PreciAbTM
PreciAb™ Platform
Antibody Design
Antibody Structure Modelling
Antibody-Antigen Complex Analysis
Computer-aided Affnity Maturation
Antibody Structure Determination
Antibody Reformatting
Antibody to ScFv Reformat
Antibody to VHH Reformat
Antibody Developability Prediction
Antibody Aggregation Prediction
Antibody Immunongenicity Prediction
Antibody Screening & Design
Company
About Us
Contact Us
Downloads
Careers
Events

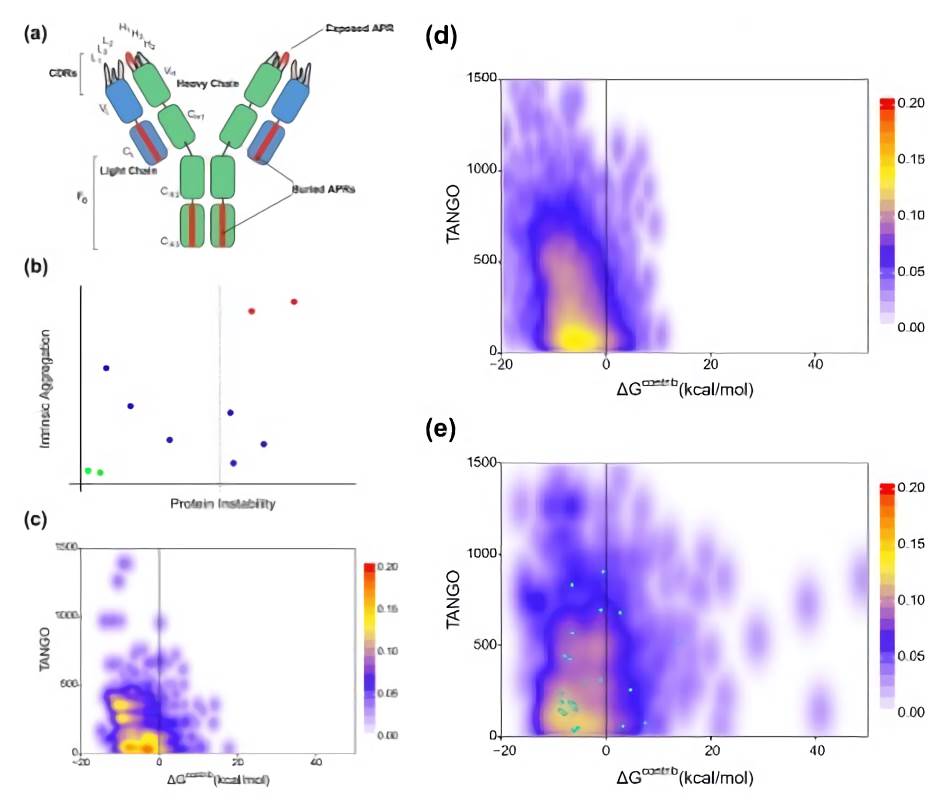 Fig.1 In silico analysis of aggregation propensity in antibody crystal structures.1
Fig.1 In silico analysis of aggregation propensity in antibody crystal structures.1

 More than 10 years of exploration and expansion
More than 10 years of exploration and expansion


