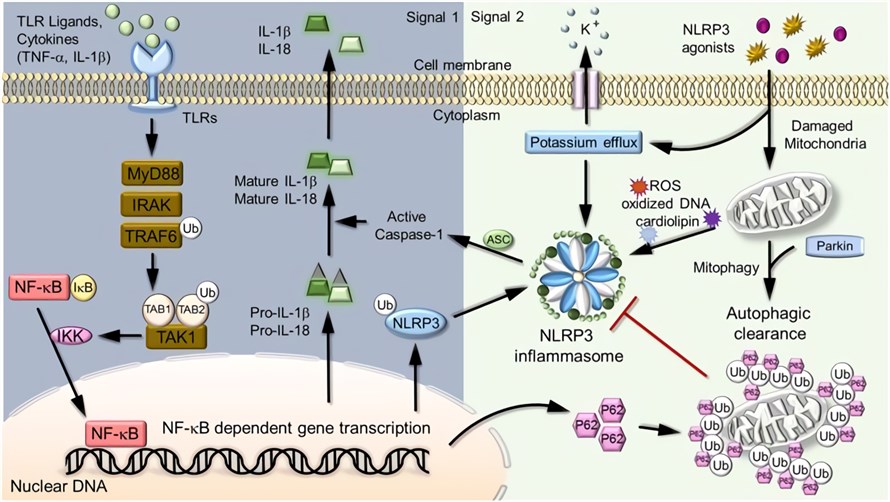 Fig.1 NF-кB signaling in inflammation. (Liu, 2017)
Fig.1 NF-кB signaling in inflammation. (Liu, 2017)
NF-кB Inhibitors for NASH Treatment
NF-кB activation is a critical factor leading to development of NASH and its progression to fibrosis. The NF-кB pathway has been confirmed to be upregulated both in rodent models and in patients with NASH, and mechanistic evidence has been provided by studies in transgenic mice. NF-кB within hepatocytes can trigger low-grade liver inflammation, steatosis, and insulin resistance, while deletion of IKK2 preserves the sensitivity to insulin. According to these results, the inhibition of NF-кB in inflammation can be a possible strategy for the treatment of NASH. One example of this kind of NF-кB inhibitor, named AS602868, is a novel pharmacological inhibitor of IKK2, was tested in human and mouse model of NASH. Daily administration of the IKK2 inhibitor can ameliorate steatosis and the proinflammatory response effectively, as shown by intrahepatic expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and TNF-α. In addition, administration of AS602868 involves more favourable metabolic profile, as detected by increased expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) α and γ, and components of enzymatic pathways involved in fatty acid metabolism. IKK2 inhibition also dramatically promoted antioxidant defenses in the pathogenesis of NASH.
Features
- Time- and labor-saving
- Versatile formats available
- Superior quality
- Skillful technique support
- Competitive price
Empowered by all kinds of approaches, Creative Biolabs is confident in offering the most professional support to our clients regarding disease target discovery and development. In addition, our scientists are also offering comprehensive target construction and custom target screening services for NASH treatment. With rich experiences for hundreds of successful cases, our skilled technical teams are capable of all kinds of troubleshooting throughout the process. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference
- Liu, T.; et al. Nf-κb signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2017, 2, 17023. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
 For Research Use Only.
For Research Use Only.