Whether you’re studying autoimmune disorders, infectious disease models, tumor immunology, or neurodegeneration, C1q seems to show up in every figure legend, every mechanism diagram, and nearly every pathway conversation.
So why is C1q everywhere? And more importantly, what does that mean for your research?
At Creative Biolabs, where complement research is at the heart of many of our service platforms, we’ve seen an enormous uptick in demand for C1q-binding assays, deposition tests, and complement-targeted screening tools.
C1q: The Classic Complement Initiator
C1q is best known as the recognition subcomponent of the classical complement pathway. Together with C1r and C1s, it forms the C1 complex, which is activated upon binding to immune complexes, apoptotic cells, or certain pathogen-associated structures.
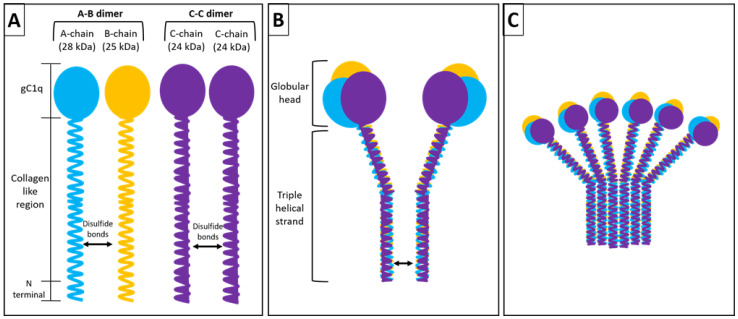
Fig. 1 Structure of C1q.1,2
Structurally, C1q resembles a bouquet, with six globular heads capable of recognizing a wide range of ligands—from immunoglobulin Fc regions (e.g., IgG or IgM) to misfolded proteins, viral particles, and lipid components. Once C1q binds to a target, it activates downstream complement pathways, unleashing a cascade of immune responses that include opsonization, inflammation, and lysis.
But what makes C1q truly unique is how it goes far beyond complement activation.
More Than Complement: C1q’s Non-Canonical Roles
In recent years, C1q has shed its “complement-only” label and taken center stage as a multifunctional modulator in diverse biological systems.
- C1q in Neurodegeneration
In diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis, C1q expression is significantly upregulated. It binds to synapses and facilitates their elimination by microglia—a process that is physiological during development but pathological when reactivated in aging or disease.
- C1q in Cancer Immunology
C1q is increasingly linked to the remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Depending on context, it can be pro- or anti-tumorigenic. It interacts with tumor cells, stromal components, and infiltrating immune cells, shaping cytokine profiles, angiogenesis, and cell survival.
Interestingly, C1q can even bind directly to cancer cell surfaces, triggering signaling independent of complement activation. This duality makes it a fascinating but complex target for cancer therapy exploration.
- C1q in Autoimmune Disease
The protein plays a major role in clearing apoptotic cells—failure to do so results in the accumulation of autoantigens and breaks in self-tolerance. Anti-C1q antibodies are often used as diagnostic biomarkers for lupus nephritis and correlate with disease severity.
Why Is Everyone Suddenly Talking About C1q?
C1q is now recognized as:
- A biomarker in neurological and autoimmune disorders
- A checkpoint in cancer immunology/li>
- A target for biologic drugs
- A readout in antibody development pipelines
This means scientists from neuroscience to immuno-oncology are now including C1q-related endpoints in their studies—and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly interested in C1q-binding profiles when screening therapeutic antibodies or nanoparticles.
The Power of C1q Binding Assays
If your molecule binds, what does that mean? The answer varies based on your system. At Creative Biolabs, we offer comprehensive C1q-binding assay solutions to address this exact question.
- Monoclonal antibodies: C1q binding affects Fc effector functions like ADCC/CDC
- Biologics safety screening: Unexpected C1q interaction may signal immunotoxicity
- Autoimmune diagnostics: Anti-C1q autoantibodies used for disease stratification
- Nanomedicine & vaccine development: C1q opsonization affects particle clearance & efficacy
Want to know if your therapeutic candidate is silently triggering the complement system? Or if a novel antibody variant has optimal C1q engagement for ADCC potential? That’s exactly what our C1q ELISA, SPR, and flow cytometry-based assays can uncover.
C1q and Drug Development: Friend or Foe?
Whether you’re engineering Fc-silent antibodies, enhancing complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), or minimizing immunogenic clearance, C1q is your molecule to watch.
Let’s break it down:
- Need silent antibodies? You want minimal or no C1q binding.
- Want to boost immune killing? You want strong and specific C1q engagement.
- Worried about off-target effects? You’ll want to screen your constructs against human C1q early in development.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide both functional and binding-based characterization, with human- and animal-derived C1q to support your preclinical programs globally.
C1q in Research Assays: Our Service Highlights
Creative Biolabs offers a spectrum of services tailored to your C1q-related questions.
- C1q Binding Assay – Quantitative assessment of the interaction between test molecules (antibodies, proteins, particles) and purified C1q.
- C1q-Mediated Complement Activation – Measure downstream complement activation (e.g., C3b deposition, C5b-9 complex) following C1q binding.
- Anti-C1q Antibody Detection – Supports autoimmune disease studies with isotype-specific detection kits and ELISAs.
Explore our full C1q Binding Assay Services to find the right test for your research needs.
C1q isn’t just an old-school complement protein. It’s now a central biomolecular switch with implications across immunology, neuroscience, oncology, and regenerative medicine. If it’s appearing in every one of your research topics, that’s not a coincidence—it’s a clue.
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in turning that clue into actionable data—whether you need custom C1q-binding profiling, disease-relevant complement models, or full immunogenicity packages.
Don’t let C1q be a blind spot. Let it be your biomarker of clarity. Get in touch with our scientists today to design your custom C1q analysis solution.
References
- Ain, Danyaal, et al. “The role of complement in the tumor microenvironment.” Faculty Reviews 10 (2021): 80. https://doi.org/10.12703/r/10-80
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
