After more than 30 years of accumulation, monoclonal antibody drugs have become well-deserved mainstream branches in the field of medicine from targets development to technologies improvement. From clinical research to commercialization strategies, all aspects have matured.
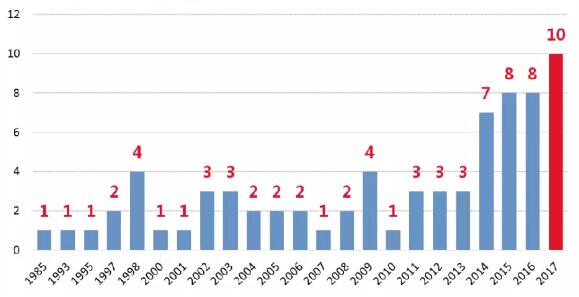
Compared with the past few years, monoclonal antibody drugs still remain popular worldwide in 2017. As of December 31, 2017, the FDA and EMA have approved 10 monoclonal antibody drugs globally, and the total number of monoclonal antibody drugs (including drugs withdrawn for various reasons after approval, excluding Fc fusion protein) has reached 73. In the clinical phase, new projects are continuously moving forward with new targets and new technologies in a proof of concept trial, which will make monoclonal antibody drugs embrace greater potential. It can be said that we are experiencing the golden age of monoclonal antibody drug development.
From the summary of new drugs approved by the major global markets, it can be proved that the total number of approved monoclonal antibody drugs has reached 73. The number of approved antibodies in a year has significantly increased since 2014 with a steady rise in the next three years. Monoclonal antibody drug development has moved from an early piecemeal stage to a large-scale development phase. In 2017, 10 new monoclonal antibodies were approved in mainstream markets around the world, reaching a record high.
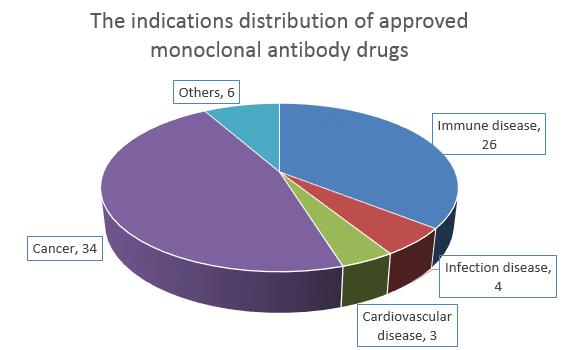
73 monoclonal antibody drugs were classified with respect to the distribution of indications into cancer (including hematological cancer and non-hematological cancer) and immune diseases (including autoimmune diseases and exogenous inflammation). There are 60 antibodies to these two diseases, accounting for 82.2% of the total, and 7 antibodies can be used to treat infection and cardiovascular disease. Meanwhile, there exist another six antibodies for the treatment of orthopedic diseases, eye diseases, rare diseases.
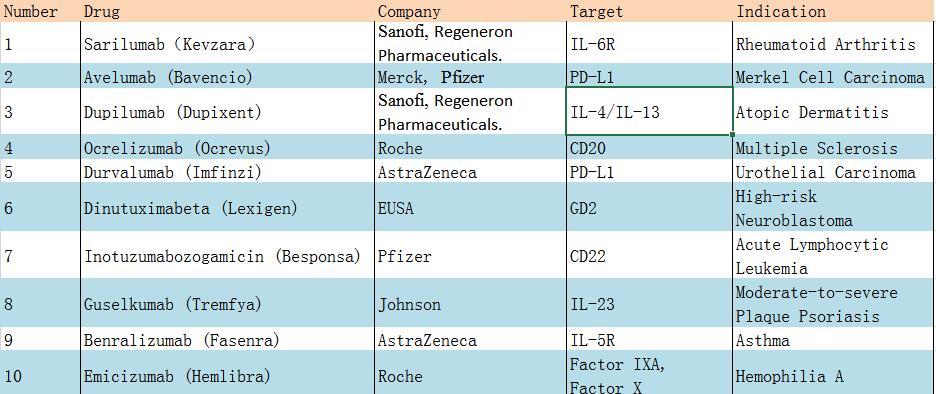
Sarilumab (Kevzara), developed in collaboration with Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, is a monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin 6 receptors approved by the FDA in May 2017 and approved by the EMA in June for moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis second-line treatment. Phase III clinical trial of adalimumab in 2016 SARAR-RA-MONARCH results show that Sarilumab is superior to adalimumab in its treatment, which means that adalimumab may experience strong competition.
Both Avelumab (Bavencio), developed in collaboration with Pfizer and Durvalumab (Imfinzi) from AstraZeneca, are monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-L1, whose approval and availability led to an increase in the number of marketed PD-1 / PD-L1 antibodies To 5, marking a more fierce competition in the tumor immunity market.
Pfizer’s Inotuzumabozogamicin (Besponsa) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) that enables small molecule toxin to precisely kill CD22-overexpressing cancer cells by its targeting. The drug was approved by the EU in June 2017, which is the fourth approved ADC, leading to increased confidence in the ADC development.
Roche’s Emicizumab (Hemlibra), the last approved monoclonal antibody drug in 2017, targets the coagulation factors IXa and X and promotes the binding of IXa and X, thereby promoting the clotting process. The availability of Emicizumab will help patients with hemophilia A reduce their frequency of use and improve life quality. At the same time, Emicizumab is also the first approved drug for bispecific antibodies in the non-cancer area.
Above all, we can conclude that not only the number of approved monoclonal antibody drugs has increased in 2017, but also drug properties.