Overview Background Workflows Case study Related Products Related Tests Protocols Features Q&A Resources
Overview of C1q-Binding Assays
As a part of the innate immune system, the complement system serves as an important auxiliary of the immune system in enhancing microbe clearance and inflammatory reactions. Generally, the complement system is activated and functions through three biochemical pathways: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway, in which the classical pathway of the complement system is considered to be the most important pathway in immune complex clearance.
The classical complement pathway is usually initiated by antigen-antibody complexes through the binding of C1q to IgM or IgG complexed with antigens. As a subcomponent of the first component (C1) of the classical pathway, C1q mainly binds to the Fc domain of IgM or IgG antibodies (the CH4 domain of IgM and the CH2 domain of IgG except for IgG4). Once binding of C1q to the antibody of the immune complex, the C1 complex becomes activated, so do the classical complement pathway and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).
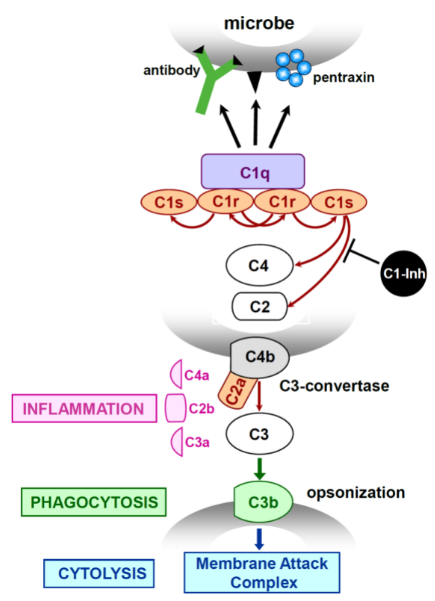 Fig.1 Activation of the classical pathway of complement. (Frachet, 2015)
Fig.1 Activation of the classical pathway of complement. (Frachet, 2015)
Introduction of C1q-Binding Assays
Why get tested?
The engineered therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with Fc fragment modification to enhance or reduce the complement activities, such as mutations or glycosylation engineering, have raised and accounted for an increasing proportion. The binding ability of developed antibodies to complement C1q and resultant complement classical cascade activation is an important aspect for measuring the efficacy and safety of therapeutic mAbs. And therefore, complement C1q-binding assay is necessary for characterization during the development process of therapeutic mAbs.
What is being tested?
Complement C1q-binding assay is mainly used for measuring the ability of antibody candidates binding to the complement C1q. For the assay, antibody samples developed by clients with different concentration gradients will be tested, and proper positive and negative controls will be included. Please mark the concentration and volume of the antibody samples when you ship the samples to us.
Which method is preferred?
Semi-quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
How long is expected to take?
1-2 weeks. The test time may vary depending on the number of antibodies, and additional time should be allowed for additional validation testing or repetition, if necessary.
Workflow of Complement C1q-Binding Assays
intuitive. During the tests, the binding of test articles to the secondary antibody will be verified first. Then, detection of the binding of samples with different concentration gradients to complement C1q by ELISA titration. EC50 of each sample will be presented and proper positive and negative controls will be included.
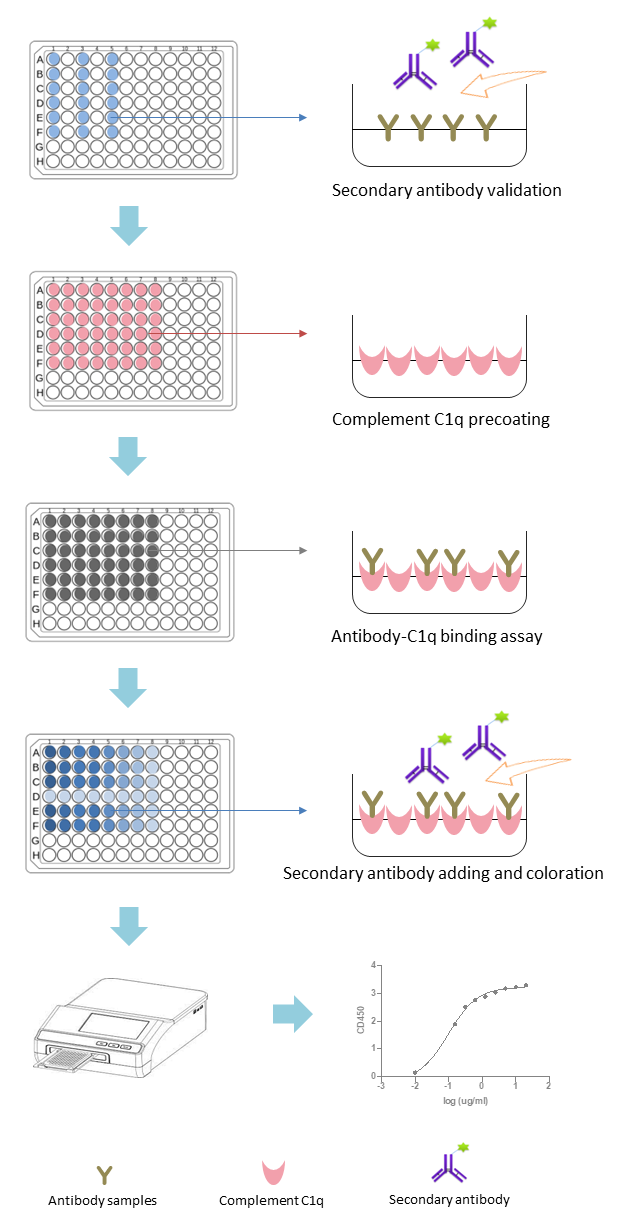 Fig.2 Workflow of Complement C1q-Binding Assays. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Workflow of Complement C1q-Binding Assays. (Creative Biolabs)
Case Study
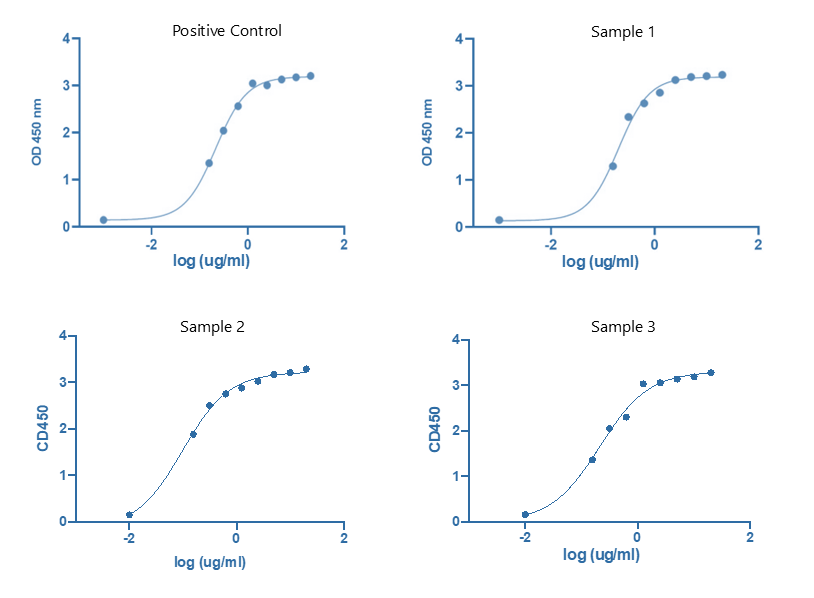 Fig.3 Complement C1q binding assay performed by ELISA titration. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.3 Complement C1q binding assay performed by ELISA titration. (Creative Biolabs)
The clients sent us 3 engineering antibody samples to characterize the binding ability of their antibody samples to complement C1q. We first perform the validation of the binding of samples to the secondary antibody, and found that all the samples had normal binding with the secondary antibody. Then we perform the complement C1q binding assay of samples by ELISA titration through setting 9 different concentration gradients. Binding curves and EC50 (not shown) of each sample were obtained based on the ELISA OD450 value. And the results indicated that all 3 samples had a normal binding to complement C1q.
Complement C1q Products at Creative Biolabs
Related Tests
Protocols
Why Creative Biolabs?
As a leading service biotech company, Creative Biolabs has armed with a powerful complement test platform,
aiming to
offer the best and most convenient complement-related services. Over the last 20 years, Creative Biolabs has
completed many customers' projects, which have allowed us to develop proprietary custom services that are unrivaled
in the industry. We will be your reliable and trustable partner featured with:
Related products and complement C1q functional assays are available
One-stop and tailored assay services based on your demands
A professional scientific team experienced in complement products and services for many years
Value on quality first and customer-centered
Resources
Creative Biolabs undertakes C1q-binding assays on behalf of clients as standalone projects or as part of larger
development projects. Our focus is to exceed your expectations while providing accurate and reliable complement test
services. To get more information, a quote, or to schedule a teleconference, please contact us.
Reference
-
Frachet, P., et al. Role of C1q in efferocytosis and self-tolerance-links with autoimmunity. Autoimmunity–Pathogenesis, Clinical Aspects and Therapy of Specific Autoimmune Diseases. Croatia: InTech, 21-51.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Activation of the classical pathway of complement. (Frachet, 2015)
Fig.1 Activation of the classical pathway of complement. (Frachet, 2015)
 Fig.2 Workflow of Complement C1q-Binding Assays. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Workflow of Complement C1q-Binding Assays. (Creative Biolabs)
 Fig.3 Complement C1q binding assay performed by ELISA titration. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.3 Complement C1q binding assay performed by ELISA titration. (Creative Biolabs)