The antigen binding regions of an antibody (variable heavy and light chain genes) are able to be isolated using phage display. Apart from altering the Fc portion of an antibody, the variable region of an immunoglobulin enables to be reformatted into a number of different fragments, including Fab, F(ab)’2, scFv, VHH, and minibodies. Due to their smaller antibody formats, increased tumour/tissue penetration, as well as relative ease of expression in non-mammalian systems, they play an increasingly important role in drug discovery and clinical research. As an undisputed lead in the antibody engineering area, Creative Biolabs provides a full range of structure-based antibody reformatting services by using in silico technology.
In silico Design for Antibody Reformatting
Generally, in order to obtain an ideal antibody fragment with good stability, high affinity, and preeminent specificity, a serious of reform procedures are required before the antibody production. Therefore, we have developed a full range of in silico techniques for antibody design and reformatting.
-
Homology modeling
-
Molecular dynamics simulation
-
In-house algorithm
-
Antibody molecule model analysis
By using these in silico techniques, we are able to identification the main residues affecting a certain characteristic of the target antibody. After that, appropriate mutations can be made on these residues to alter the antibody properties. In this way, the target antibody molecule can maintain a relatively stable physicochemical property after reformat and keep the original affinity and function. In addition, the external environment of the modified molecular model can be set up, and which can be evaluating by RMSD, RMSF, as well as the potential energy inside the molecule.
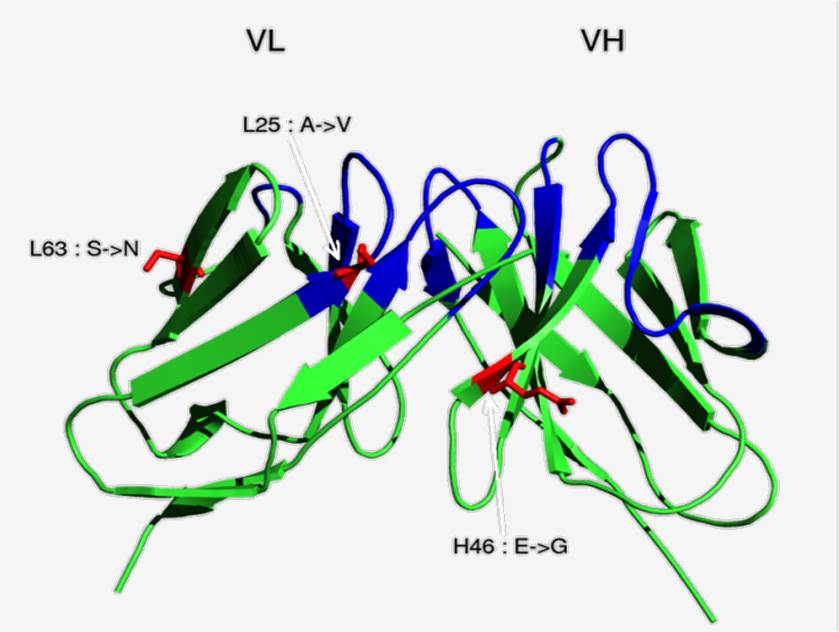 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the HuLys11 scFv (pdb 1BVK).1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the HuLys11 scFv (pdb 1BVK).1
The Variable Region Engineering for Reformatting
We developed several approaches to facilitate the variable region engineering for reformatting antibody, including:
-
Engineering the antigen binding properties in silico
Generally, computational design is based on two capabilities: accurate energetic evaluation and conformational search. Antigen binding properties design mainly refers to affinity maturation, altering the specificity.
-
Improving the pharmacokinetics: isoelectric point engineering and engineering PH dependency.
-
Improving the Pharmaceutical Properties: thermal stability improvement, solubility improvement, chemical stability improvement, and heterogeneity improvement.
-
Reducing the Immunogenicity
At present, a variety of in silico tools to predict effector T-cell epitopes have been designed. Based on these advanced in silico tools, the presence of effector T-cell epitope in each antibody sequence are able to be predicted, making the potential immunogenicity of the antibody therapeutics to be decreased by selecting a sequence with the minimum number of effector T-cell epitopes.
Reformat into scFv and VHH
Currently, the success of antibody therapeutics has led to the rapid development of novel therapeutic antibody forms, such as scFv and VHH. Researchers develop so-called second or third generation antibodies with clinical differentiation by using various engineering and optimization technologies. Antibody variable region is responsible to bind antigen, however, it is also the major source of antibody diversity and its sequence affects a number of properties important for developing antibody therapeutics. Besides, the CDR3 length of camelid antibodies is significantly greater than that of classical antibodies for use as starting points for peptidomimetic and small molecule design, as reagents for cell biology or as potential therapeutic agents. Creative Biolabs provide high quality reformatting into scFv and VHH services with optimal variable region and molecule model.
-
Reformat into scFv
Currently, generation of single-chain fragment variable (scFv) has become a common strategy applied to generate a completely functional antigen-binding fragment in bacterial systems. Besides, the scFv antibody fragments can also be used in the construction of immunotoxins, therapeutic gene delivery, as well as anticancer intrabodies for therapeutic purposes.
-
VHH
Camelids generate functional antibodies lack of light chains, of which the single N-terminal domain is fully capable of antigen binding. These single-domain antibody fragments are named as VHHs, which have a variety of advantages for biotechnological applications.
With our comprehensive structure-based antibody reformatting services, designing and engineering novel antibodies into scFv and VHH is available. We customize the service according to the specific requirements from the customers. We also provide other epitope-specific antibody design services. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Reference
-
Opuni, K. F. M., et al. "In silico epitope mapping of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase: A Rheumatoid arthritis autoantigen." Journal of Proteomics & Bioinformatics 10.3 (2017): 60-72. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification
All services provided on this site are intended to support preclinical research only. Do not use our services or final products on humans.

 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the HuLys11 scFv (pdb 1BVK).1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the HuLys11 scFv (pdb 1BVK).1

 More than 10 years of exploration and expansion
More than 10 years of exploration and expansion


